Foam concrete, also known as Lightweight Cellular Concrete (LCC), Low-Density Cellular Concrete (LDCC), discrete, foamed concrete, foam create, cellular lightweight concrete or reduced density concrete, is defined as a cement-based slurry, with a minimum of 20% (per volume) foam entrained into the plastic mortar. As mostly no coarse aggregate is used for the production of foam concrete the correct term would be called mortar instead of concrete, it may be called “foamed cement” as well. The density of foam concrete usually varies from 400 kg/m³ to 1600 kg/ m³. The density is normally controlled by substituting fully or part of the fine aggregate with foam.
Manufacturing
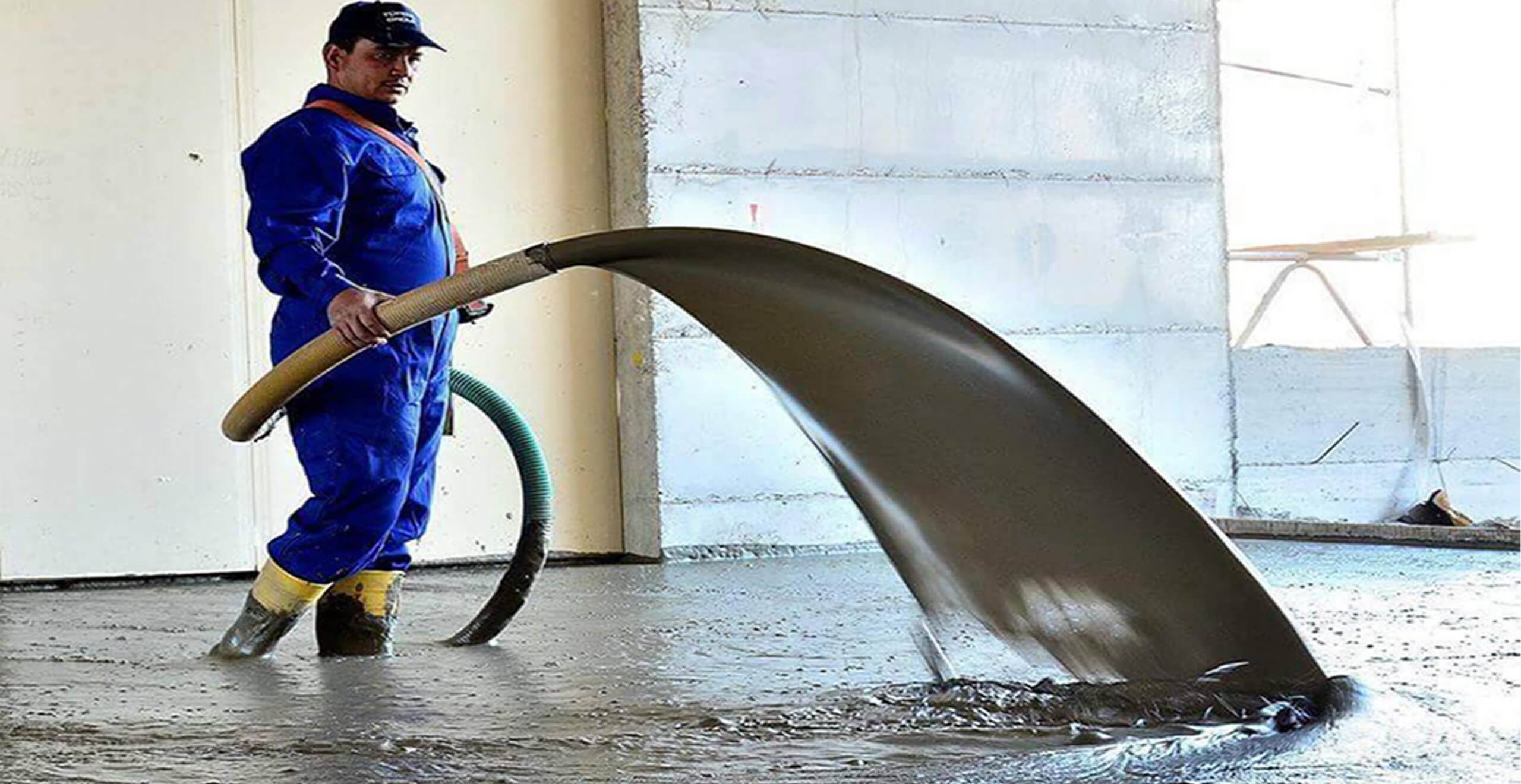
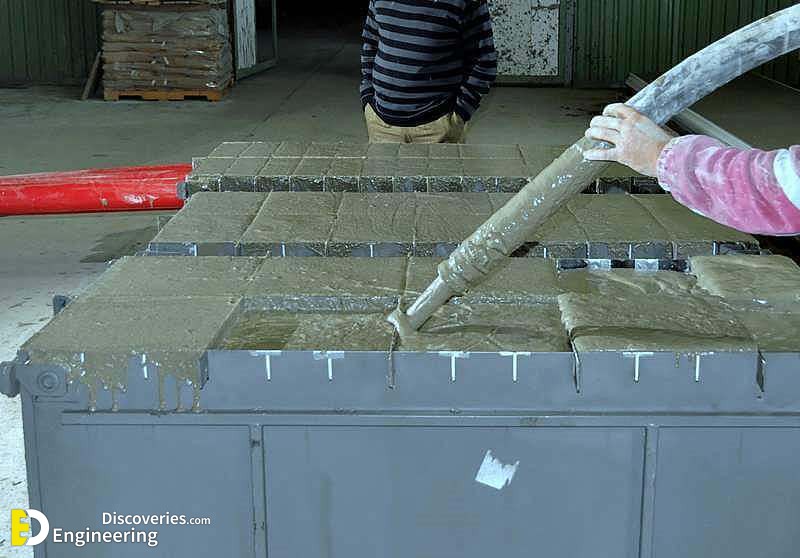
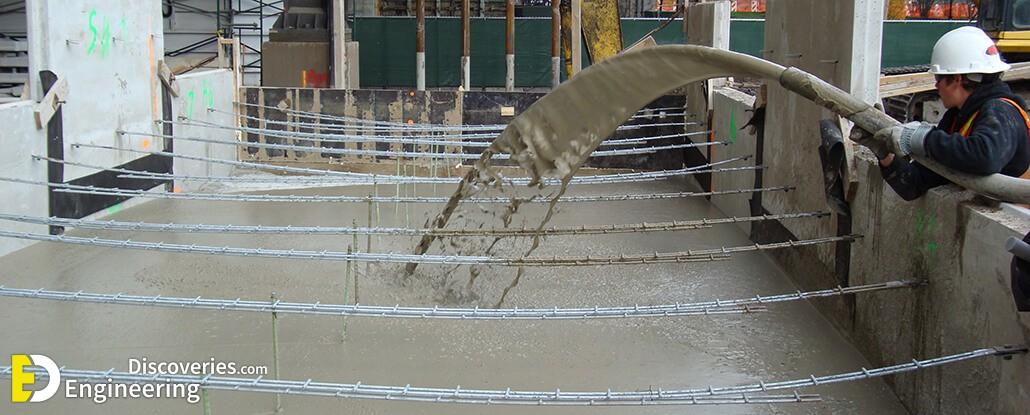
Foamed concrete typically consists of a slurry of cement or fly ash and sand and water, although some suppliers recommend pure cement and water with the foaming agent for very lightweight mixes. This slurry is further mixed with a synthetic aerated foam in a concrete mixing plant. The foam is created using a foaming agent, mixed with water and air from a generator. The foaming agent used must be able to produce air bubbles with a high level of stability, resistant to the physical and chemical processes of mixing, placing and hardening.
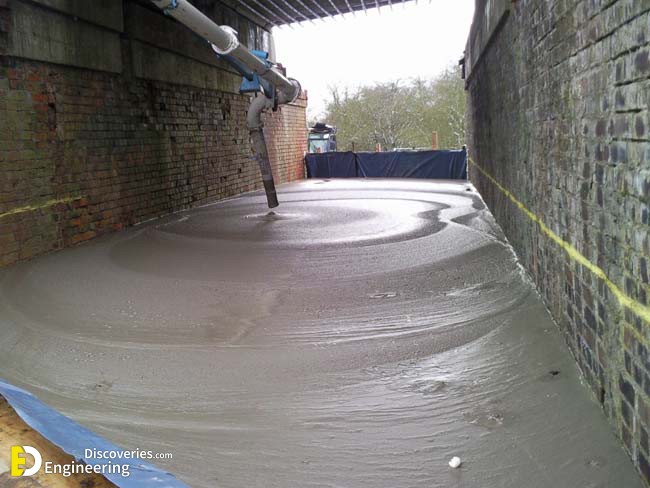
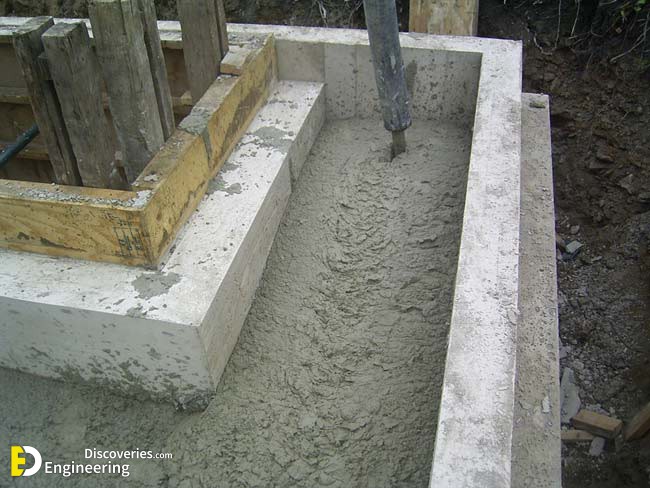
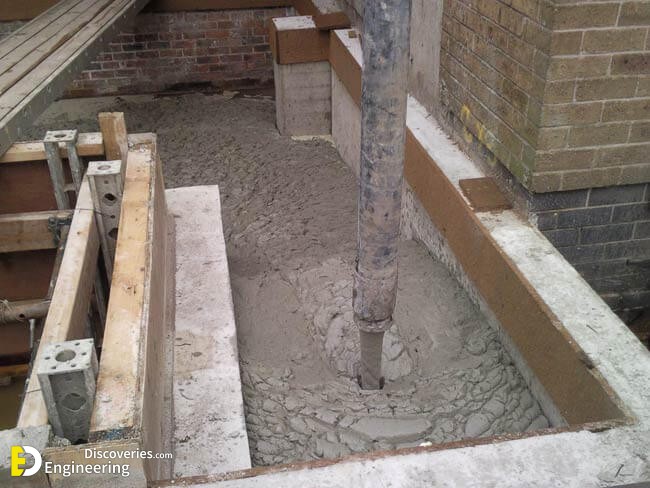
The foamed concrete mixture may be poured or pumped into moulds, or directly into structural elements. The foam enables the slurry to flow freely due to the thixotropic behaviour of the foam bubbles, allowing it to be easily poured into the chosen form or mould. The viscous material requires up to 24 hours to solidify (or as little as two hours if steam cured with temperatures up to 70 °C to accelerate the process.), depending on variables including ambient temperature and humidity. Once solidified, the formed produce may be released from its mould.
Properties
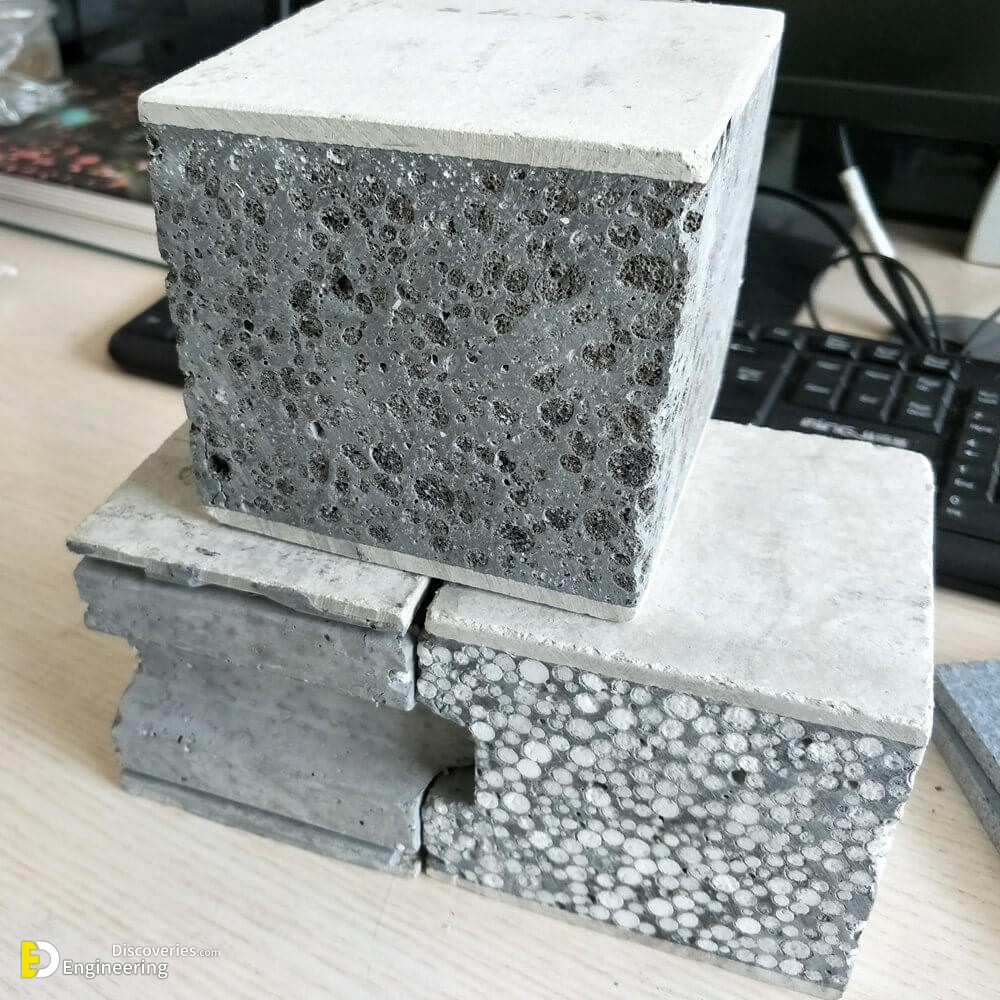
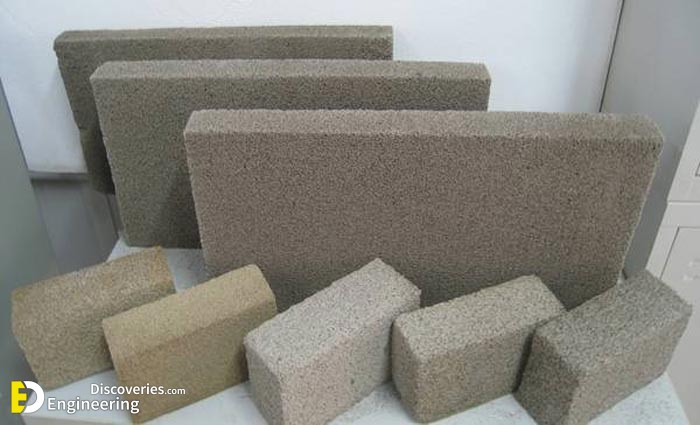
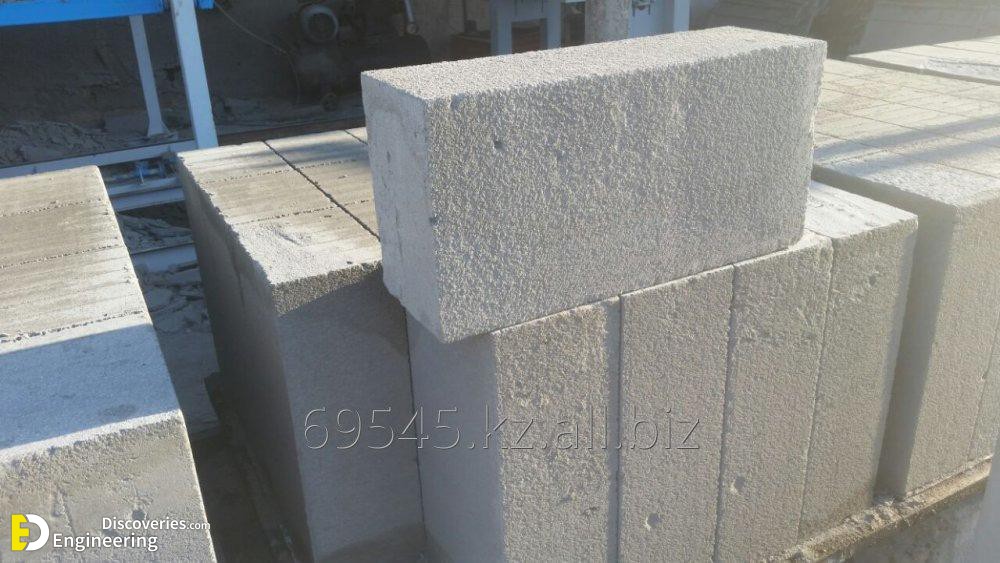
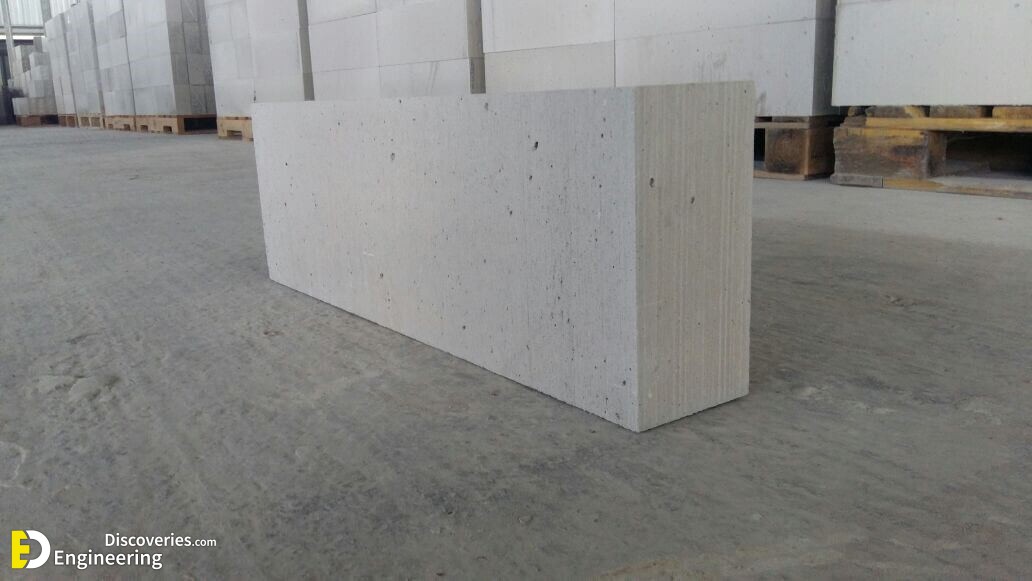
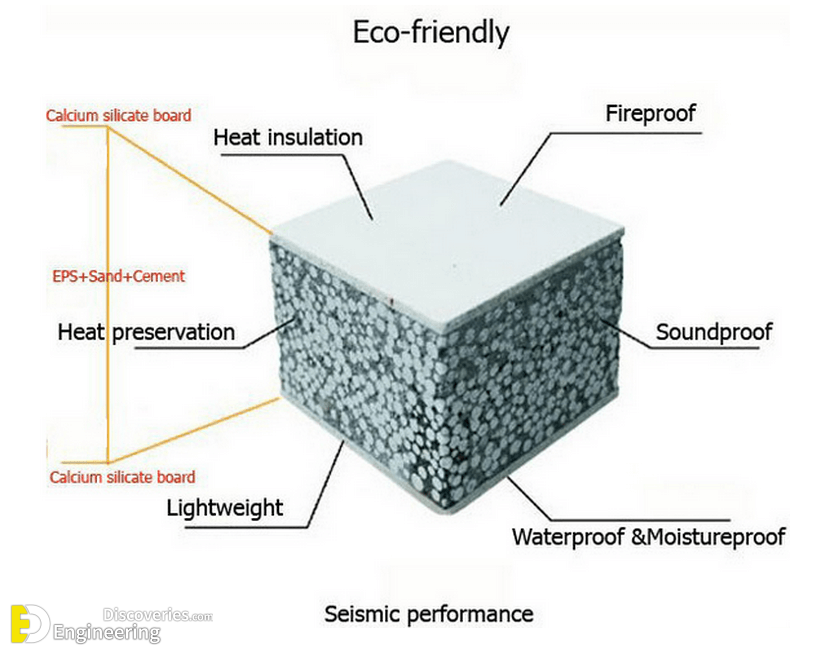
Foam concrete is a versatile building material with a simple production method that is relatively inexpensive compared to autoclave aerated concrete. Foam concrete compounds utilising fly ash in the slurry mix is cheaper still and has a less environmental impact. Foam concrete is produced in a variety of densities from 200 kg/m³ to 1,600 kg/m³ depending on the application. Lighter density products may be cut into different sizes. While the product is considered a form of concrete (with air bubbles replacing aggregate), its high thermal and acoustical insulating qualities make it a very different application than conventional concrete.
Applications
Foamed concrete can be produced with dry densities of 400 to 1600 kg/m³, with 7-day strengths of approximately 1 to 10 N/mm² respectively. Foam concrete is fire resistant, and its thermal and acoustical insulation properties make it ideal for a wide range of purposes, from insulating floors and roofs, to void filling. It is also particularly useful for trench reinstatement.
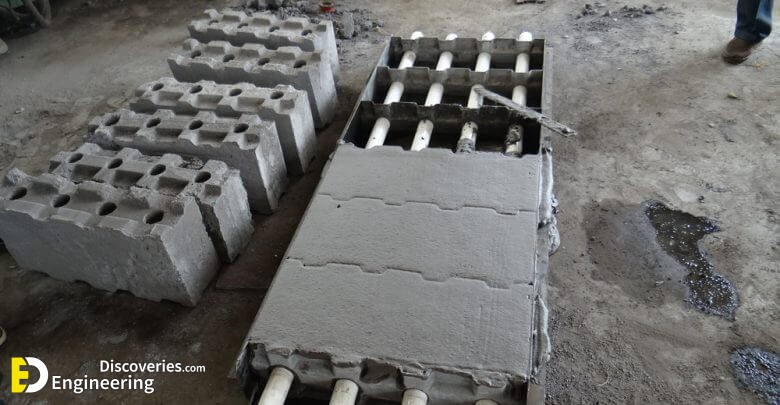
A few of the applications of foam concrete are:
1- bridge approaches / embankments
2- pipeline Abandonment / annular fill
3- trench backfill
4- precast blocks
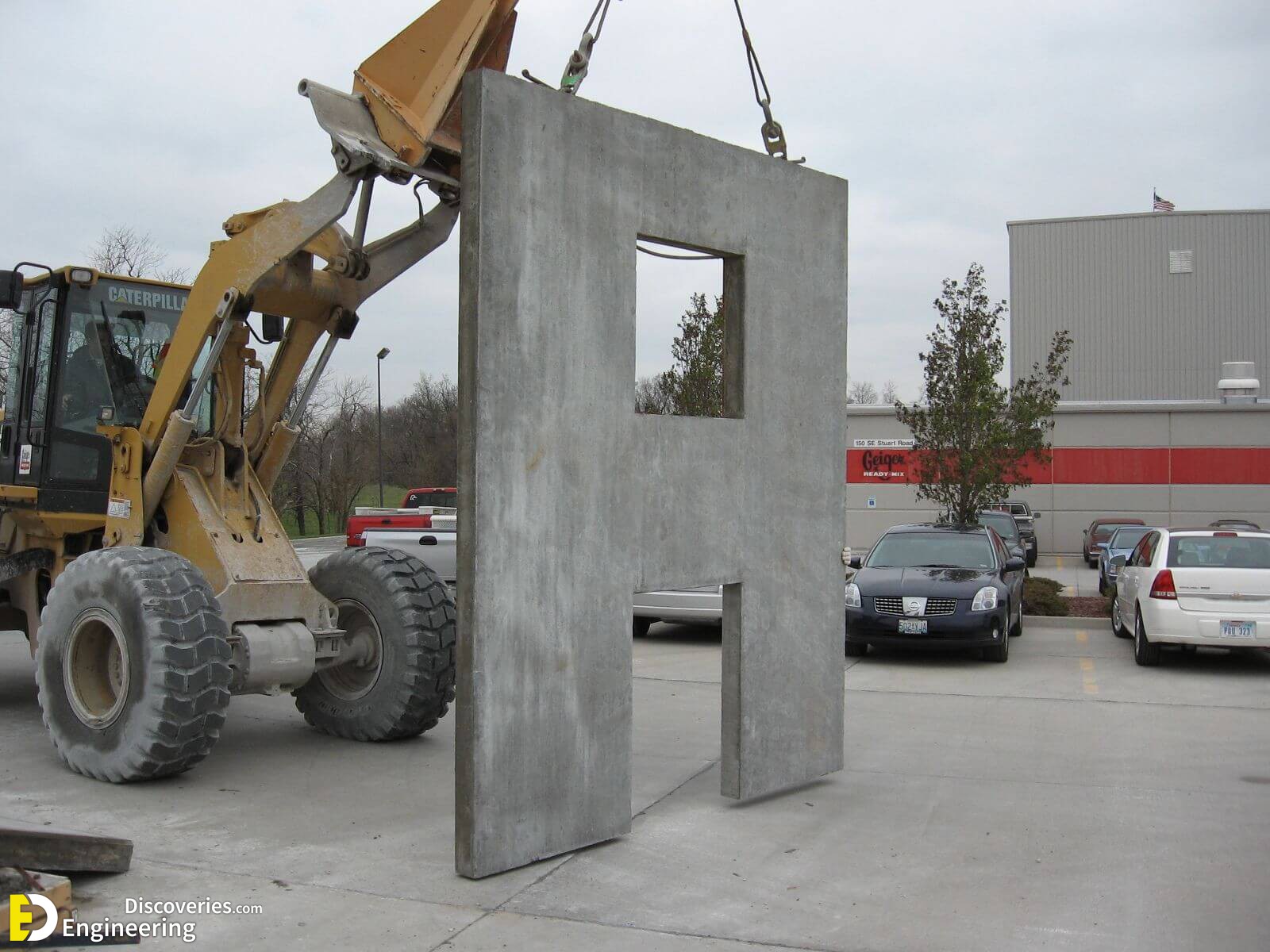
5- precast wall elements/panels
6- cast-in-situ / cast-in-place walls
7- insulating compensation laying
8- insulation floor screeds
9- insulation roof screeds
10- sunken portion filling
11- trench reinstatement
12- sub-base in highways
13- filling of hollow blocks
14- prefabricated insulation boards
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org