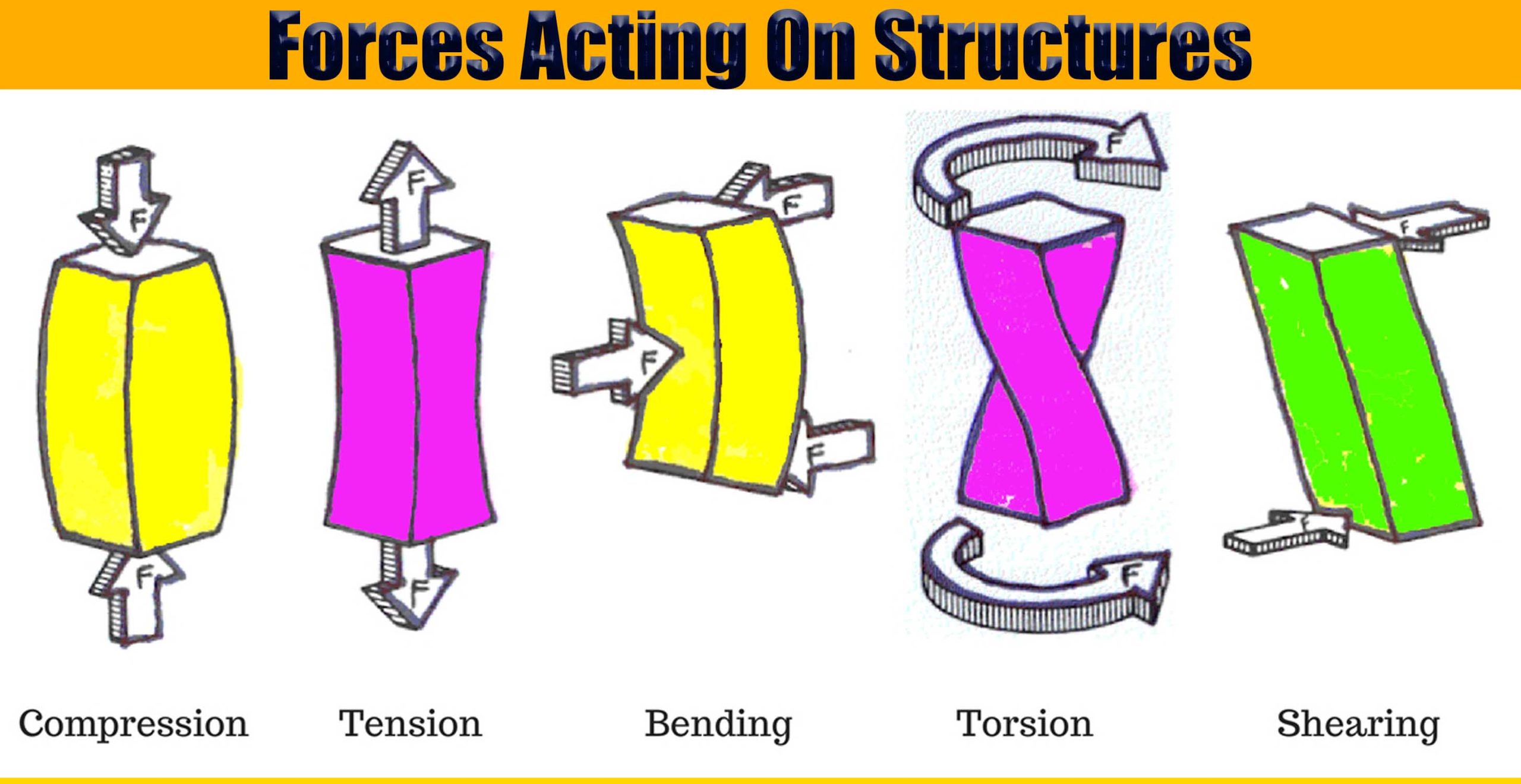
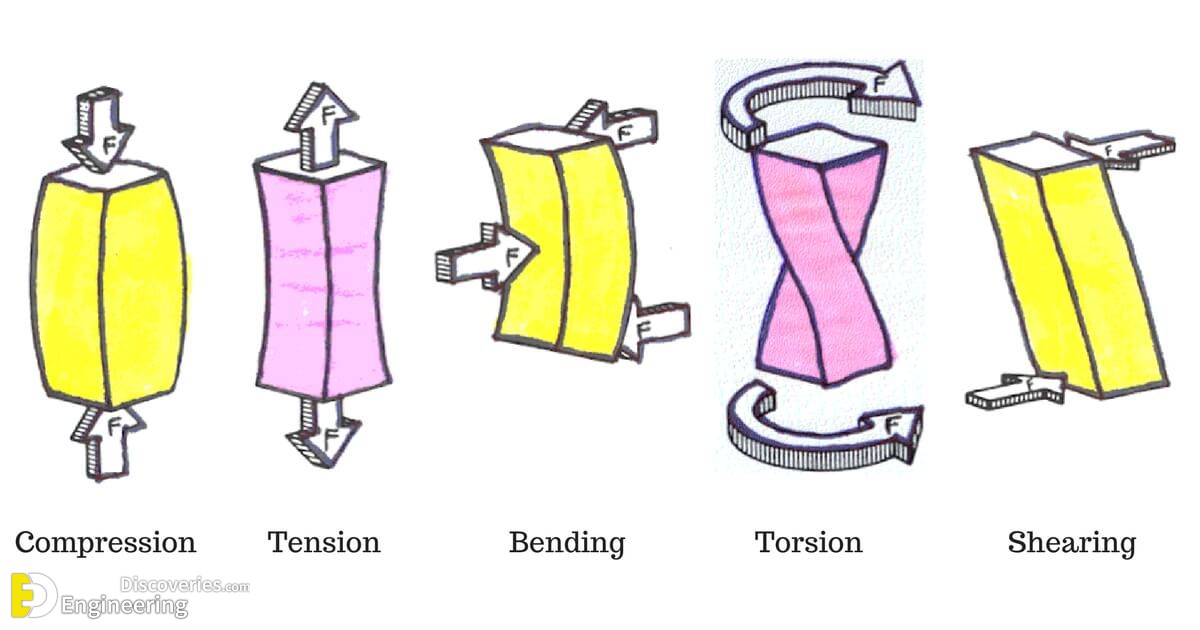
Compression
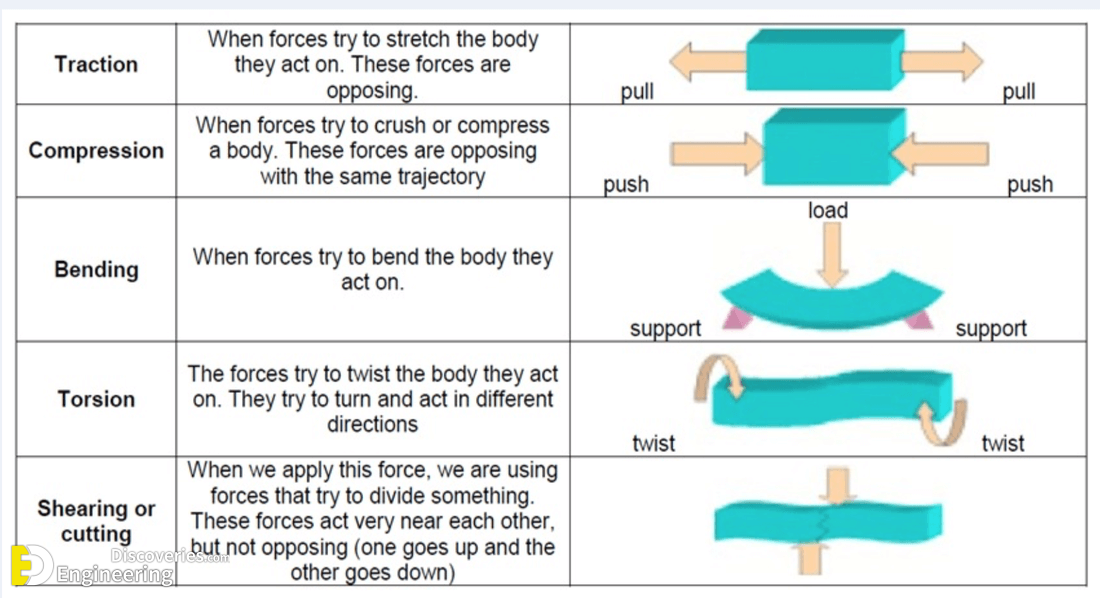
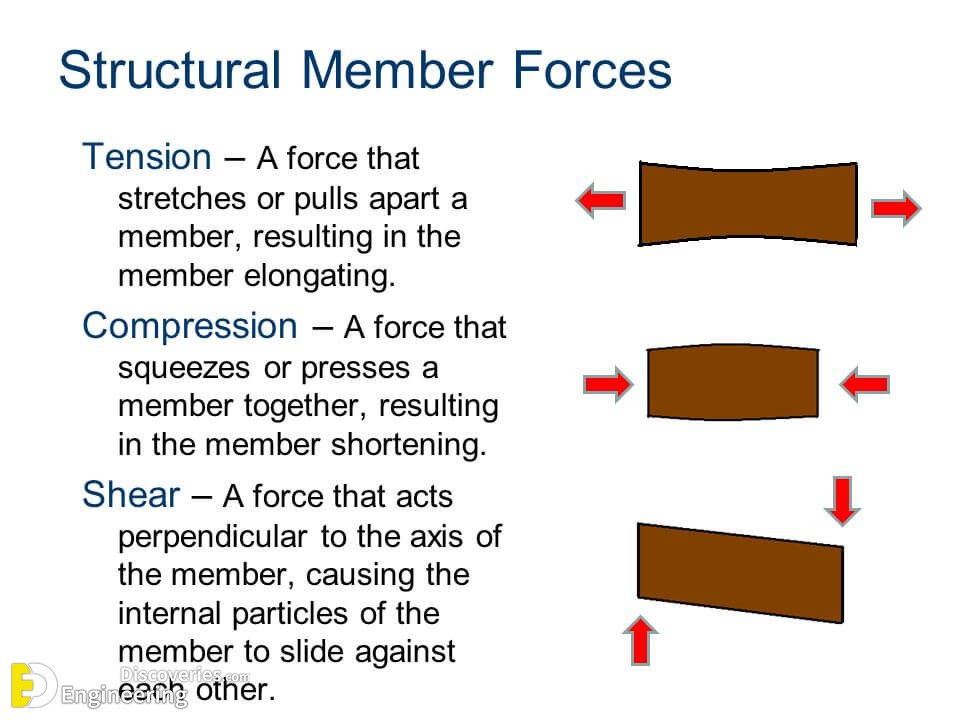
Compression Force is the application of power, pressure, or exertion against an object that causes it to become squeezed, squashed, or compacted. Objects routinely subjected to compression forces include columns, gaskets, disc brakes, and the components of fuel cells. Since columns are used to support structures, they are always subjected to axial compression forces. By studying columns, one can get an understanding of the failures caused by compression forces. The effects of such forces depend upon the geometry of the column and the physical properties of the column material.
Tension
When a string or rope is tugged on the force that is applied to it when it is tugged on is termed as tension. The tension force is felt by every section of the rope in both the directions, apart from the endpoints. The endpoints experience tension on one side and the force from the weight attached. Throughout the string, the tension varies in some circumstances. According to its definition, “Tension is a pulling force applied by a string or chain on another body”.
Bending
Bending is a process by which metal can be deformed by plastically deforming the material and changing its shape. The material is stressed beyond the yield strength but below the ultimate tensile strength. The surface area of the material does not change much. Bending usually refers to deformation about one axis.
Torsion
Torsion is an important structural action that increases member shear strength. It occurs when it is twisted causing twisting force acting on the member, known as torque, and the resulting stress is known as shear stress. This stress is added to the existing shear stress due to vertical and lateral applied loads. Torsion means twisting. If you are applying a force to a manual screwdriver, you are applying torsion. Similarly, a rod being turned by a mechanism around its longitudinal axis is experiencing a torsion force.
Shearing
Shear is a directional word referring to forces or stresses. A shear force goes parallel to the surface of an object or material. Shear stress can happen between two objects or within the same object. Shear stress between two objects occurs when a force pulls the object along the same plane as the face of the object abutting another object that is being pulled in the opposite direction. Shear stress within an object will occur when a force parallel to the plane causes one plane of the material to want to slip against another, thus deforming the material.
Click Here To See Brief Description About Stress And Strain Diagram