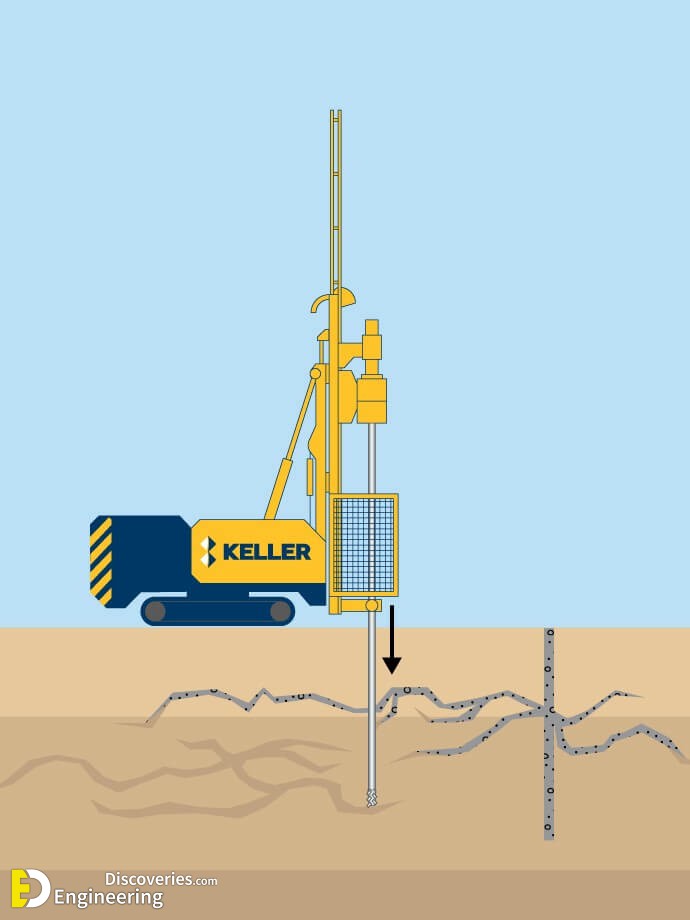
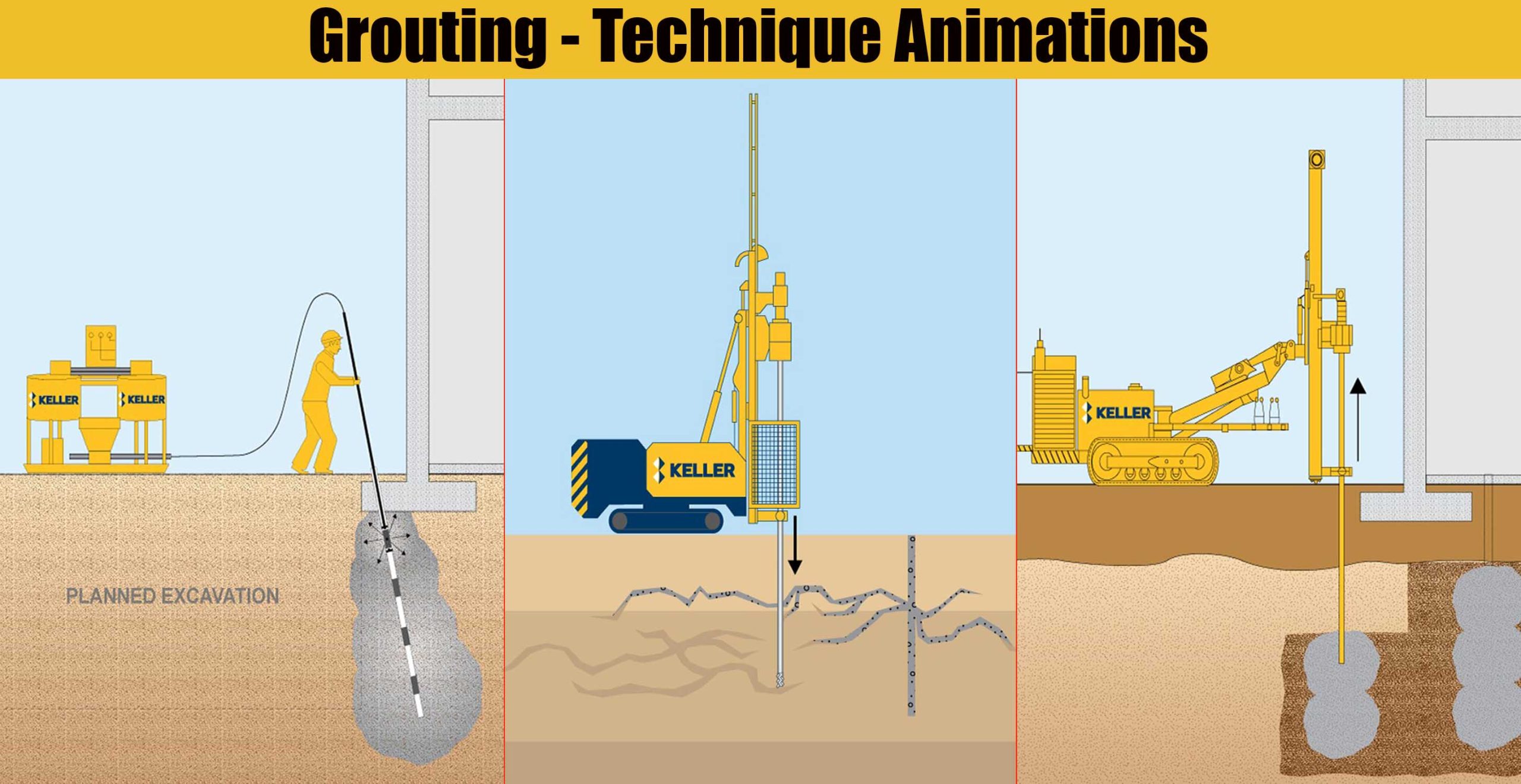
1- Cement Grouting
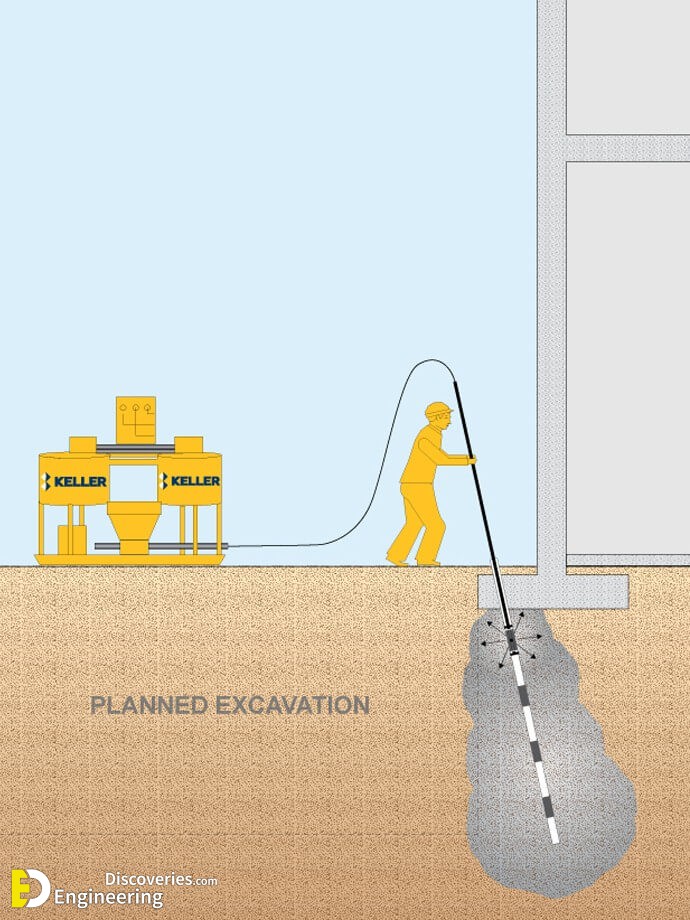
Cement grouting, also known as slurry grouting or high mobility grouting, is a grouting technique that fills pores in granular soil or voids in rock or soil with flowable particulate grouts. Depending on the application, Portland cement or microfine cement grout is injected under pressure at strategic locations either through a single port or multiple port pipes
2- Chemical Grouting
Chemical grouting is a grouting technique that transforms granular soils into sandstone-like masses, by permeation with a low viscosity grout.
3- Compaction Grouting
Compaction grouting, also known as Low Mobility Grouting, is a grouting technique that displaces and densifies loose granular soils, reinforces soils and stabilizes subsurface voids or sinkholes, by the staged injection of low-slump, low mobility aggregate grout.
4- Fracture Grouting
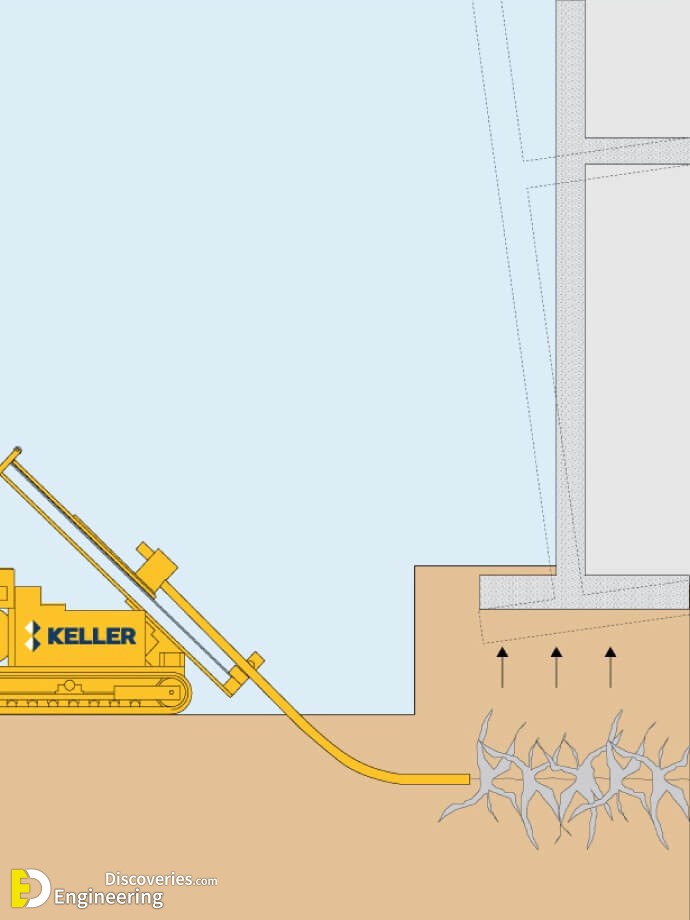
Fracture grouting, also known as compensation grouting, is a grouting technique that hydro fractures in situ soil, using neat fluid grout.
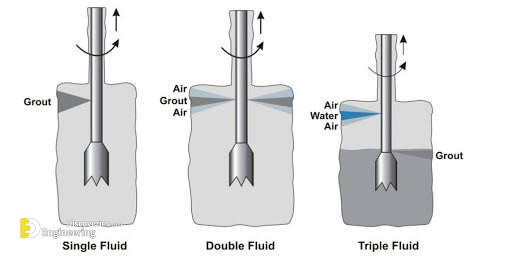
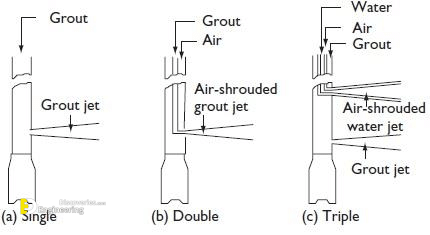
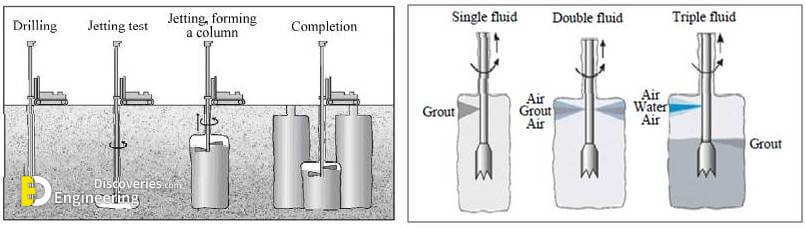
5- Jet Grouting – Single Fluid
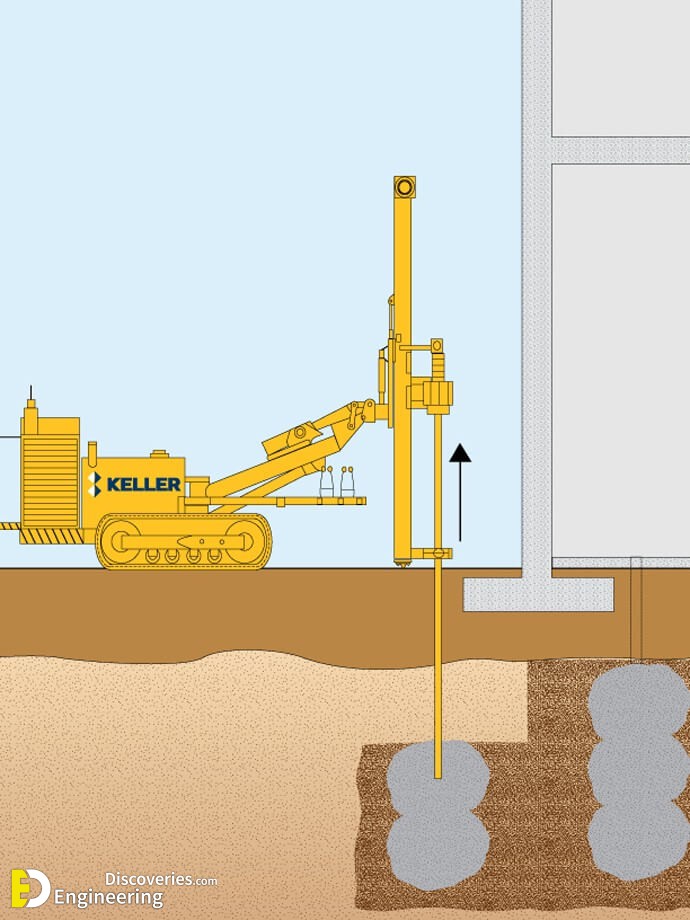
Single Fluid System Jet Grouting is a versatile Ground Modification system in which a high-velocity cement slurry jet hydraulically cuts and mixes soils in-situ to create designed geometries of silcrete.
6- Jet Grouting – Double Fluid
Double Fluid System Jet Grouting is a versatile Ground Modification system in which a high-velocity cement slurry jet shrouded by an air jet for increased efficiency hydraulically cuts and mixes soils in-situ to create designed geometries of silcrete.
7- Jet Grouting – Triple Fluid
Triple Fluid System Jet Grouting is a versatile Ground Modification system in which a high-velocity water jet shrouded by an air jet for increased efficiency hydraulically erodes soils which are then mixed with a jet of cement slurry in-situ to create designed geometries of silcrete.
8- Polyurethane Grouting
Polyurethane grouting is a grouting technique that involves the injection of expanding polyurethane to cut off water flow through concrete joints or cracks or to fill voids beneath slabs or behind subsurface concrete walls.