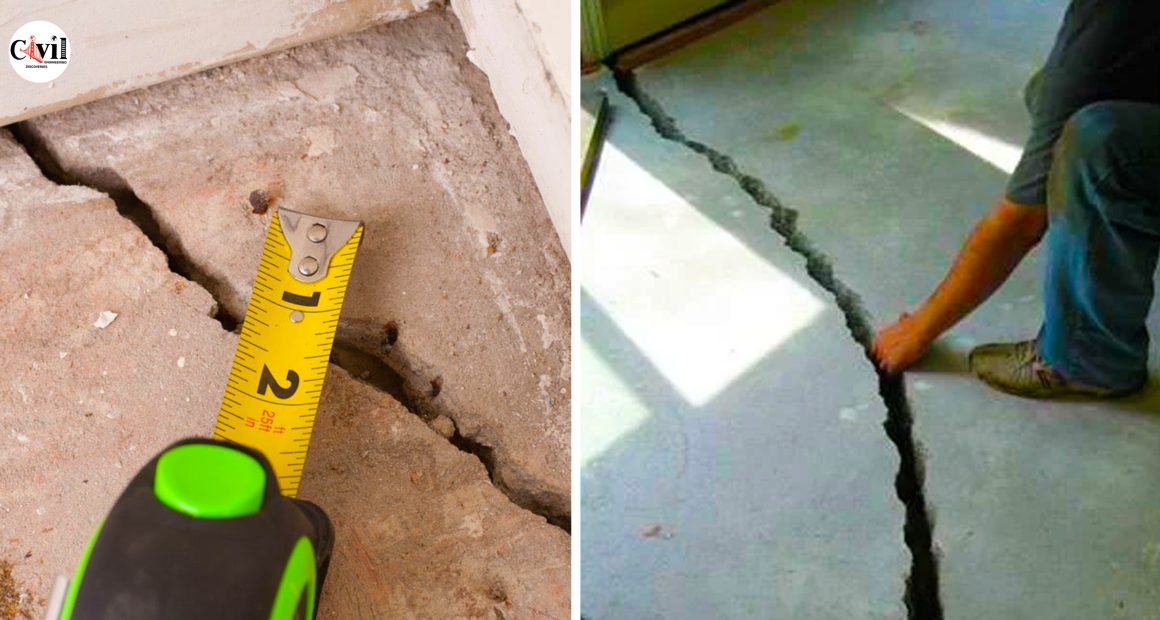
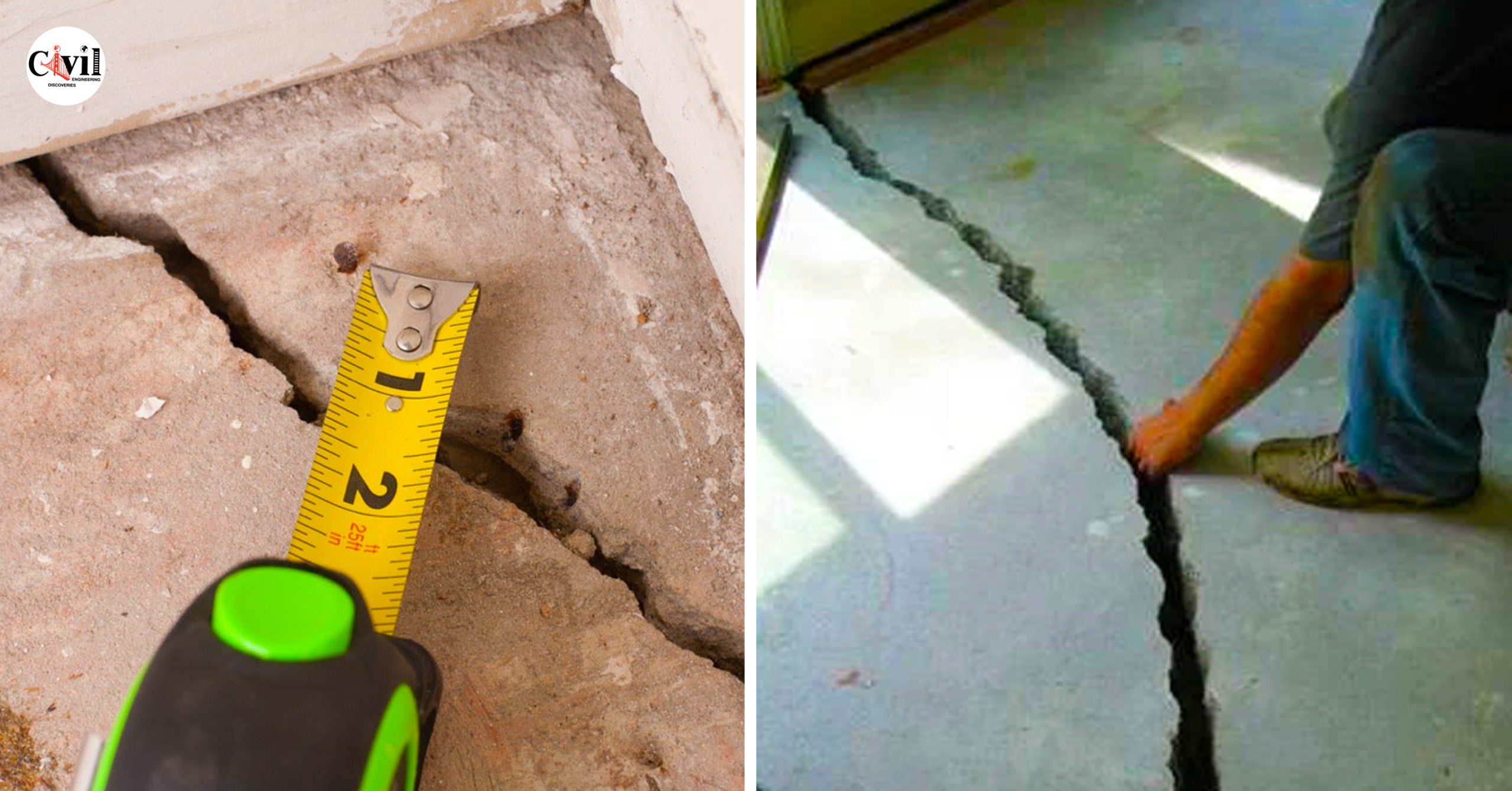
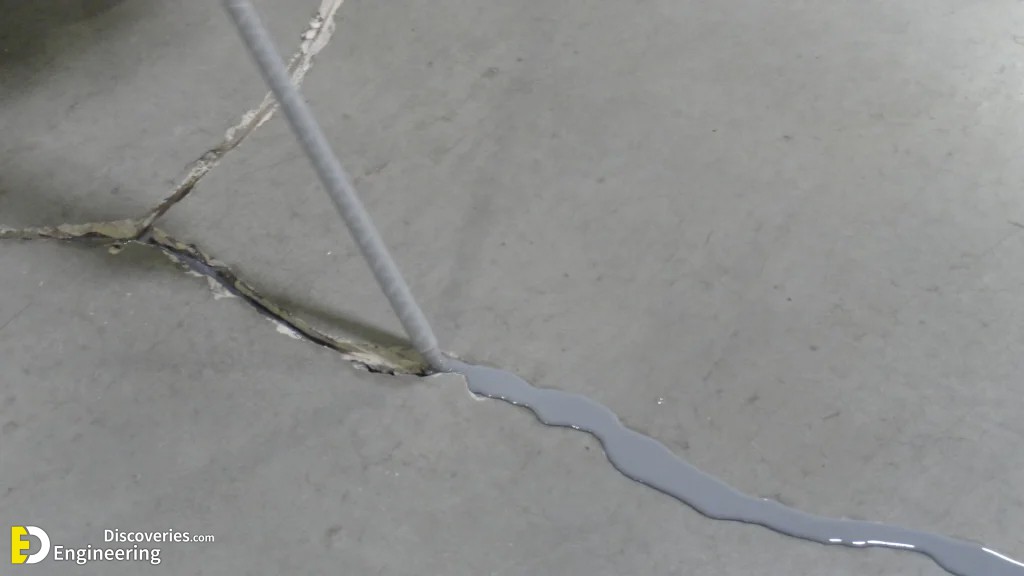
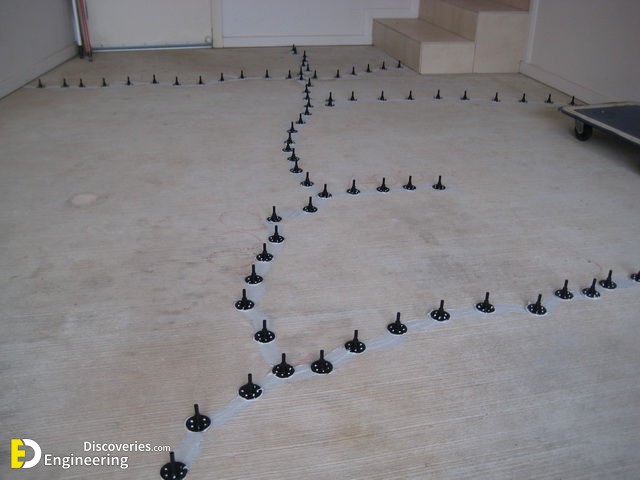
To repair concrete cracks, you must understand the cause of the cracks, and select the appropriate repair technique. Here are five standard concrete repair methods.
1. Routing and Sealing
- Suitable for dormant (inactive), non-structural cracks.
- Can be used for flat horizontal and vertical cracks with the proper sealant.
- Materials include epoxies, silicones, urethanes, and polymer mortars.
- The flexibility and hardness of the sealant affect its performance.
- Involves widening the crack, cleaning it, and filling it with sealant.
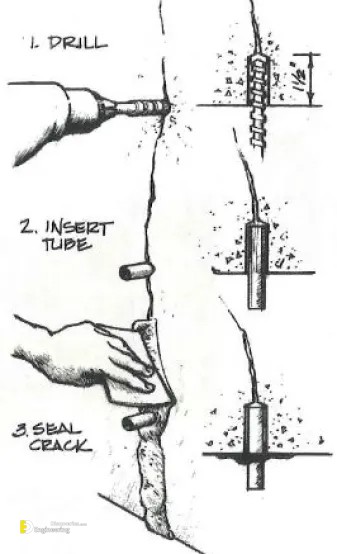
2. Injection Grouting
- Used for reducing, filling, or repairing structural cracks, foundation issues, and waterproofing.
- Various grout types include polymer-based, fiber-reinforced, or cement-sand.
- Involves drilling holes, cleaning cracks, placing injection ports, and injecting grout.
- Helps reinforce, repair, or strengthen the concrete structure.
3. Epoxy Injection
- Common for structural crack repairs, especially in foundations and basements.
- Epoxies have varying viscosities for different crack sizes.
- Requires crack to be dormant and dry; not suitable for active cracks.
- May use injection ports for certain crack types.
- Restores concrete structure to original strength.
4. Stitching
- Suitable for reinforcing and repairing active cracks.
- Doesn’t fully close the crack but stops its movement.
- Uses U-shaped metal bars placed perpendicular to the crack.
- Involves drilling a trench, inserting U-bars, and filling it with grout or epoxy.
5. Drilling and Plugging
- Used for active cracks that are relatively straight and accessible at one end.
- Common for vertical cracks in retaining walls.
- Involves drilling a hole along the length of the crack and filling it with grout or epoxy.
- Creates a “key” to lock the crack and prevent further movement.
The choice of repair method depends on factors such as crack type, size, and whether it’s active or dormant. It’s essential to identify and address the source of the crack for the best results, and consulting a local concrete specialist is recommended for non-specialists.