Concrete is one of the most widely used construction materials, offering a variety of types to suit different building needs. Each type of concrete has specific applications, from simple mixtures to complex reinforced options. This article will explore the major types of concrete and their unique benefits.
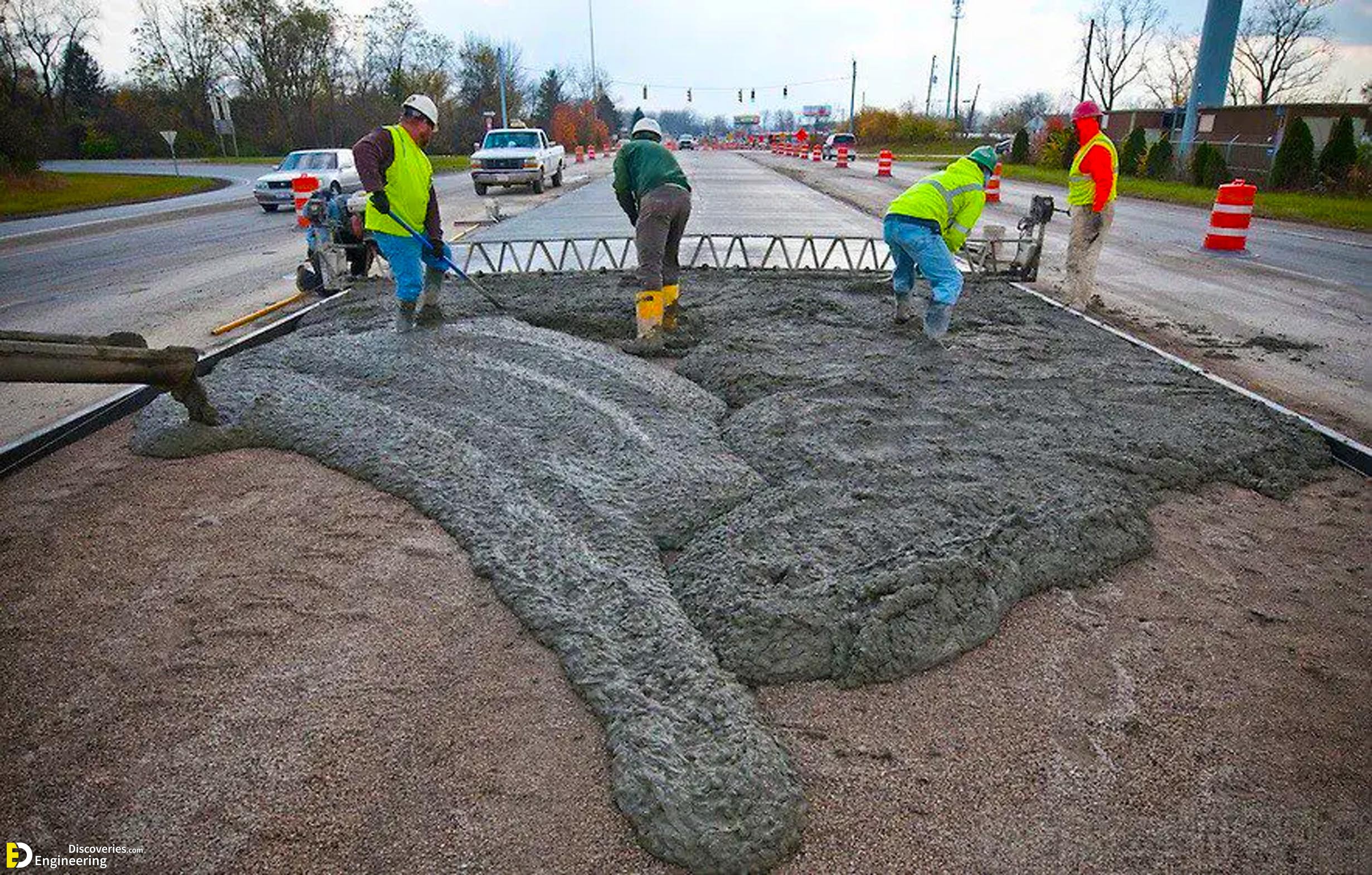
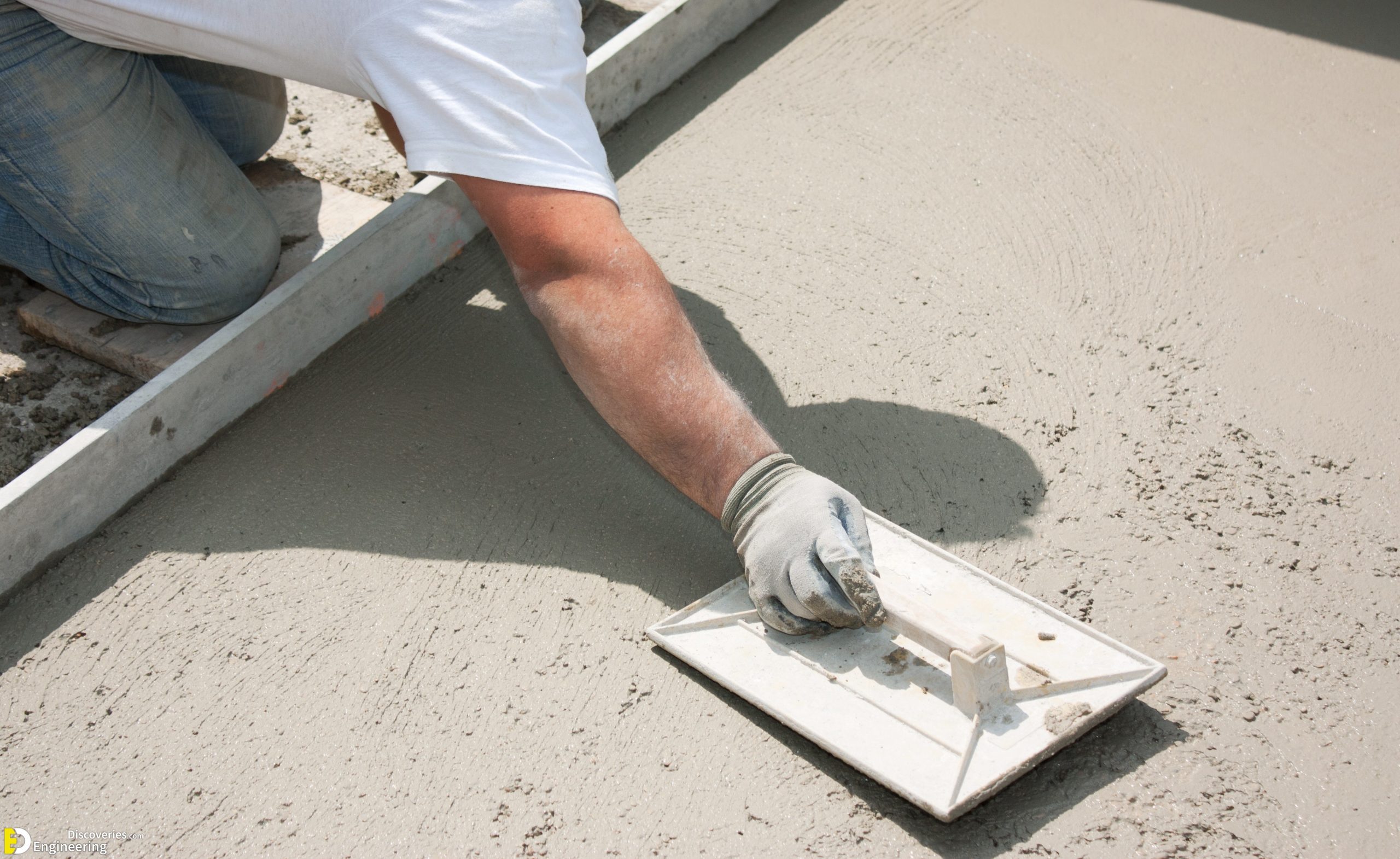
1. Plain Cement Concrete (PCC)
Plain Cement Concrete, also known as PCC, is a mixture of cement, sand, and aggregates without any reinforcement. It offers high compressive strength, making it ideal for non-load-bearing structures such as flooring or pavements. However, its low tensile strength limits its use in heavy-load applications.
Key Features of Plain Cement Concrete:
- Simple composition: Cement, sand, and aggregates.
- Strong compression: Excellent compressive strength for basic construction.
- Weak in tension: Not suitable for tensile loads or structural frames.
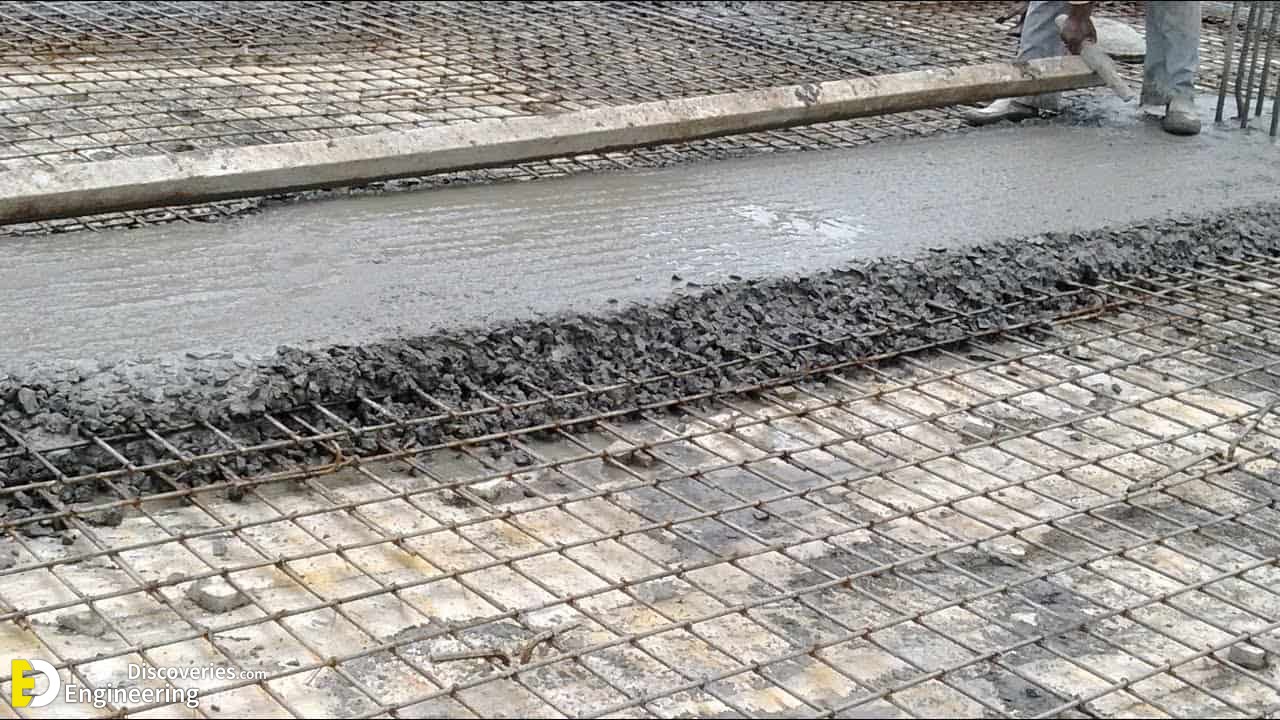
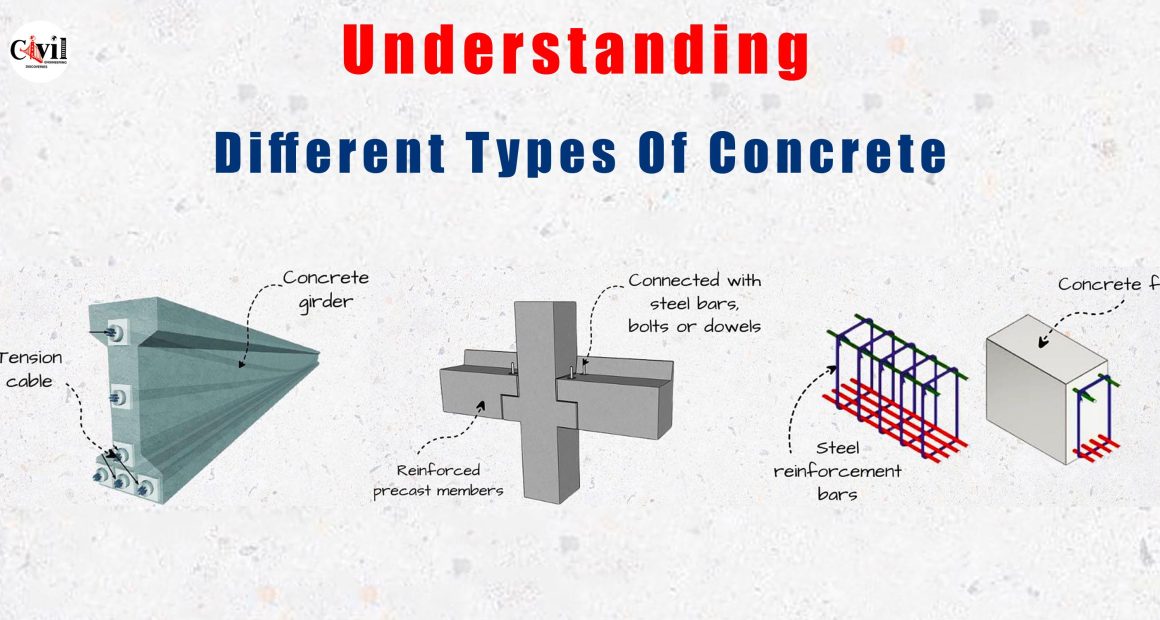
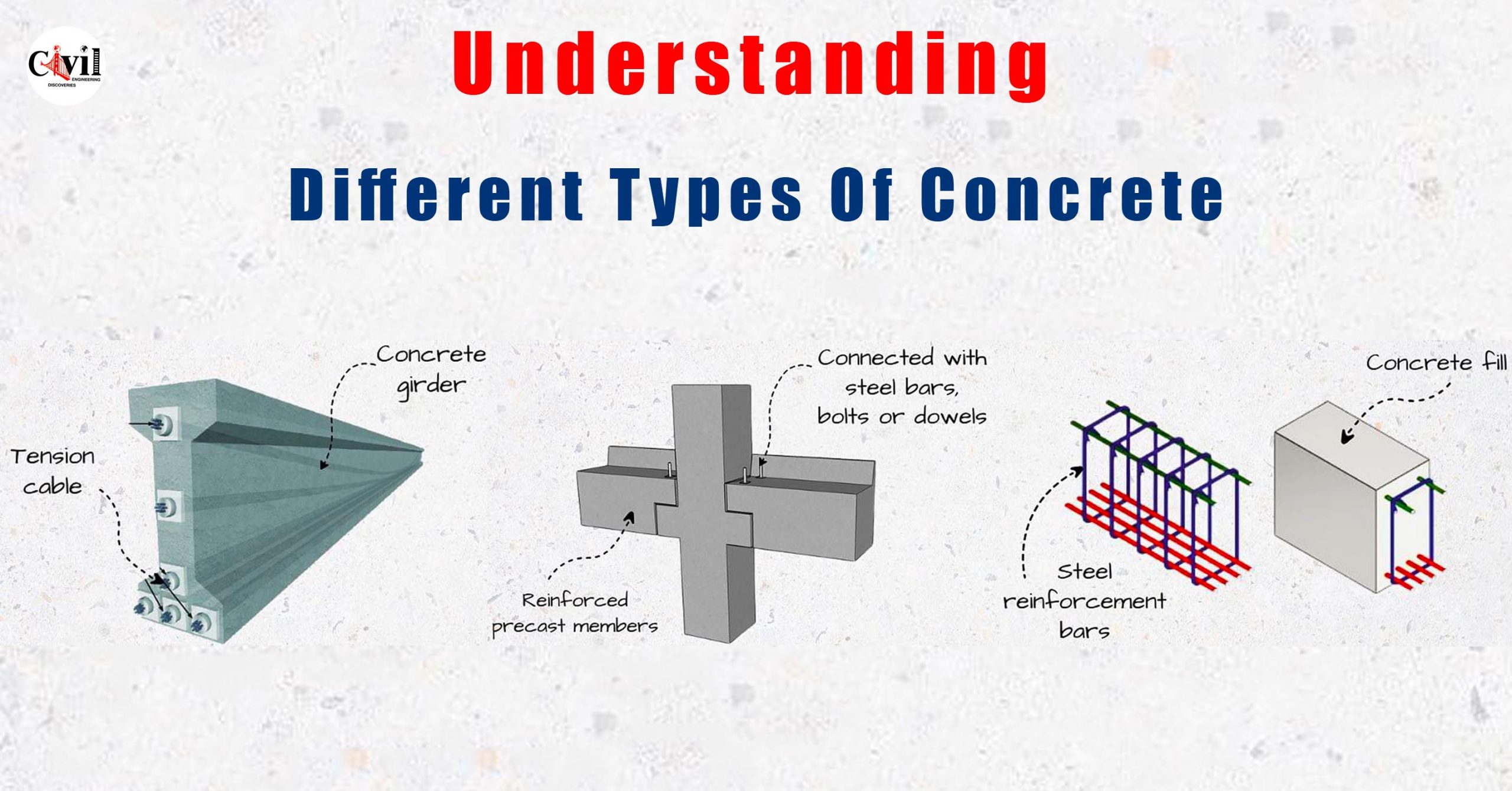
2. Reinforced Concrete (RCC)
Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) incorporates steel bars to enhance tensile strength. The combination of steel and concrete creates a durable structural material capable of supporting both compressive and tensile forces. RCC is commonly used in large-scale constructions such as bridges, buildings, and dams.
Advantages of Reinforced Concrete:
- Strength: Reinforcement with steel provides superior tensile strength.
- Durable framework: Ideal for long-lasting structural integrity.
- Versatile use: Suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial projects.
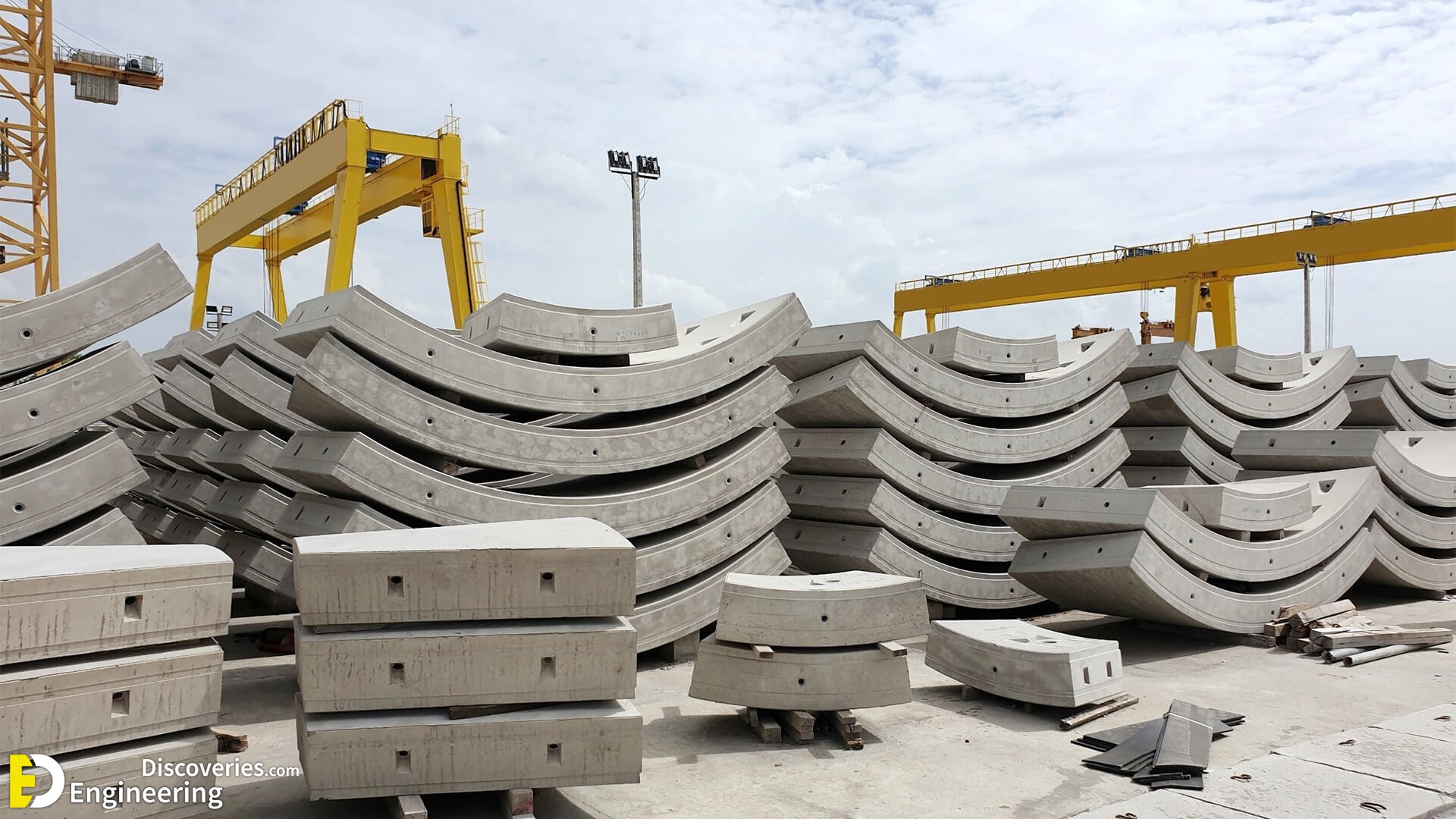
3. Precast Concrete
Precast concrete is produced by casting and curing concrete in a controlled environment. The cured components are then transported to the construction site, where they are assembled. This method speeds up the building process and ensures uniform quality.
Benefits of Precast Concrete:
- Controlled production: Manufactured in controlled environments for better quality.
- Faster construction: Reduces onsite labor time.
- Durability: Ensures consistent performance in a wide range of applications.
4. Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete is created by incorporating lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or slate. This results in a material that is easier to handle and offers better thermal insulation. Lightweight concrete is often used in the construction of lightweight blocks and insulation panels.
Characteristics of Lightweight Concrete:
- Lower density: Easier to transport and install.
- Thermal properties: Offers improved insulation compared to standard concrete.
- Cost-effective: Reduces overall material weight and construction costs.
5. Prestressed Concrete
Prestressed concrete is engineered for heavy loads and large spans. High-strength steel cables are tensioned before the concrete is poured, creating a pre-compressed structure that is highly resistant to tensile stress. This type of concrete is typically used in bridge construction and large industrial buildings.
Why Choose Prestressed Concrete:
- High load capacity: Ideal for large-span structures and heavy loads.
- Enhanced performance: Pre-tensioning boosts strength and durability.
- Efficient design: Reduces the need for additional support structures.
Click Here To See The Importance of a Drainage Swale in Protecting Your Home










it is good, mined storm
Really you feeding me mind food