Earthquakes seriously threaten buildings and infrastructure, often leading to severe structural damage and even collapse. One of the critical elements in earthquake-resistant design is the structural frame, which must be capable of withstanding seismic forces while maintaining stability. A common issue in earthquake structural failures is the inadequate distribution of force on footings, which can lead to excessive rotations, stress concentration, and soil pressure imbalance.
In this article, we analyze the effects of earthquakes on structural frames and demonstrate the importance of using connecting beams in foundation design to improve seismic resistance.
How Earthquakes Affect Structural Frames
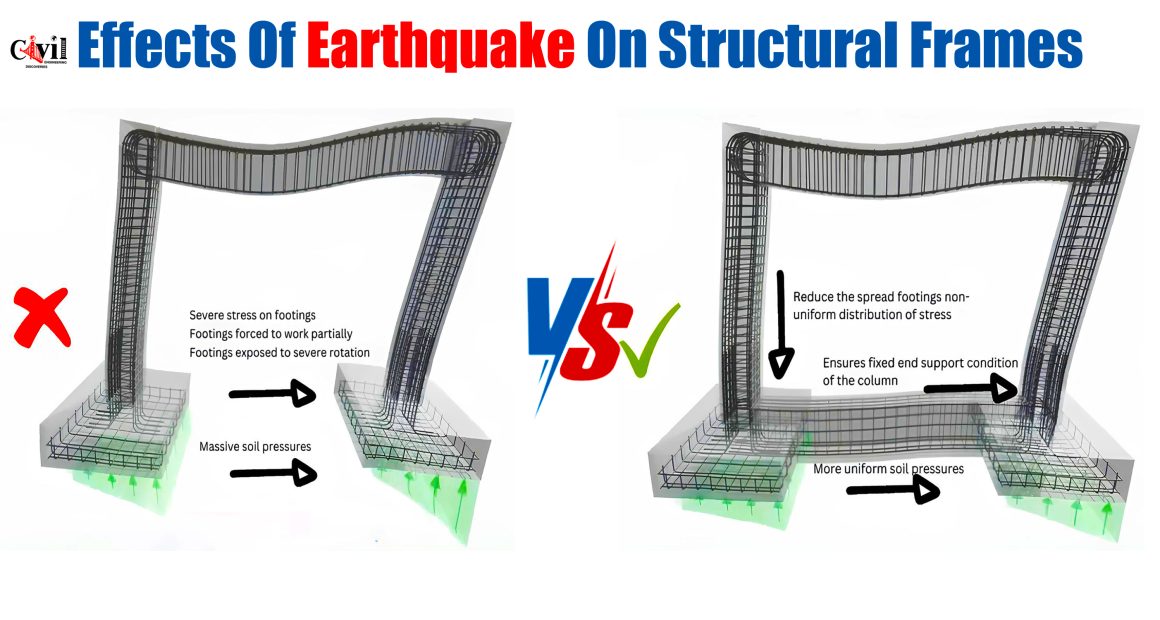
During an earthquake, seismic waves generate strong lateral forces that impact the structure’s frame, affecting columns, beams, and footings. The absence of a properly designed connecting beam in the foundation results in non-uniform stress distribution, causing several issues:
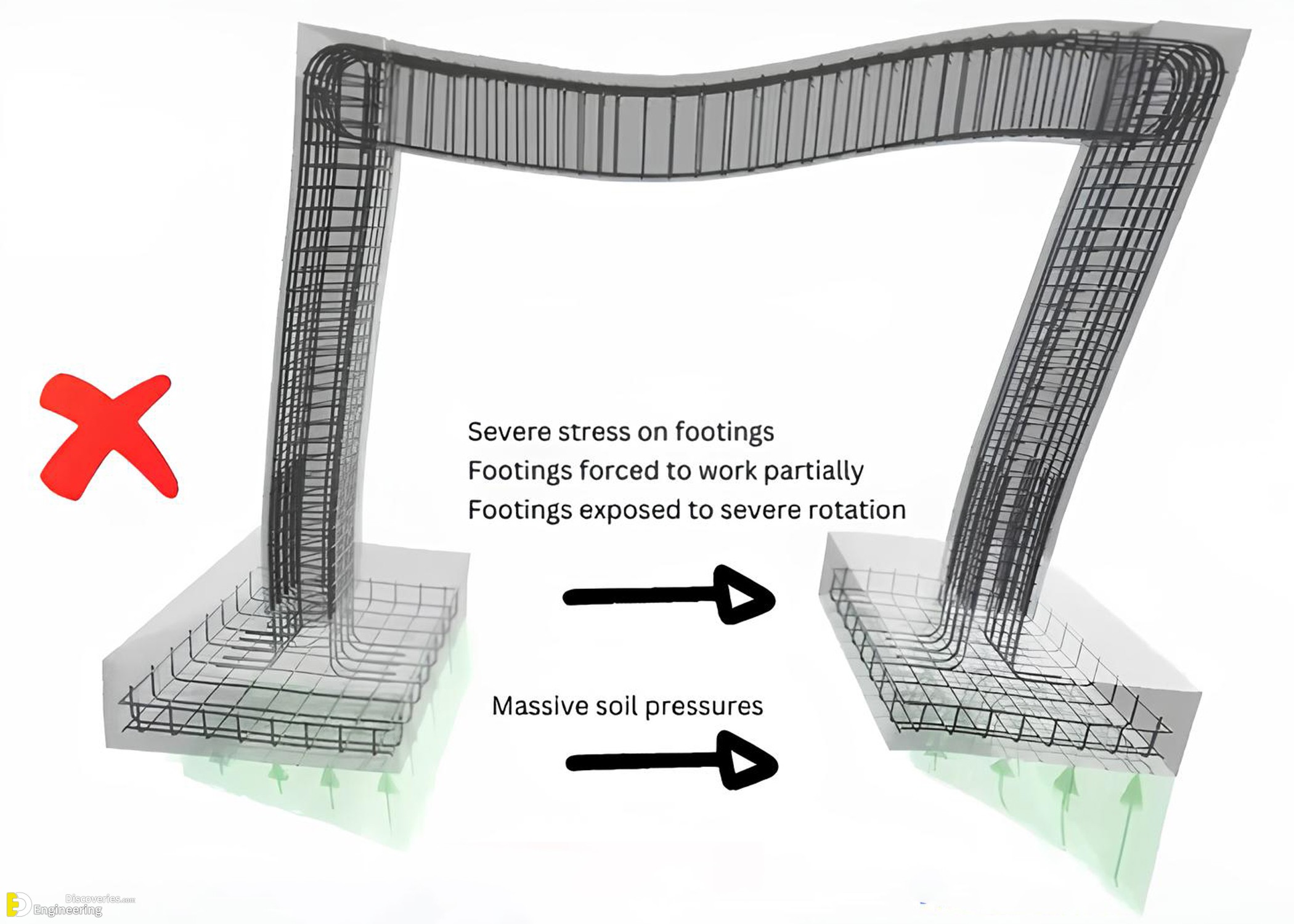
- Severe Stress on Footings – Without a connecting beam, the footings experience excessive stress as they are forced to support the structure independently.
- Unequal Load Distribution – The lack of a connection between footings results in non-uniform force transfer, making certain parts of the foundation more vulnerable.
- Severe Rotation of Footings – Isolated footings tend to rotate significantly when subjected to seismic forces, leading to instability and potential structural failure.
- Massive Soil Pressure Variations – An unbalanced load distribution causes certain areas to experience excessive soil pressure, leading to differential settlement and weakening of the foundation.
The Role of Connecting Beams in Earthquake Resistance
A connecting beam in the foundation significantly enhances the structure’s ability to withstand seismic forces. It works by distributing stress more evenly and ensuring that footings function as a unified system rather than isolated supports. The key benefits of adding a connecting beam include:
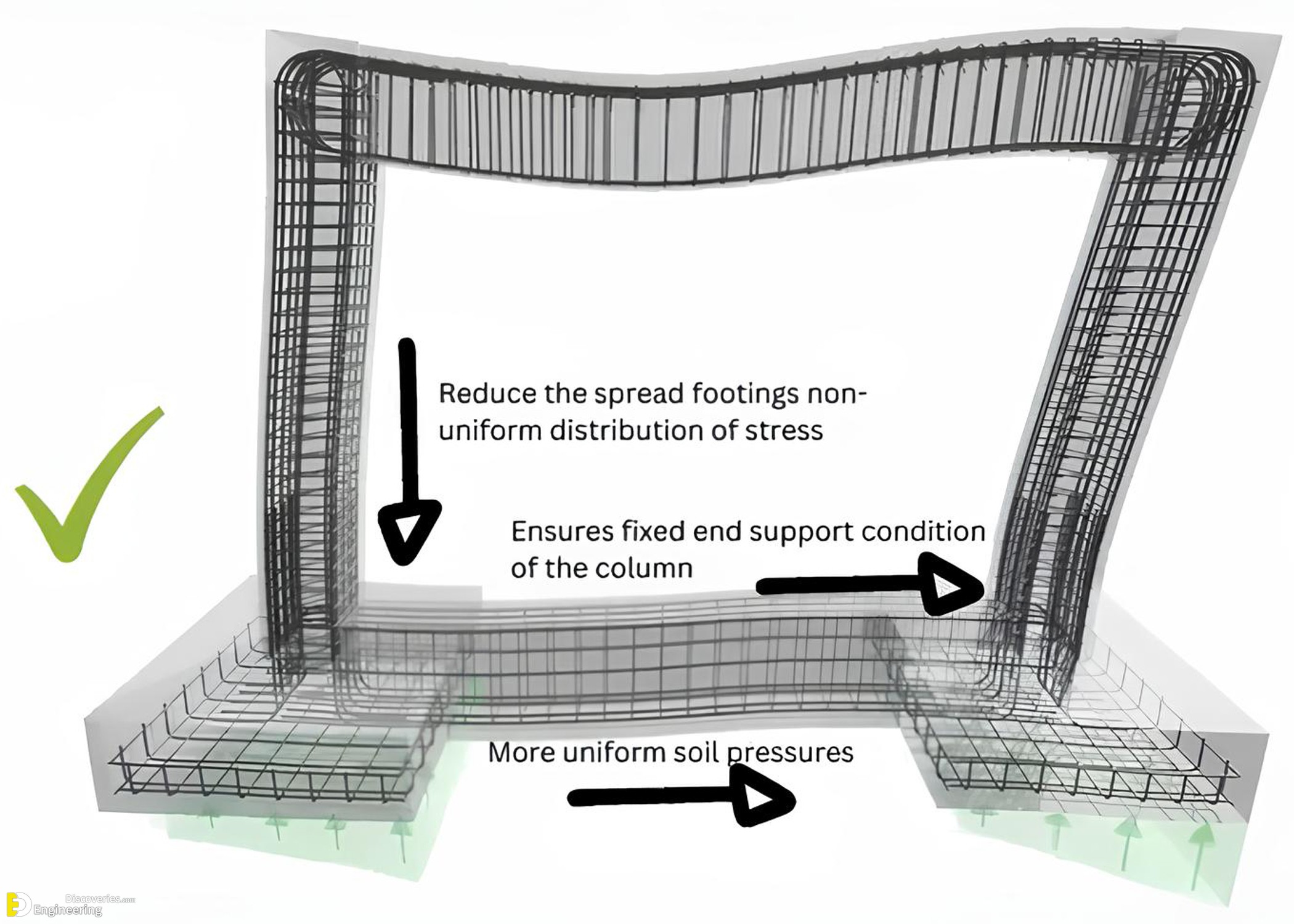
- Reduces the Spread of Non-Uniform Stress Distribution – Connecting beams help distribute loads more evenly across footings, preventing excessive stress concentration in certain areas.
- Ensures Fixed-End Support Conditions for Columns – The addition of a connecting beam stabilizes columns, reducing the risk of bending and failure under seismic loads.
- Improves Soil Pressure Distribution – A connected foundation ensures that soil pressure remains uniform, minimizing the risk of differential settlement and foundation instability.
- Enhances Overall Structural Rigidity – By integrating footings through a connecting beam, the structure gains additional rigidity, which helps it resist seismic forces more effectively.
Comparing Structures With and Without Connecting Beams
To further illustrate the importance of connecting beams in seismic design, let’s compare two scenarios:
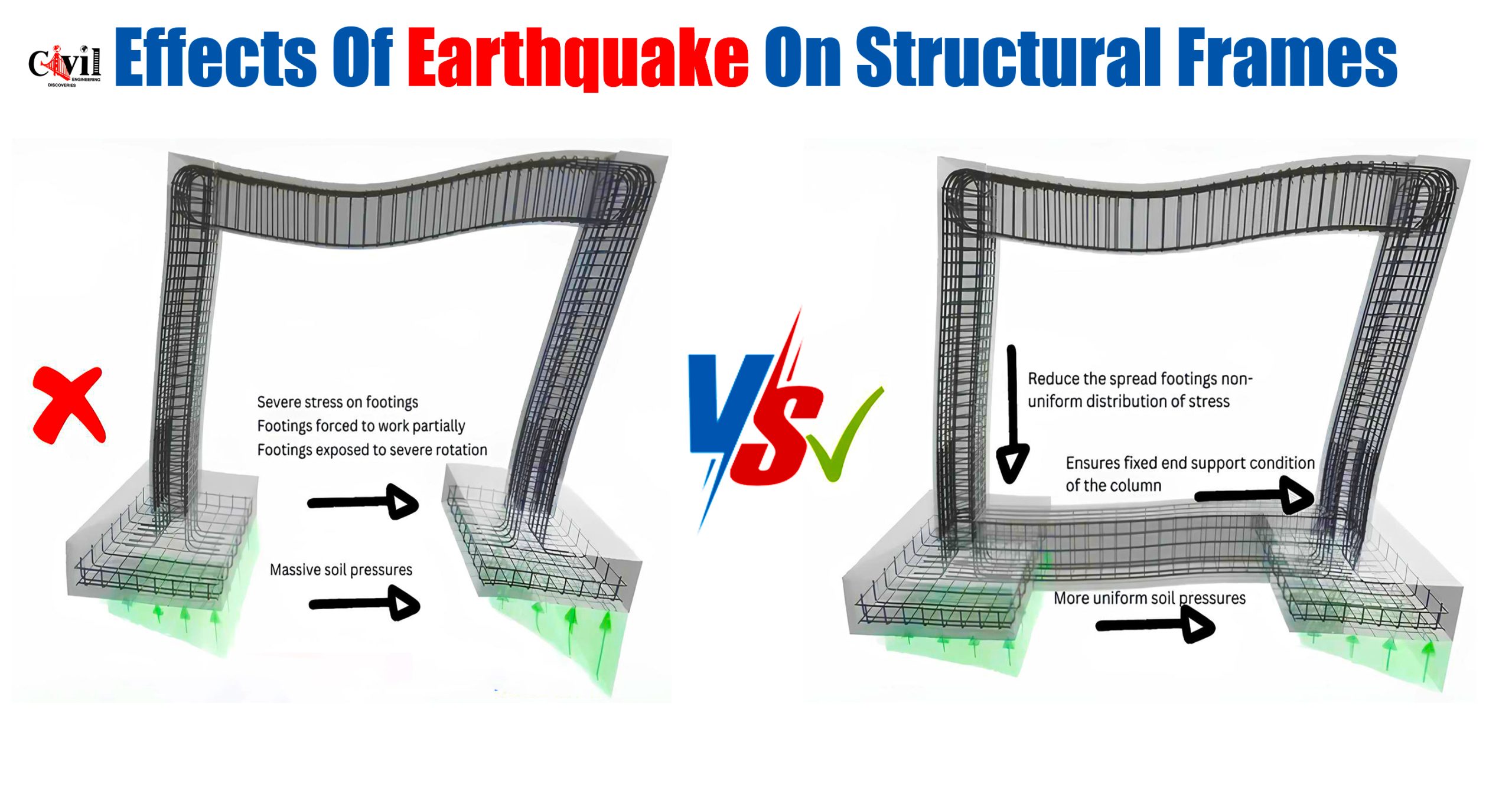
Case 1: Structure Without a Connecting Beam
- Footings experience severe rotation due to uneven force distribution.
- High-stress concentrations lead to potential foundation failure.
- Soil pressure is non-uniform, increasing the risk of settlement and instability.
- The structural frame becomes vulnerable to collapse under seismic forces.
Case 2: Structure With a Connecting Beam
- Stress is evenly distributed across all footings, reducing localized pressure.
- Footings remain stable with minimal rotation, ensuring a stronger foundation.
- Soil pressure is more uniform, preventing excessive settlement.
- The structural frame gains increased resistance to earthquake-induced forces.





Can you please post a theory on using base isolators / dampers to resist the earthquake?
https://engineeringdiscoveries.com/the-science-behind-base-isolators-and-dampers-in-earthquake-resistance/