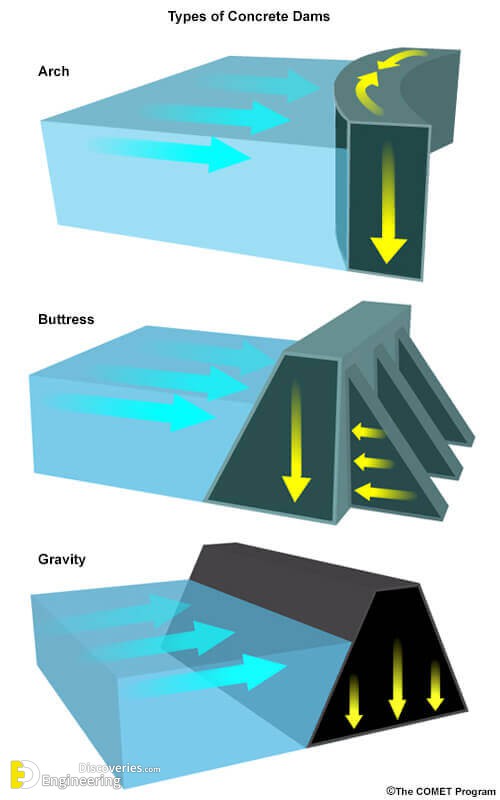
A Dam is an obstruction or barrier built across a stream or river and it is a structure built to retain water.
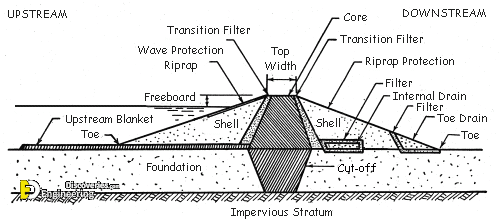
1- Embankment dam
• Constructed from compacted soil (“earth fill”) or rock (“rockfill”) with an impervious core
• Designed to transfer the entire water load downward
• 80% of all large dams in the U.S. are embankment dams
• Used to retain water across wide river valleys or for flood control
• Typically shorter and wider than other types of dams
2- Gravity dam
• Constructed of concrete or stone masonry
• Designed to transfer the entire water load downward
• Typically span narrow river valleys with bedrock abutments and foundations
• Retain water by utilizing the weight of the dam to resist the horizontal water load pushing against it
• Each section of the dam is independently stable
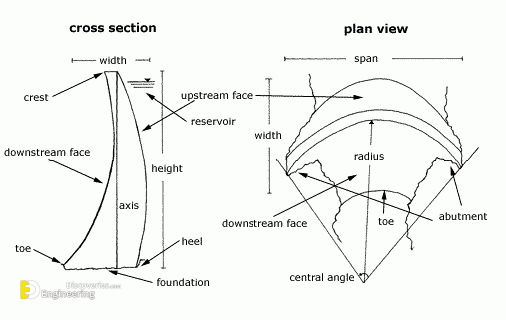
3- Arch dam
• Constructed of concrete
• Designed to transfer water loads to the adjacent rock formations
• Constructed only in canyons with solid rock walls that are able to resist the pressure of the dam
• Because the canyon walls bear the bulk of the load, arch dams are thinly constructed, requiring less material than other types of dams
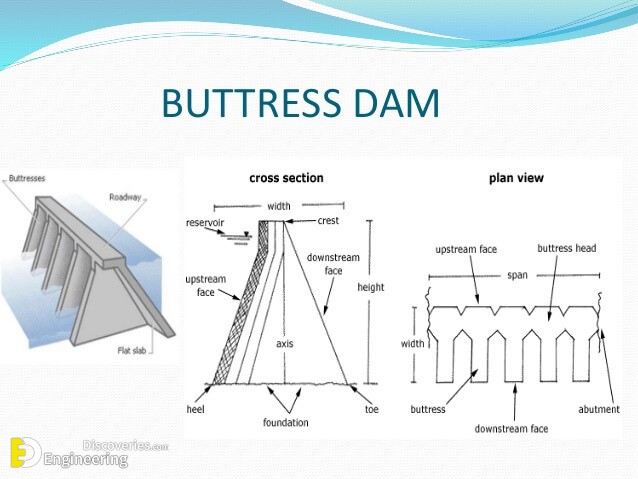
4- Buttress dam
• Constructed of reinforced concrete
• Designed to transfer the waler load both downward and to the buttresses
• Hollow gravity dams with a solid upstream face and a buttressed downstream side
• Buttresses are supports that transmit the water force to a bedrock foundation
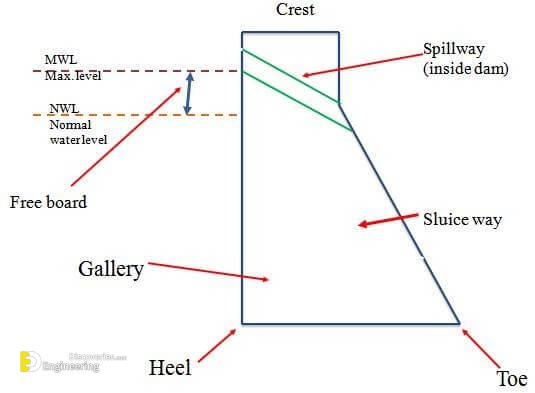
Componentes of dam
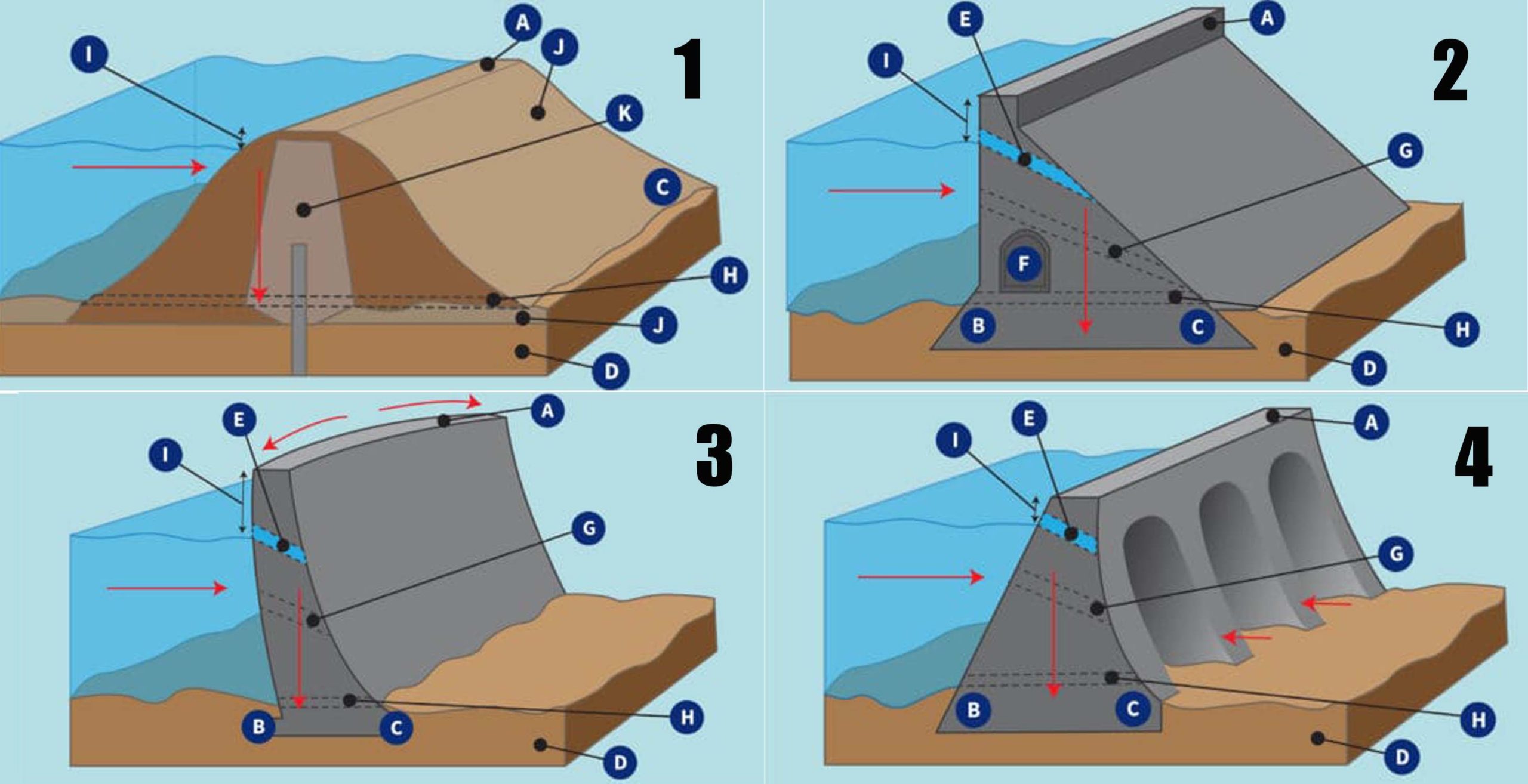
A Crest: The top of the dam, in some cases used to provide a roadway or walkway over the dam
B Heel: The part of the dam in contact with the ground or the upstream side
C Toe: The part of the dam in contact with the ground on the downstream side
D Foundation: Excavated surface or undisturbed material
E Spillway: Structure that provides for Controlled conveyance of water flows
downstream of the dam.
F Gallery: Small room within large dams used to monitor the performance of the dam, with a drain on the floor for water seepage.
G Outlet: Also called sluiceway, used to release water from the reservoir for water supply, irrigation, and hydropower
H Blowoff: Opening within the dam near the base to drain the reservoir.
I Freeboard: Vertical distance between the spillway level and the crest of the dam
J Previous Material: Substances that allow water to pass through
K Impervious Material: Substance that does not allow water to pass through