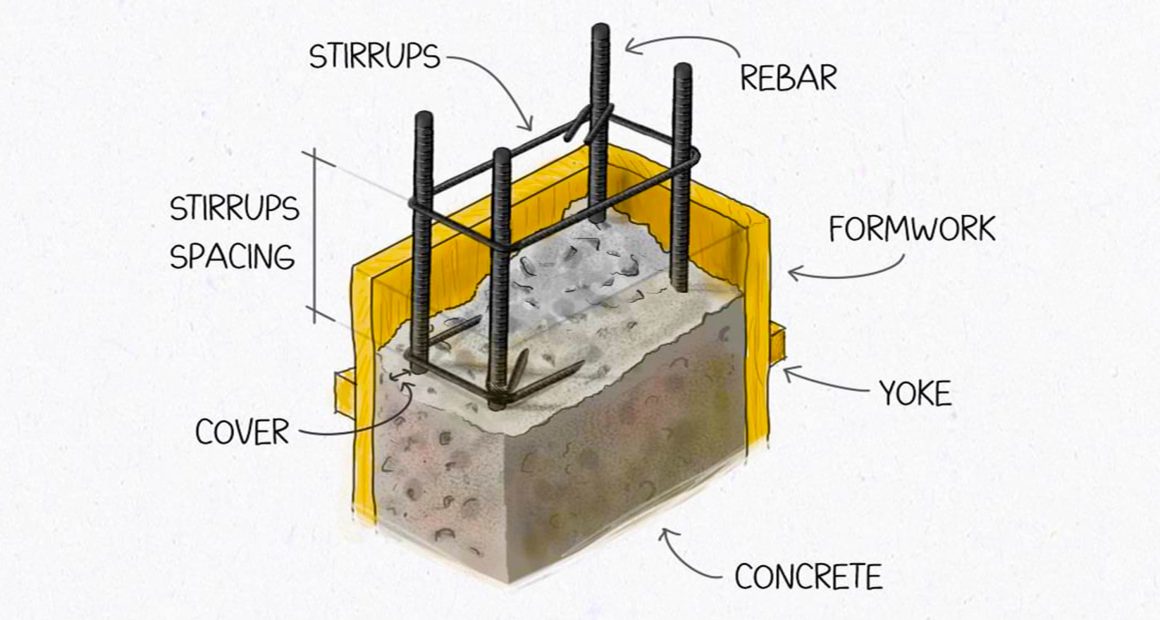
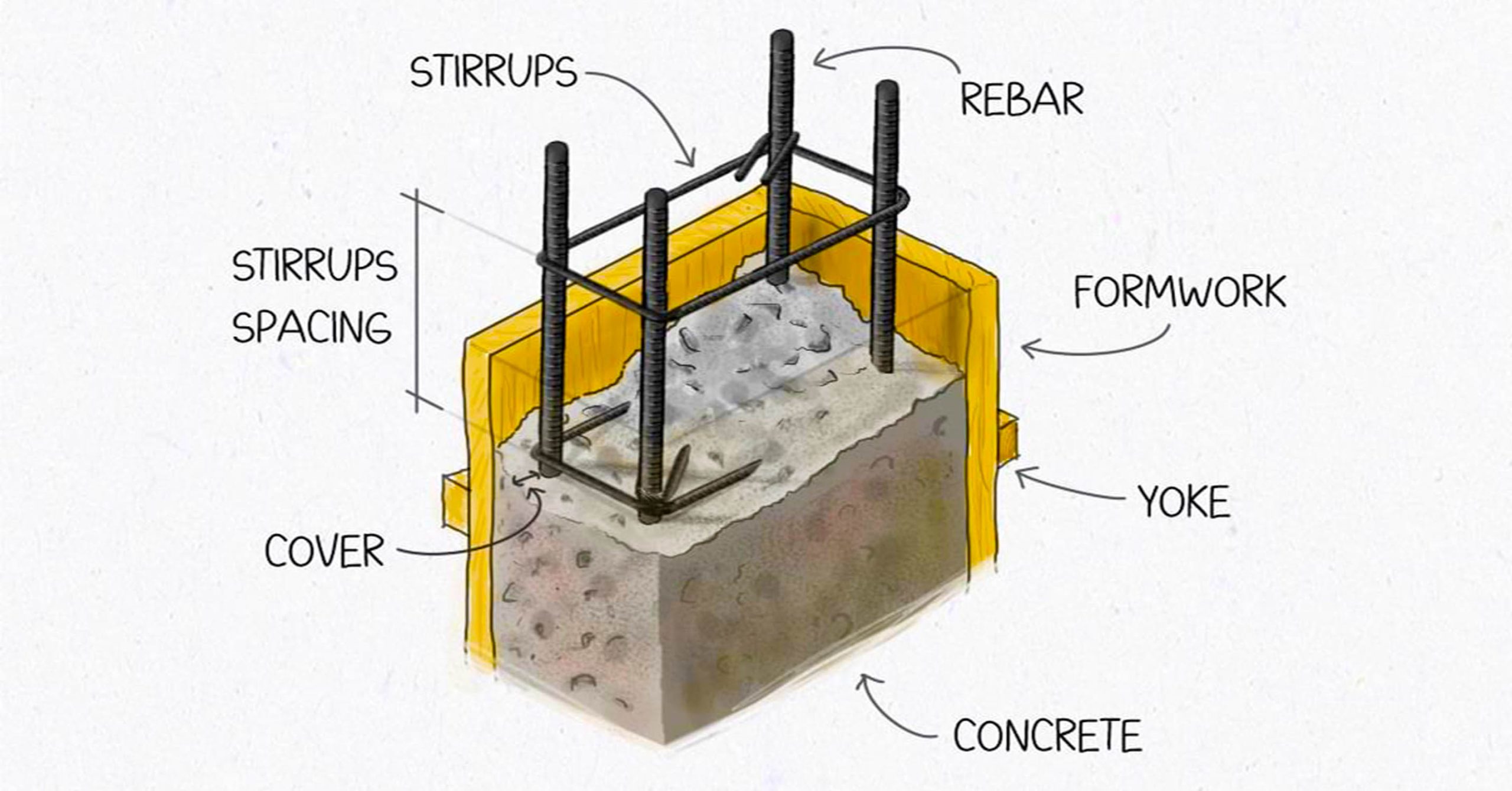
Reinforced concrete columns are integral to modern construction, supporting various structures. This article delves into the anatomy of reinforced concrete columns, focusing on their key components and their roles in ensuring structural stability.
What Is a Reinforced Concrete Column?
A reinforced concrete column is a vertical structural element designed to bear loads and transfer them to the foundation. The combination of steel reinforcement and concrete creates a robust and durable system capable of withstanding compressive and tensile forces.
Key Components of Reinforced Concrete Columns
1. Concrete
Concrete forms the bulk of the column, providing compressive strength and durability. It is made by mixing cement, sand, aggregates, and water. When cured properly, concrete forms a solid matrix capable of bearing immense loads.
- Function: Acts as the primary material to resist compressive forces.
- Benefits: Highly durable, fire-resistant, and versatile.
2. Reinforcement Bars (Rebar)
Rebars are steel bars embedded in the concrete to enhance tensile strength. These bars are strategically placed within the column to counteract forces that could cause cracking or deformation.
- Role: Provides tensile strength and prevents failure under load.
- Common Materials: High-strength steel or stainless steel.
3. Stirrups
Stirrups are horizontal or circular steel ties that surround the vertical rebars. These elements hold the rebars in place and prevent them from buckling under pressure.
- Purpose: Provides lateral support to rebars, preventing displacement.
- Spacing: Uniform stirrup spacing is critical for optimal structural performance.
4. Cover
The cover refers to the protective layer of concrete that surrounds the reinforcement. It acts as a barrier against environmental damage, such as corrosion or exposure to moisture.
- Significance: Protects rebars from corrosion and ensures fire resistance.
- Standard Thickness: Varies depending on structural requirements and environmental exposure.
5. Formwork
Formwork is the temporary mold used to shape and hold the concrete while it sets and gains strength. It is typically made from wood, steel, or plastic and is removed after the concrete hardens.
- Function: Shapes the column and ensures proper alignment.
- Types: Can be reusable or disposable, depending on the material used.
6. Yoke
Yokes are additional supports or braces placed around the formwork to ensure stability during the pouring and curing process. They prevent the formwork from bulging or shifting.
- Importance: Maintains formwork integrity for uniform concrete setting.
The Role of Spacing and Alignment
Proper spacing of stirrups and alignment of rebars are crucial in reinforced concrete columns. Irregular spacing or misalignment can compromise the column’s ability to bear loads, leading to structural issues.
- Stirrups Spacing: Ensures even distribution of lateral forces.
- Rebar Alignment: Maintains the structural integrity of the column.
Why Reinforced Concrete Columns Are Essential
Reinforced concrete columns are indispensable in construction due to their ability to support heavy loads while resisting various stresses. The combination of concrete’s compressive strength and steel’s tensile strength makes them ideal for high-rise buildings, bridges, and industrial structures.
- Durability: Withstands harsh environmental conditions.
- Versatility: Suitable for diverse architectural designs.
Click Here To See Comprehensive Guide To Stairs On Beams: Design And Structural Details
Photo Credit: Matheus Borges