Parking lots are often the first point of contact for visitors to any establishment, be it a shopping mall, office complex, or public transit station. Designing these spaces requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure functionality, safety, and user satisfaction. Whether accommodating buses, cars, or other vehicles, adhering to design principles and standards is essential for creating efficient and accessible parking facilities. The design of parking lots plays a crucial role in facilitating smooth traffic flow, enhancing safety, and optimizing space utilization. By adhering to established principles and standards, designers can create parking facilities that meet the diverse needs of users while minimizing environmental impact.
General Layout and Circulation:
- Maximize Efficiency: Rectangular layouts with long sides paralleling the parking spaces optimize space.
- Traffic Flow:
- One-way traffic lanes (24ft wide) minimize congestion.
- Two-way lanes require wider spaces (30ft) for safe passing.
- Avoid 90-degree parking with one-way flow.
- Designate separate entry/exit points for smooth traffic flow.
Parking Space Dimensions:
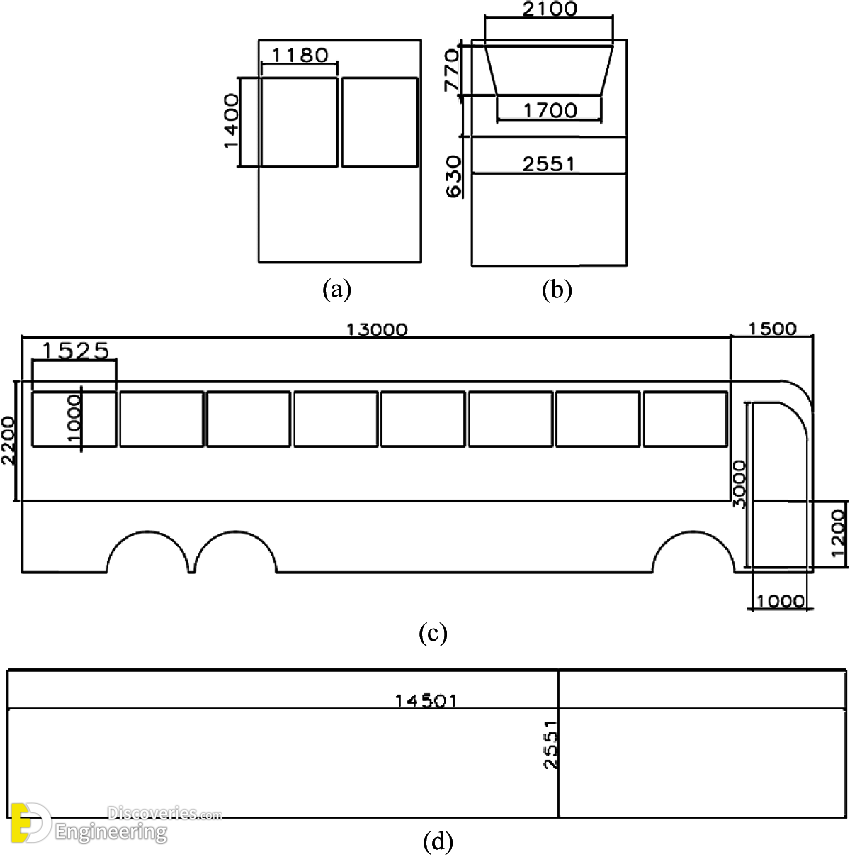
Parking Space Standards for Buses:
- Dimensions vary based on bus size (standard city bus vs. school bus).
- Factor in length, width, turning radius, and overhang for safe maneuvering.
- Allocate extra space around buses for passenger movement and accessibility
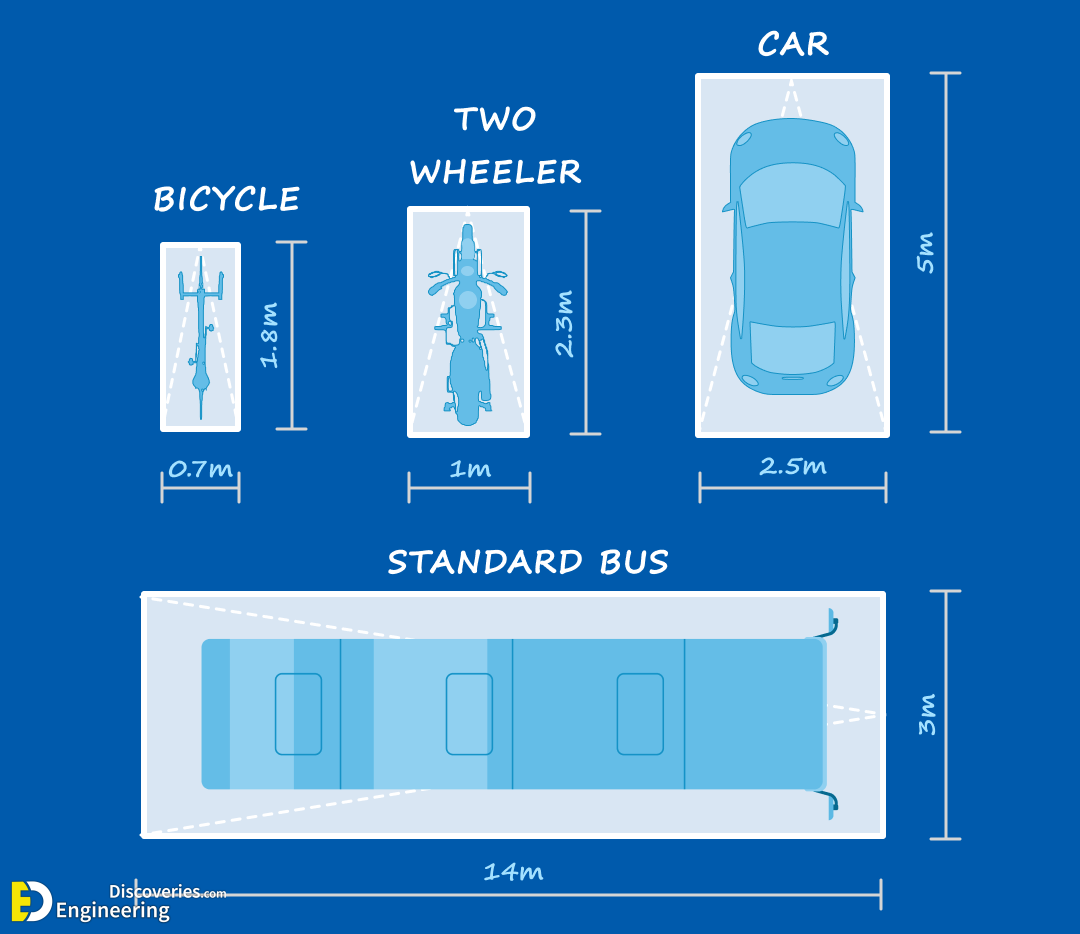
- Buses typically require parking stalls that are at least 14 feet wide and between 40 and 60 feet long, depending on the size of the buses.
- Parking Space Standards for Cars:
- The standard parking space size is generally 9 feet by 18 feet.
- The minimum parking space size is 8 feet by 16 feet.
- Accessible parking spaces should have a minimum width of 8 feet with an 8-foot wide access aisle.
Pedestrian Safety and Accessibility:
- Separate designated walkways with clear markings for pedestrians.
- Prioritize pedestrian circulation over vehicle movement.
- Accessible parking spaces for people with disabilities following local regulations.
Signage and Markings:
- Clear signage for regular parking, handicapped parking, and traffic flow directions.
- Properly marked lanes and crosswalks for better visibility.
Additional Considerations:
- Landscaping: Integrate landscaping for shade, aesthetics, and stormwater management, but ensure it doesn’t obstruct sightlines.
- Lighting: Provide adequate lighting for safety and security throughout the parking lot.
- Drainage: Ensure proper drainage to prevent flooding during rain or snow.
- Snow Removal: Allocate designated areas for snow plowing to avoid blocking traffic flow or parking spaces.
Local Regulations:
Always adhere to local building codes and zoning regulations which often dictate minimum parking space requirements and design specifications. Remember, these are general principles. Consulting a qualified engineer or architect is recommended for designing parking lots that meet specific needs and comply with local regulations.