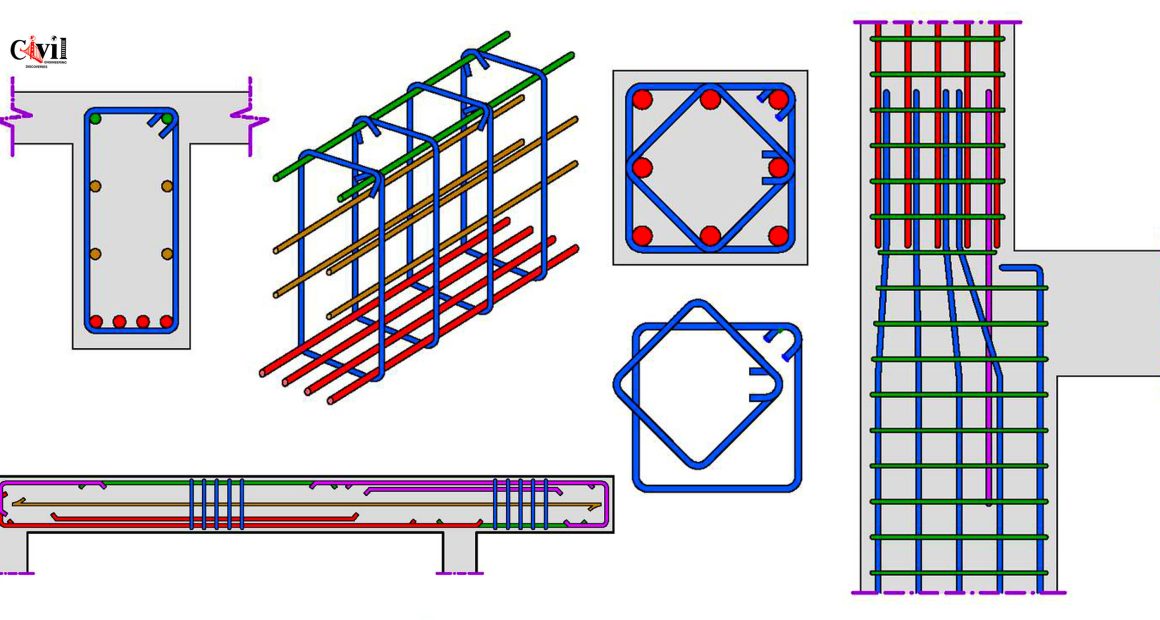
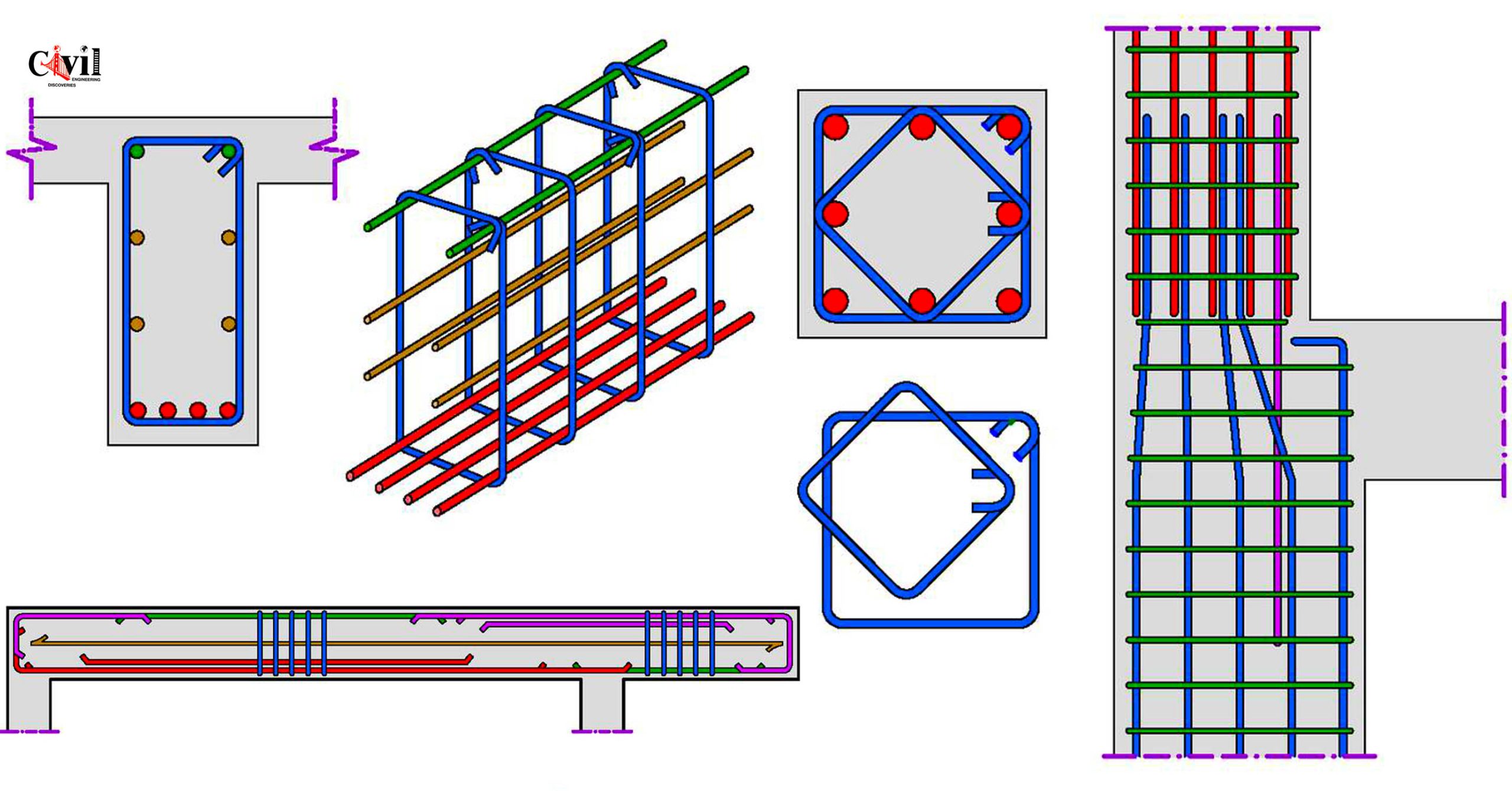
Reinforced Concrete Design is a cornerstone of structural engineering, focusing on creating durable, efficient, and safe structures. Engineers must understand essential details, such as load distribution, where forces from various structural elements are transferred to the foundation safely. The design accounts for tension members, which resist pulling forces, by incorporating steel reinforcement to counteract concrete’s weakness in tension. Key considerations also include shear force and bending moments, which influence the dimensions and reinforcement of beams to prevent cracking or failure. For foundations, stability against soil pressure and settlement is critical, requiring precise calculations. Slabs must be designed for adequate thickness and reinforcement to support loads while minimizing deflection. In stairs, load transfer and reinforcement detailing ensure both safety and durability. Other vital aspects include durability considerations, construction feasibility, adherence to building codes, and addressing thermal and shrinkage stresses, collectively ensuring the structure’s long-term performance.
Click Here To See Reinforced Concrete Explained: Details Of Reinforced Concrete Structural Elements
Photo Credit: Yasser El Leathy