Understanding the Factored Load
The factored load considers additional safety by increasing the actual load. This ensures stability and prevents failure.
Let’s assume:
Dead Load = 1200 kN
Live Load = 600 kN
Now, increase the total load by 50% for safety:
Pu = 1200 + 600 = 1800 kN
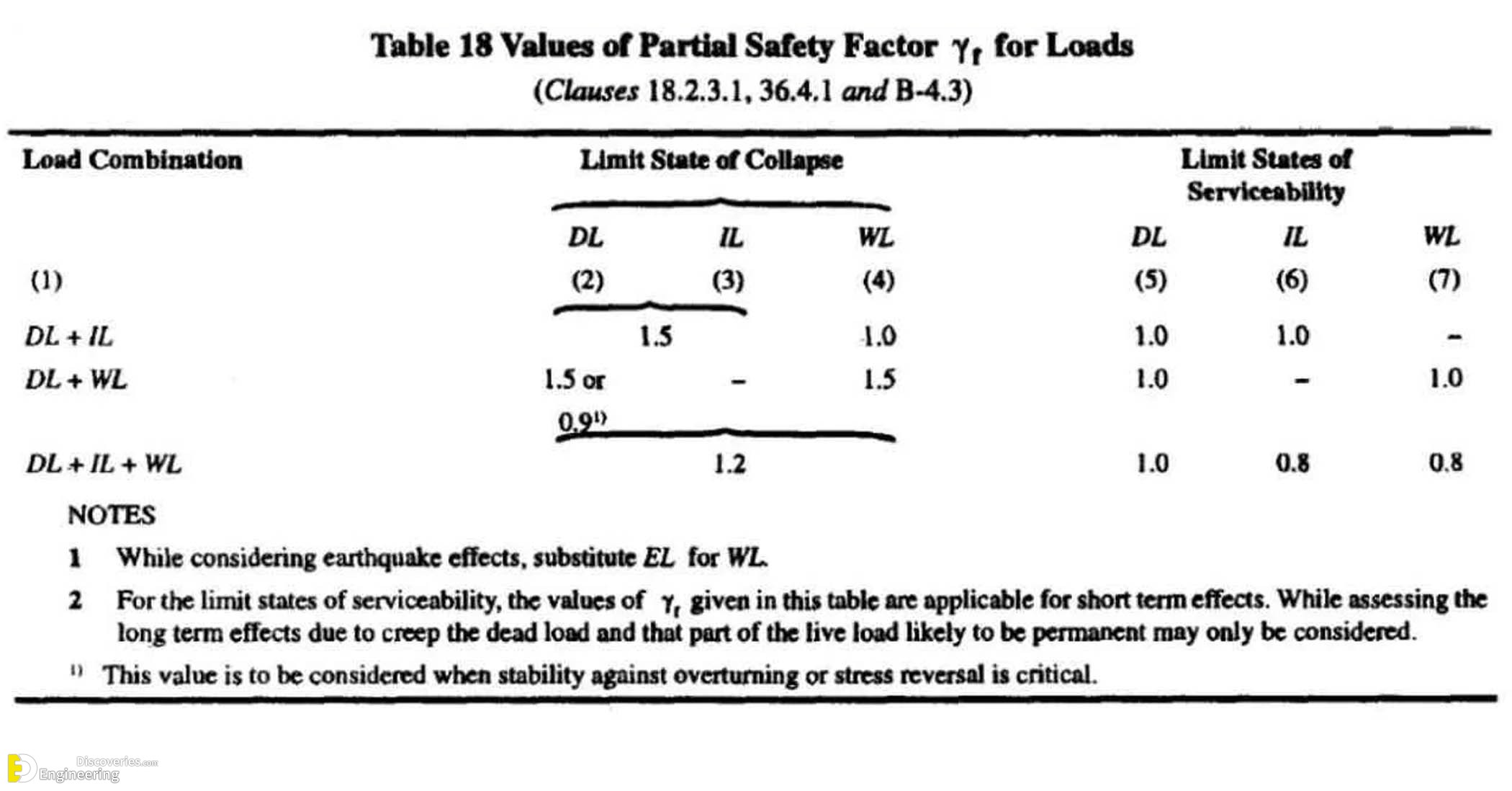
Alternatively, as per IS 456: Table 18,
This value will be used in further calculations.
Essential Design Parameters
According to IS 456 guidelines, the following parameters apply:
Concrete Grade (fck) = M30
Steel Grade (fy) = Fe 500
Factored Load (Pu) = 1800 kN
Use the IS 456 equation for axial load-bearing columns:
Pu = 0.4fckAc + 0.67fyAsc
Where:
Ac = Area of concrete
Asc = Area of steel
Ag = Gross area of column section
Assume:
Asc = 1% of Ag
Ac = 99% of Ag
This gives:
Asc = 0.01Ag,
Ac = 0.99Ag
Column Area Calculation
Now, apply the values to the equation:
1800 × 10³ = 0.4 × 30 × 0.99Ag + 0.67 × 500 × 0.01Ag
Simplify the equation:
1800000 = 11.88Ag + 3.35Ag
1800000 = 15.23Ag
Solve for Ag:
Ag = 1800000 / 15.23
Ag ≈ 118187.78 mm²
Now take the square root to find side length (assuming a square column):
√118187.78 ≈ 343.78 mm
For practicality and simplicity, round it:
Adopted Column Size = 350 mm × 350 mm
Final Recommended Column Size
Based on the above calculation:
Column Dimensions = 350 mm × 350 mm
This size ensures the column safely supports the applied load.
The design adheres to IS 456 provisions for safety and performance.
Click Here To See How To Calculate The Total Load Over RCC Footings?








Yes I’m interest