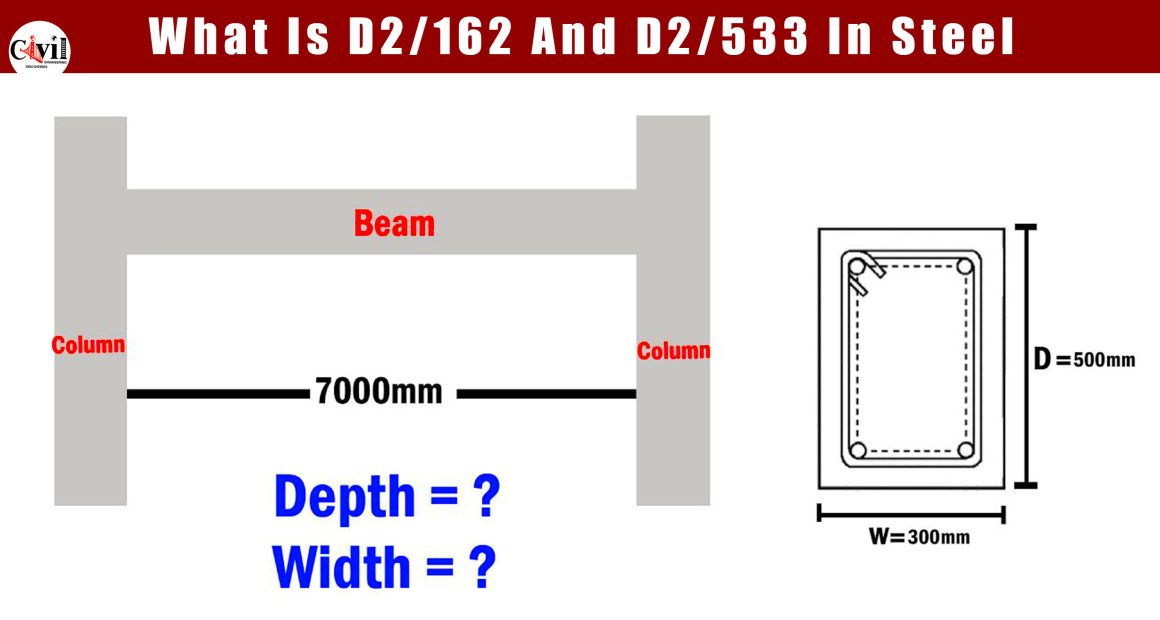
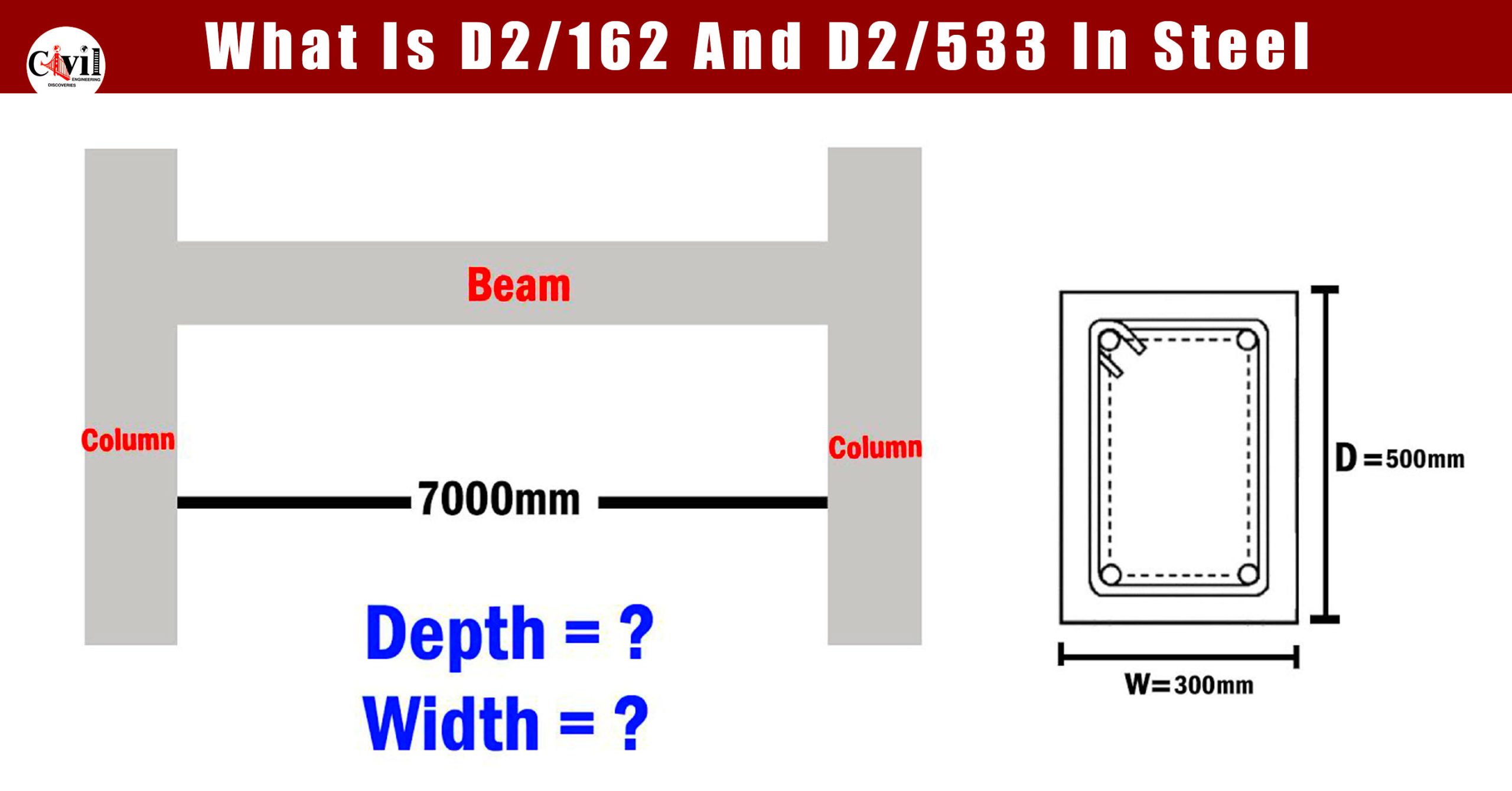
Designing a beam involves careful consideration of its dimensions and structural integrity. Here’s a detailed guide to help you calculate the depth and width of a beam effectively.
Understanding Beam Design Basics
Beam design ensures structural stability and load-bearing capacity. To determine a beam’s size, factors such as load, span length, and material strength play crucial roles.
Why Are Beam Dimensions Important?
- Depth: Affects the bending strength and deflection resistance.
- Width: Contributes to the beam’s stability and lateral support.
Balancing these dimensions is critical to achieving optimal performance.
Step-by-Step Beam Calculation
1. Assess the Load Requirements
- Identify the total load (dead and live loads).
- Calculate uniformly distributed and concentrated loads.
Use formulas like:
Total Load (W) = Dead Load + Live Load
2. Determine the Span Length
Measure the clear span between supports. Longer spans require deeper beams for strength.
3. Use the Thumb Rule for Beam Sizing
For preliminary designs, apply these thumb rules:
- Depth (D): Span/10 for residential buildings.
- Width (B): D/2 to D/3.
For example:
- Span = 6 meters → Depth ≈ 600 mm.
- Width ≈ 200 mm to 300 mm.
4. Check the Bending Moment
The bending moment influences the beam’s depth. Use:
M=wL^2/8
Where:
- w= Load per unit length
- L = Span length
5. Calculate the Moment of Inertia
I = B⋅D^3/12
Ensure it matches the structural requirements.
6. Verify Shear Strength
The width determines the shear resistance. Check against the material’s shear strength limit.
Material Considerations
Concrete Beams
- Use steel reinforcement to enhance tensile strength.
- Ensure proper cover thickness for durability.
Steel Beams
- Select appropriate sections (e.g., I-beam, T-beam) based on load and span.
- Factor in lateral torsional buckling.
Beam Design Tips
1. Optimize Depth and Width
Avoid excessive dimensions to save material costs while ensuring structural safety.
2. Follow Building Codes
Refer to local codes like ACI 318 or Eurocode for precise calculations.
3. Use Structural Software
Tools like STAAD or ETABS provide accurate beam sizing and load analysis.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overestimating or underestimating loads.
- Ignoring deflection limits.
- Neglecting lateral stability in wide beams.
Conclusion
Calculating the depth and width of a beam requires precision and adherence to standards. By considering load, span, and material, you can ensure safety and efficiency in structural design. Always double-check calculations and consult professionals for critical projects.
Click Here To See Choosing The Perfect Column And Beam Sizes For A 25ft Span