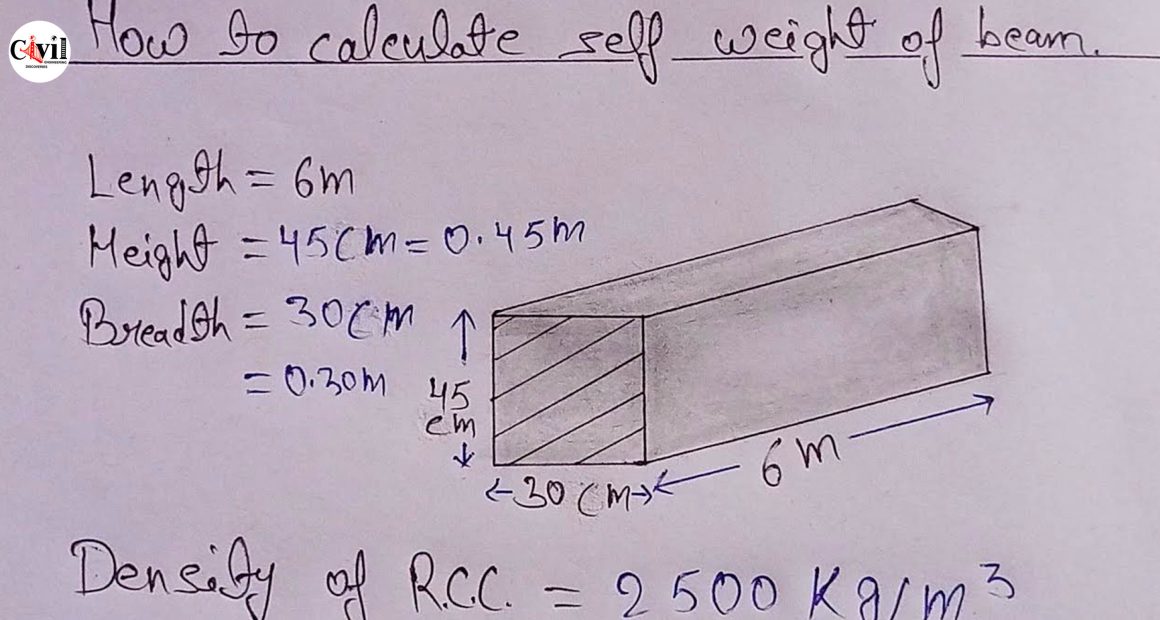
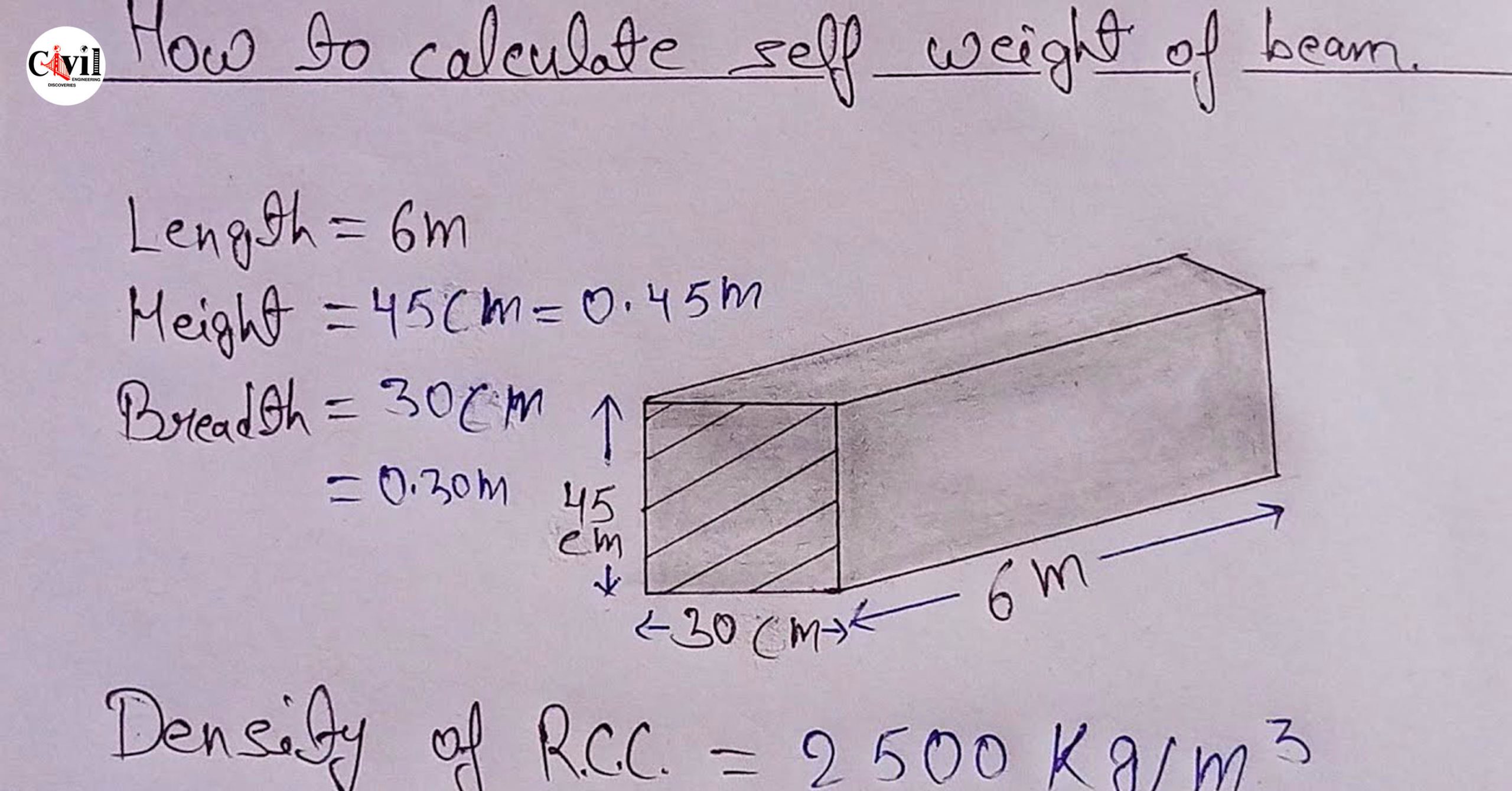
The self-weight of a beam refers to the weight of the beam itself due to its material density and dimensions. It is essential for accurate structural calculations.
Why Calculating Self-Weight is Crucial?
Determining the self-weight helps engineers ensure stability and safety in construction. It also assists in designing the foundation and other load-bearing structures.
Formula to Calculate Self-Weight
To calculate the self-weight of a beam, use the following formula:
Self-Weight = Volume × Density
Key Components of the Formula
- Volume: Determine the beam’s dimensions (length, width, height) to calculate its volume.
- Density: Obtain the material’s density (e.g., steel, concrete, wood)
Step-by-Step Calculation
Step 1: Measure Dimensions
Measure the beam’s length, width, and height. Ensure the units are consistent.
Step 2: Calculate Volume
Use the formula:
Volume = Length × Width × Height
Step 3: Multiply by Density
Find the material’s density and multiply it with the volume.
Example Calculation
For a beam made of concrete with:
- Length: 5 meters
- Width: 0.3 meters
- Height: 0.5 meters
- Volume = 5 × 0.3 × 0.5 = 0.75 m³
- Self-Weight = 0.75 × 2400 = 1800 kg
Tips for Accurate Calculations
- Always use consistent units.
- Verify the material density from reliable sources.
- Double-check measurements to minimize errors.
Common Materials and Their Densities
- Steel: 7850 kg/m³
- Concrete: 2400 kg/m³
- Wood: 600-700 kg/m³
Applications in Construction
- Load Analysis: Incorporate self-weight in total load calculations.
- Foundation Design: Ensure proper load distribution.
- Beam Strength: Evaluate if the beam can support additional loads.
Click Here To See How To Calculate The Self-Weight Of Column









Interested