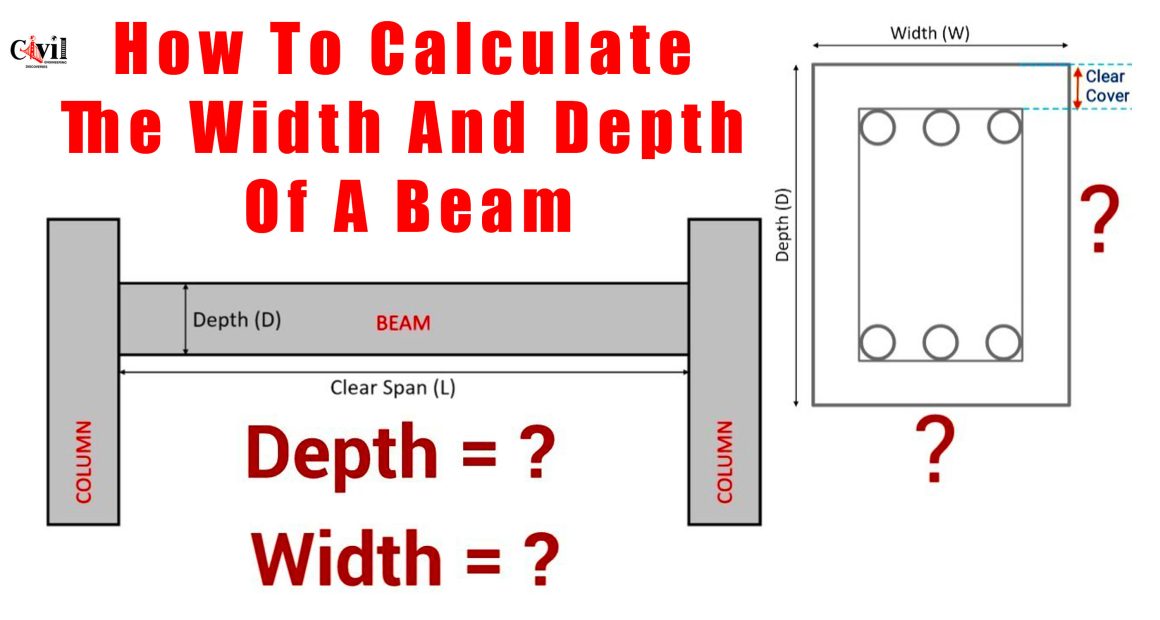
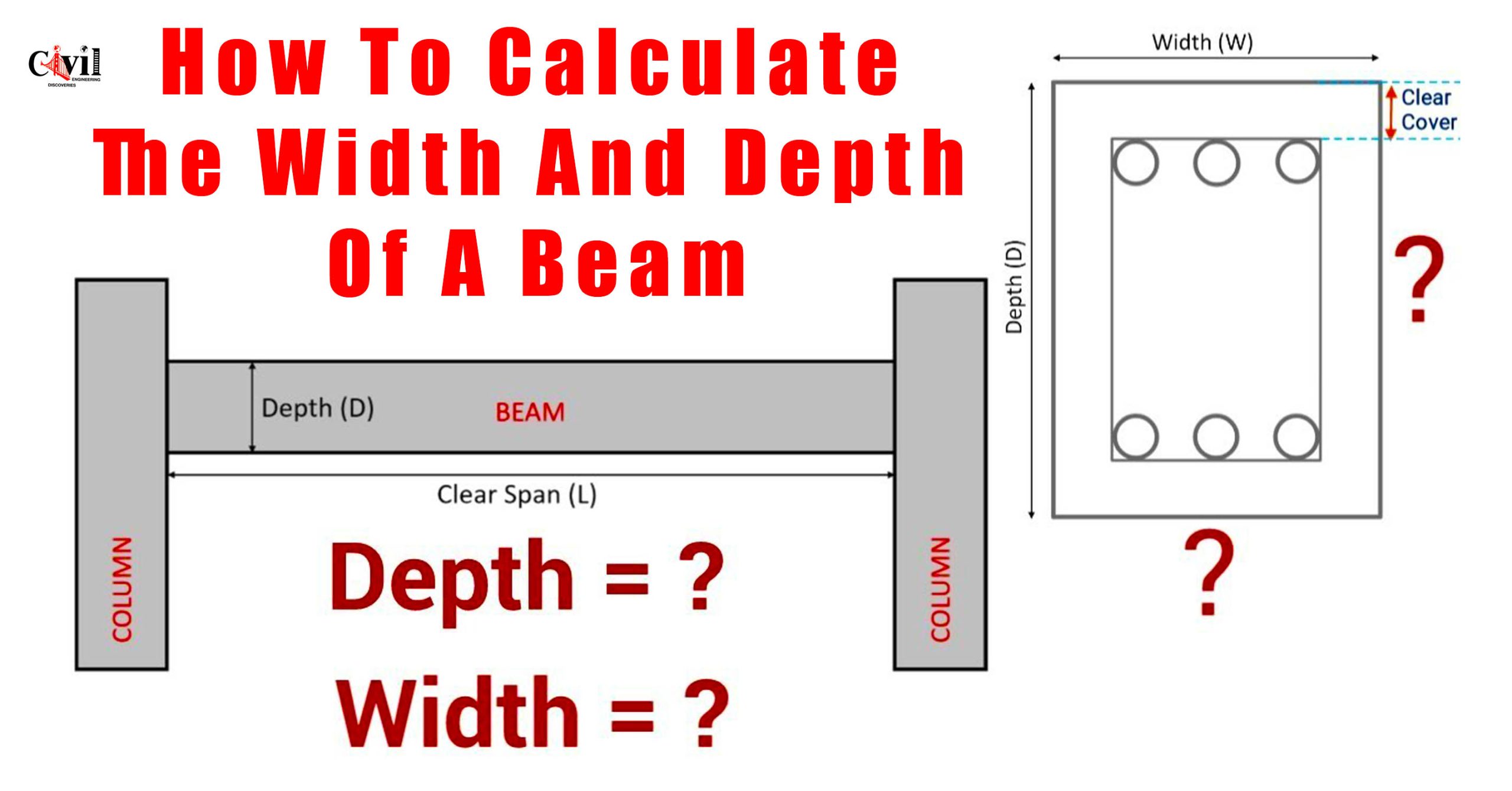
Beam dimensions, including width and depth, ensure structural stability. Accurate calculations prevent failures and enhance safety. The width and depth of a beam determine its load-carrying capacity and overall strength.
Importance of Width and Depth in Beam Design
The width and depth of a beam are key parameters in structural engineering. They affect the beam’s ability to resist bending, deflection, and shear forces. Properly designed beams ensure optimal performance while reducing material waste.
Steps to Calculate Beam Width and Depth
1. Identify Load Requirements
Determine the total load the beam will carry, including:
- Dead loads (permanent fixtures).
- Live loads (temporary weights like furniture).
- Environmental loads (wind or seismic forces).
2. Choose Beam Material
Select a suitable material for the beam, such as:
- Steel for high-strength applications.
- Concrete for heavy-duty structures.
- Wood for lightweight construction.
Each material has unique properties that influence width and depth calculations.
3. Use Structural Formulas
Moment of Inertia (I)
The moment of inertia depends on the beam’s cross-sectional shape:
- For a rectangular beam:I = (b × h³) / 12
Where:
- b = beam width (in meters or inches).
- h = beam depth (in meters or inches).
Flexural Formula
To resist bending, use the formula:
σ = M / I× y
Where:
- σ = allowable stress.
- M = maximum bending moment.
- y = distance from the neutral axis.
4. Apply Design Codes
Consult design codes like:
- ACI (American Concrete Institute) for concrete.
- AISC (American Institute of Steel Construction) for steel.
- Local building regulations for wood.
Design codes offer minimum and maximum dimensions guidelines to ensure compliance and safety.
5. Optimize Dimensions
Adjust width and depth to balance material usage and strength. For instance:
- Increasing depth improves bending resistance.
- Increasing width reduces the risk of shear failure.
Practical Example: Calculating a Beam for Residential Use
Suppose a wooden beam must support a 10-foot span with a total load of 500 pounds:
- Determine the bending moment: M = Load × Span / 4
- M = 500 × 10 / 4 = 1250 foot-pounds.
- Select a stress value for wood (e.g., 1000 psi).
- Calculate dimensions using the formulas above, adjusting as needed for safety factors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Neglecting environmental factors.
- Ignoring design codes.
- Underestimating safety margins.
Conclusion
Accurate calculation of a beam’s width and depth is essential for structural integrity. By following systematic steps, considering material properties, and adhering to design codes, you can ensure optimal performance and safety for any project.