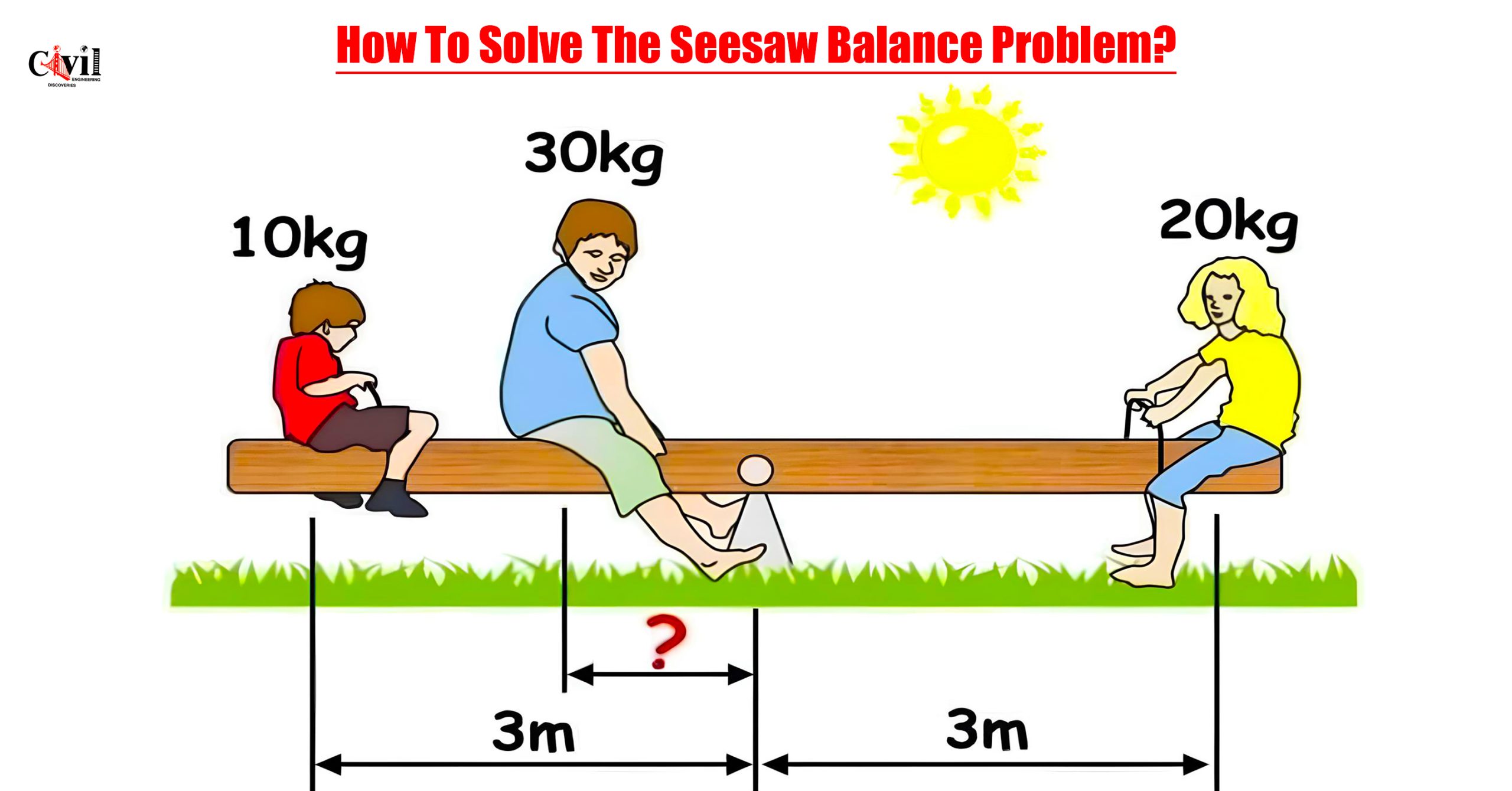
Balancing a seesaw is a common physics problem that applies the principles of torque and equilibrium. In the given image, three individuals with different weights are positioned on a seesaw, and the task is to determine the location of the fulcrum to maintain balance.
Understanding the Physics Behind the Seesaw Problem
A seesaw works based on the principle of moments (torque). The moment of a force is given by the formula:
For the seesaw to be balanced, the total torque on one side must be equal to the total torque on the other side:
Given Data from the Image
- Left Side:
- Child (10 kg) sitting at 3 m from the fulcrum.
- Adult (30 kg) sitting closer to the center, at unknown distance (x).
- Right Side:
- Person (20 kg) sitting at 3 m from the fulcrum.
The task is to find x, the distance at which the adult (30 kg) should sit from the fulcrum so that the seesaw remains balanced.
Step-by-Step Solution
- Calculate the Torque on the Right Side
- The total moment on the right side (clockwise torque) is: 20 x 3 = 60kg. m
- Calculate the Torque on the Left Side
- The child contributes a counterclockwise torque: 10 x 3 = 30 kg. m
- The adult contributes a counterclockwise torque: 30 x x kg. m
- Set Up the Balance Equation: 30 + 30x = 60
- Solve for x = 1m
Final Answer
To balance the seesaw, the adult (30 kg) should sit 1 meter from the fulcrum.
Conclusion
By applying the principle of moments, we determined the correct positioning required to balance the seesaw. This concept is widely used in real-world applications, such as lever systems, bridges, and mechanical structures.
Click Here To See 50 Stunning Front Elevation Designs That Will Make Your Home Stand Out!



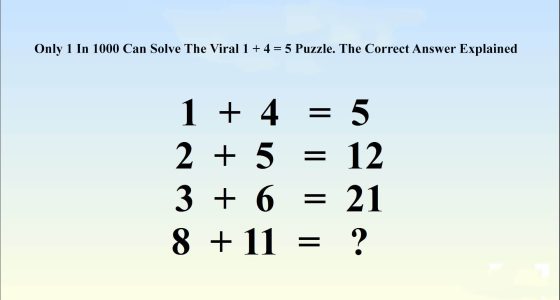
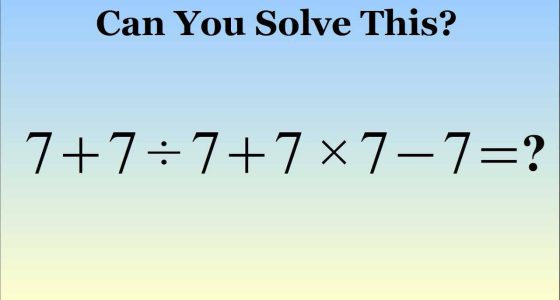

greatsa