What is RCC Isolated Footing?
RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) isolated footing is a structural element used to transfer and distribute the load of columns to the underlying soil. It ensures stability and prevents uneven settlement. This type of footing is typically used for buildings with light to moderate loads.
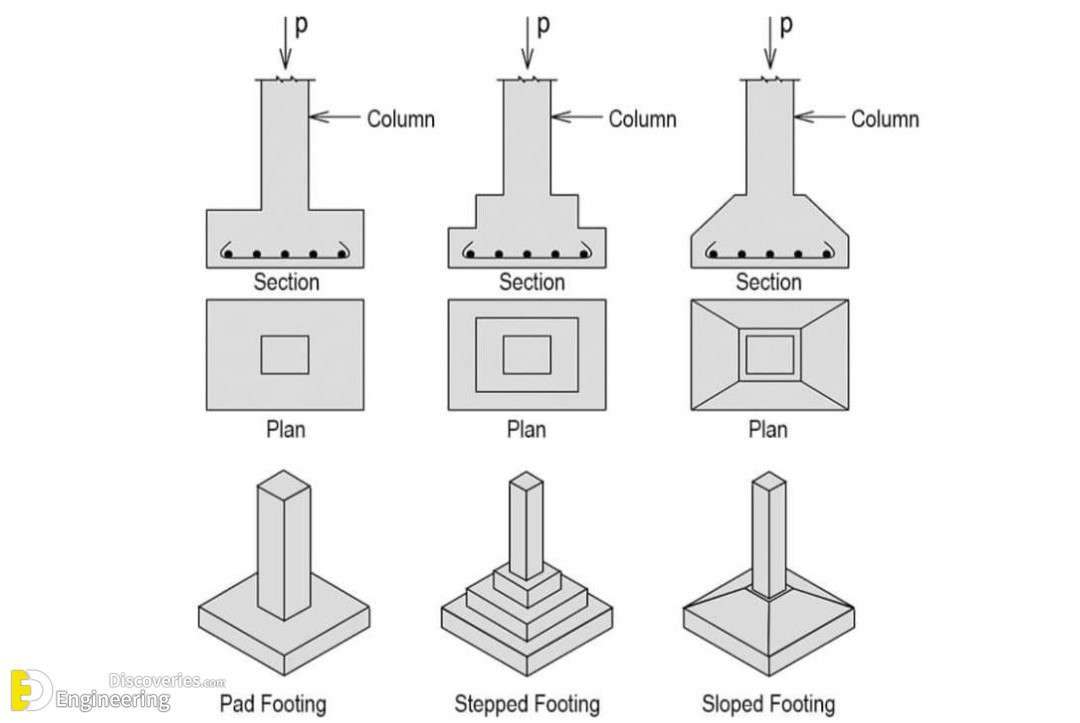
Types of RCC Isolated Footing
1. Sloped Footing
This type of footing has a sloped top surface, which helps reduce material consumption while maintaining structural strength.
2. Stepped Footing
In this design, the footing steps down in layers to spread the load efficiently across the soil.
3. Flat Footing
Flat footing has a uniform thickness and is suitable for small structures where the load is distributed evenly.
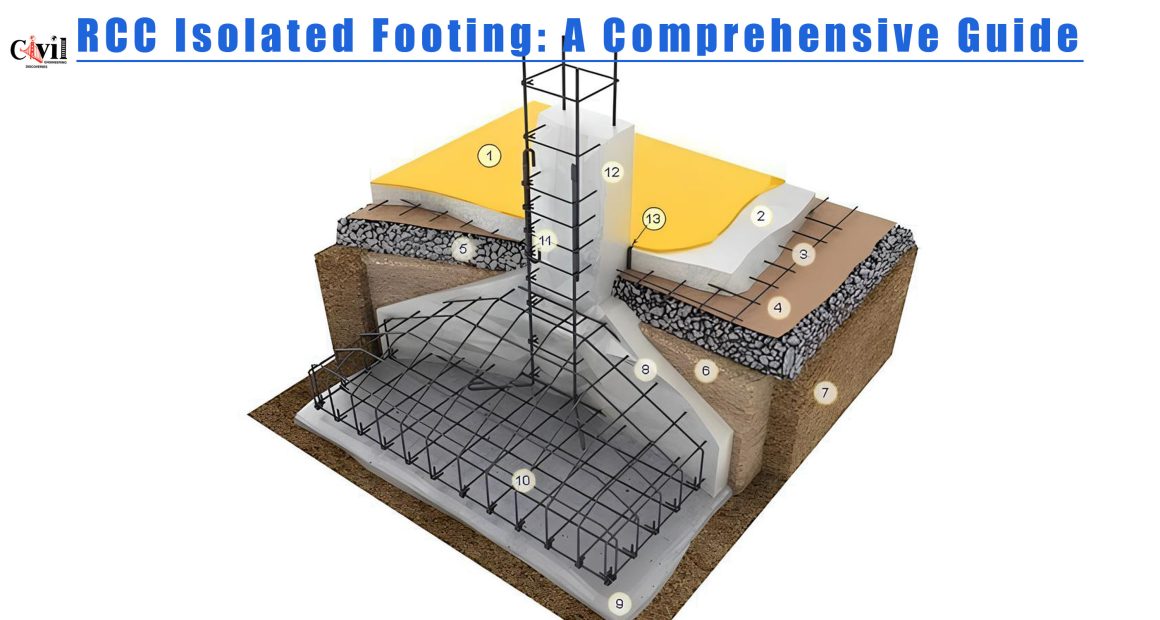
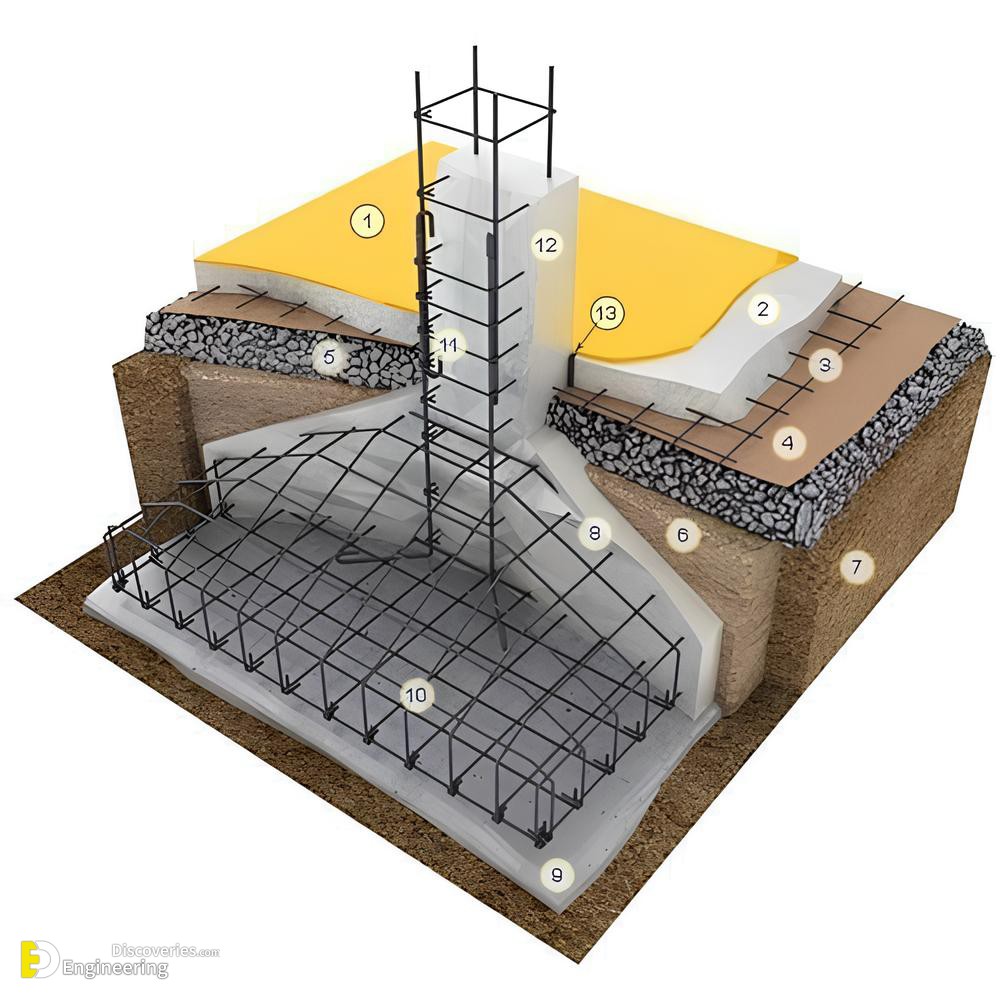
Key Components of RCC Isolated Footing
Reinforcement Steel
Steel bars are placed in a grid pattern to provide tensile strength and enhance the footing’s durability.
Cement Concrete
A well-proportioned concrete mix ensures that the footing can withstand heavy loads and adverse conditions.
Formwork
Temporary molds are used to shape and support the concrete until it hardens.
Design Considerations for RCC Isolated Footing
1. Load Distribution
The footing should evenly distribute the load from the column to the ground.
2. Soil Bearing Capacity
Assessing the soil’s ability to bear the structural load without settling is essential.
3. Reinforcement Detailing
Proper placement and detailing of steel bars help prevent cracks and enhance the footing’s longevity.
4. Depth and Thickness
The depth and thickness of the footing depend on the column load and soil properties.
Construction Process of RCC Isolated Footing
Step 1: Site Preparation
Clear the construction area and excavate the soil to the required depth.
Step 2: Formwork Installation
Install formwork to define the shape and dimensions of the footing.
Step 3: Reinforcement Placement
Place steel reinforcement bars in the designated pattern and secure them properly.
Step 4: Concrete Pouring
Pour the concrete mix into the formwork and compact it to eliminate air voids.
Step 5: Curing
Allow the concrete to cure for the specified duration to achieve maximum strength.
Advantages of RCC Isolated Footing
- Cost-Effective: Requires less material compared to other foundation types.
- Efficient Load Distribution: Spreads the load evenly to prevent structural failures.
- Flexible Design: Suitable for various soil conditions and structural requirements.
- Easy Construction: Simple and quick installation process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Improper Soil Analysis: Failing to assess soil properties can lead to structural issues.
- Inadequate Reinforcement: Insufficient steel bars may result in cracks and failure.
- Poor Curing Practices: Skipping or reducing curing time weakens the concrete.
- Incorrect Formwork Installation: Faulty formwork can cause misalignment and structural defects.
Click Here To See How To Calculate Steel Quantity For A Footing: A Step-by-Step Guide






I’m doing that now at work. 307 we must do te