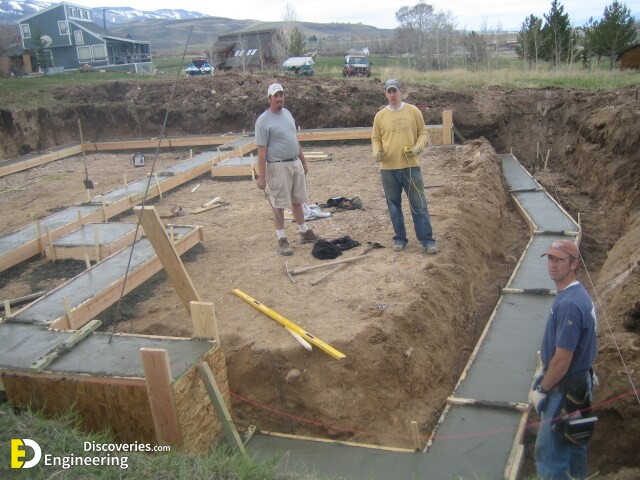
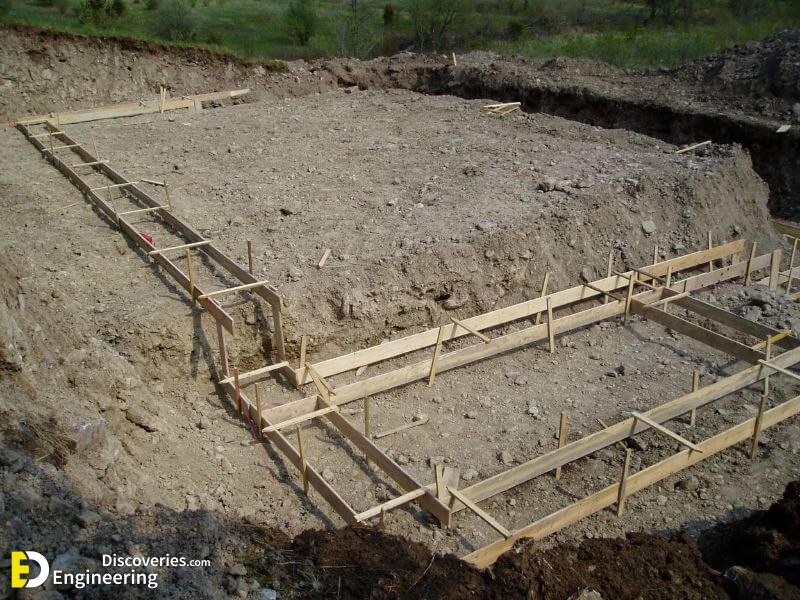
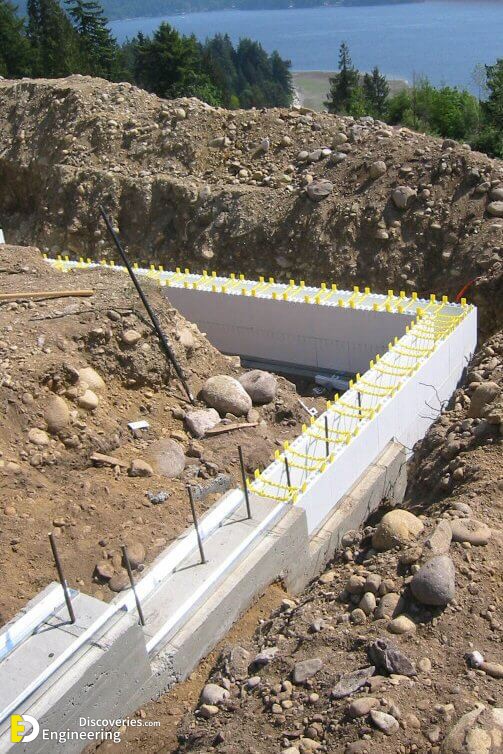
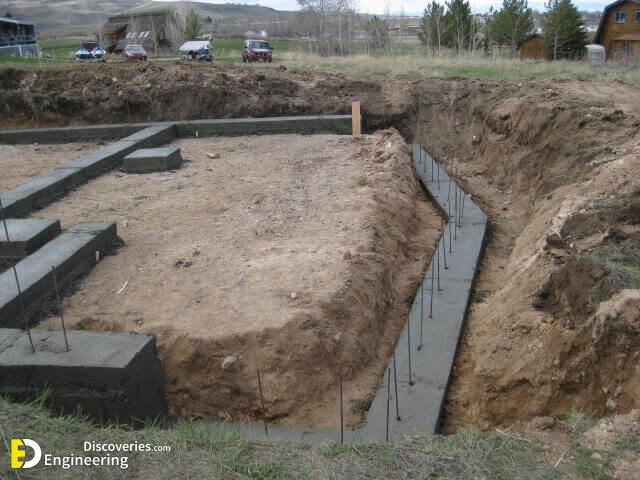
Foundations provide support for structures, transferring their load to layers of soil or rock that have sufficient bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics.
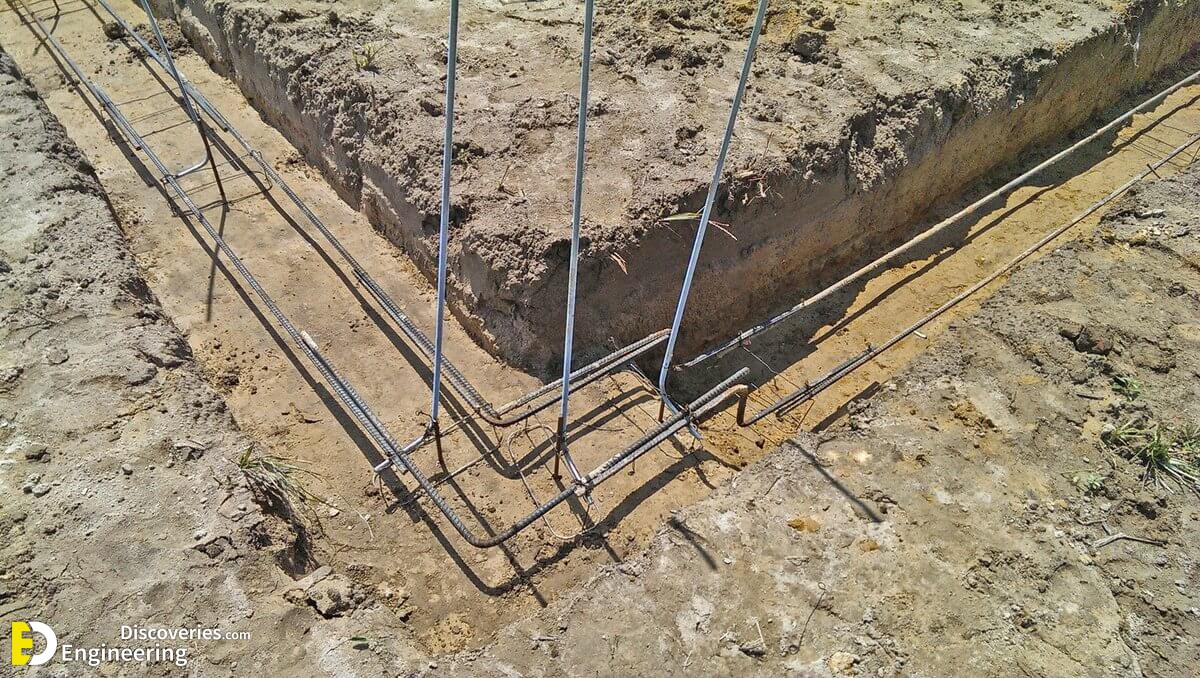
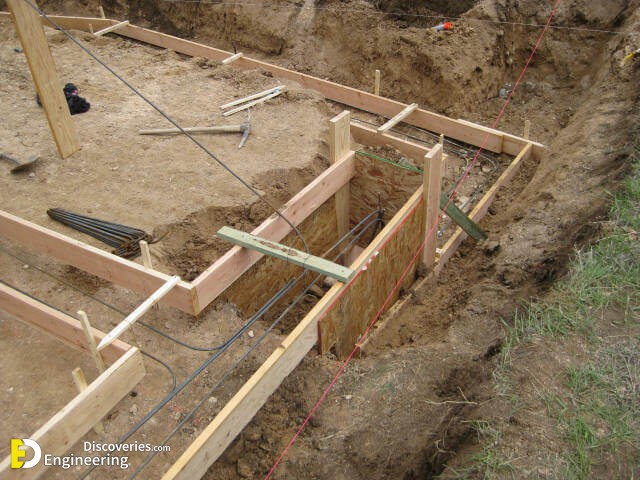
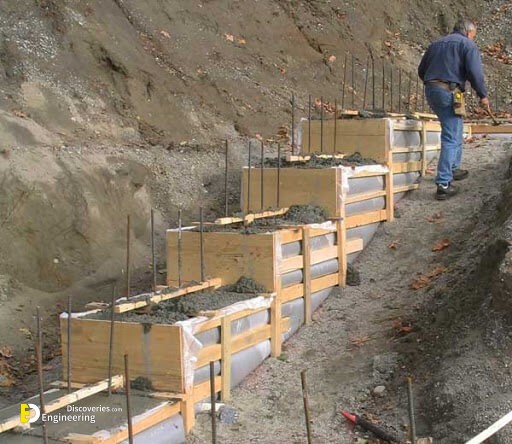
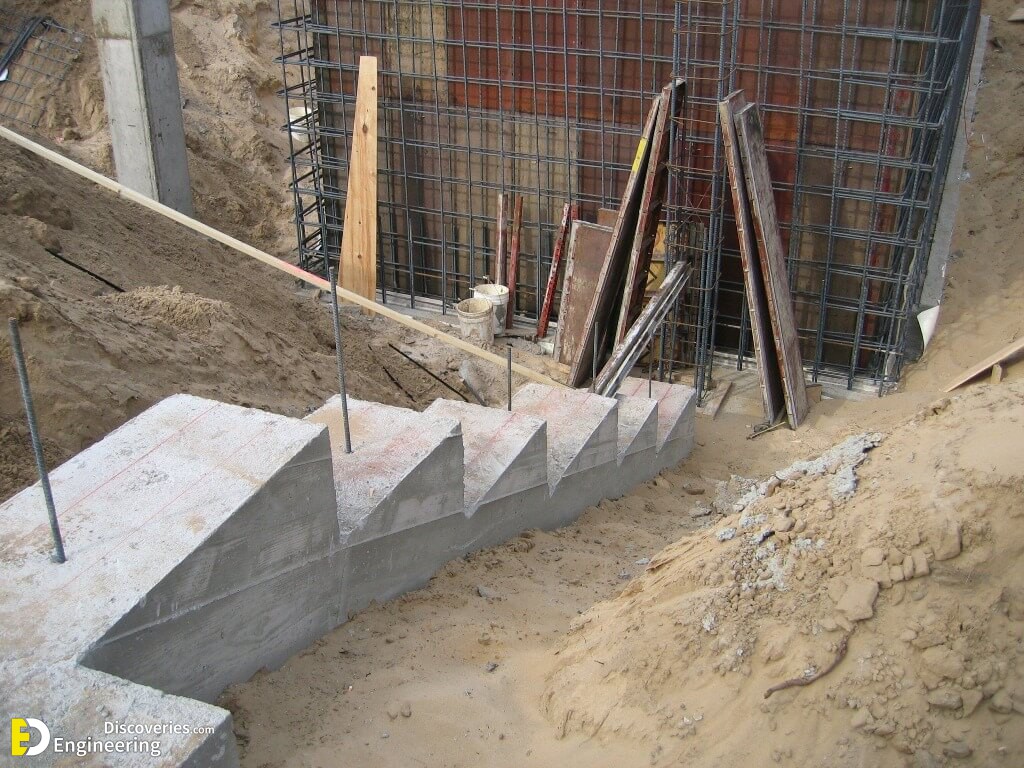
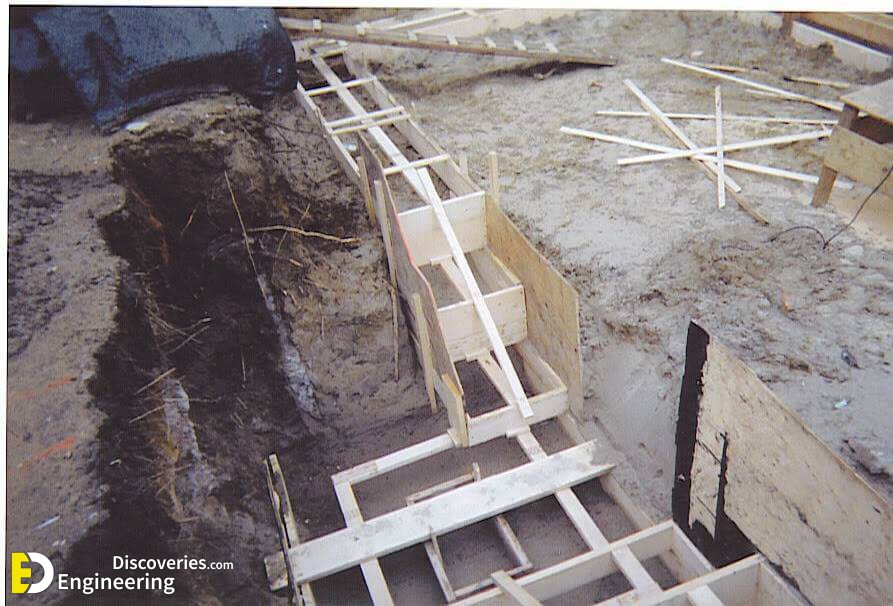
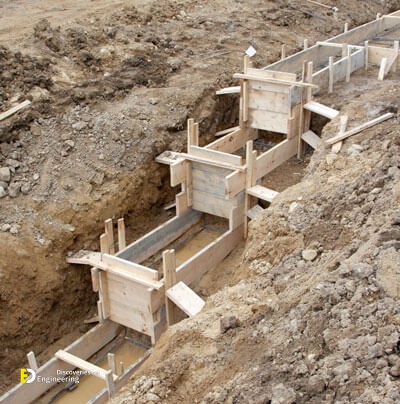
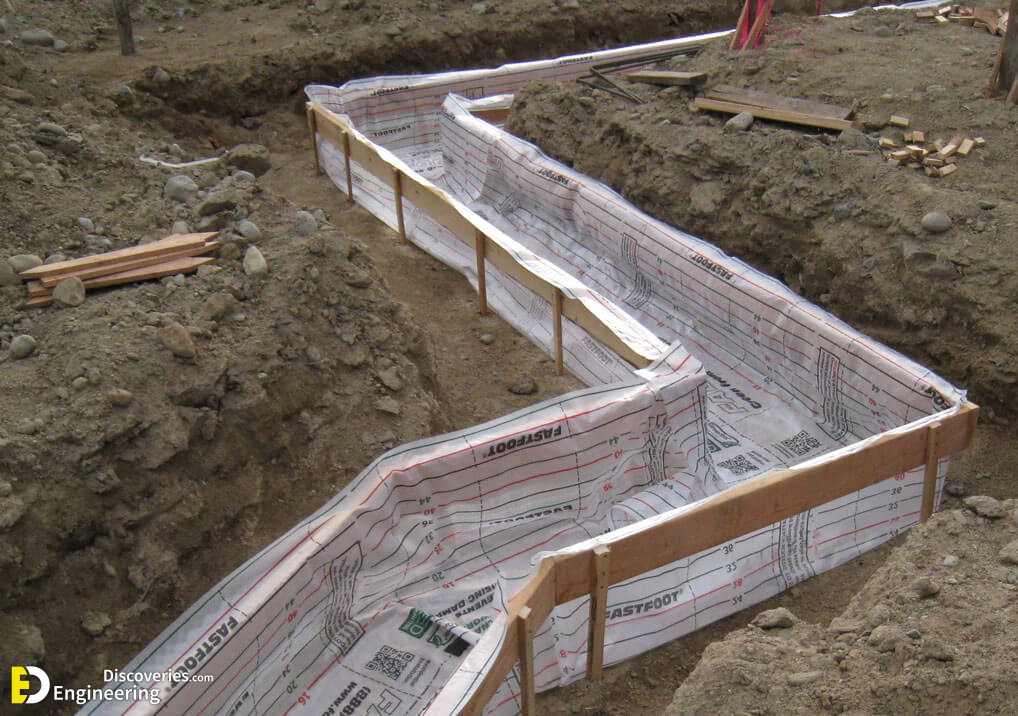
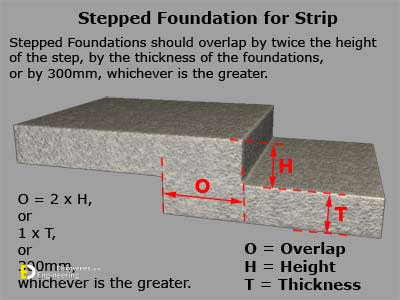
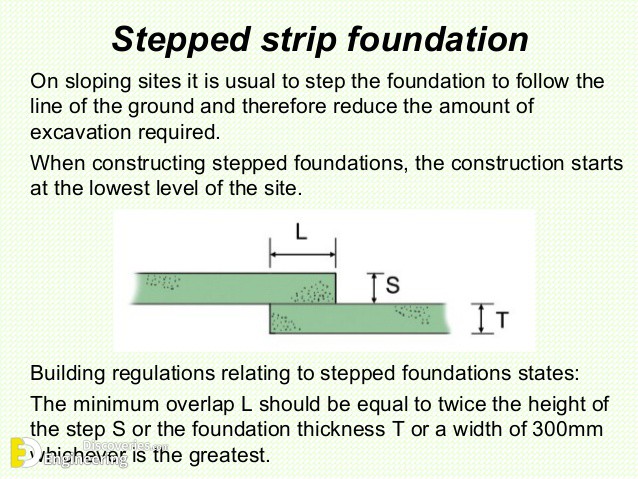
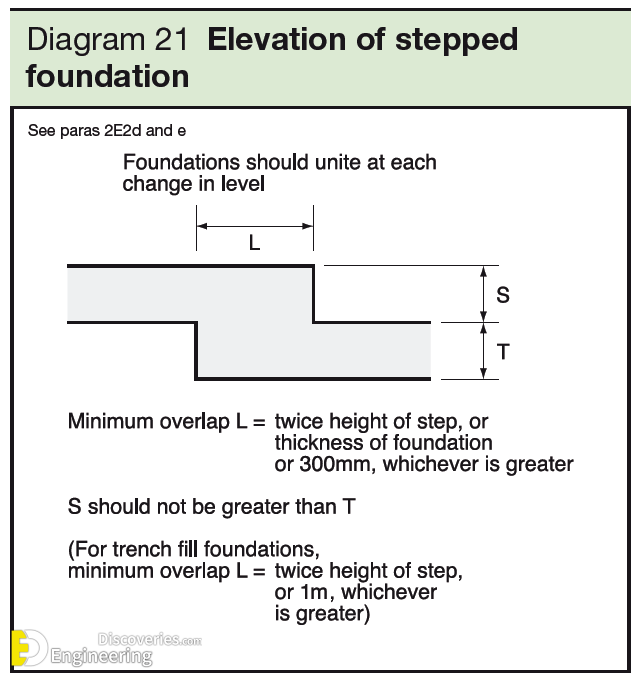
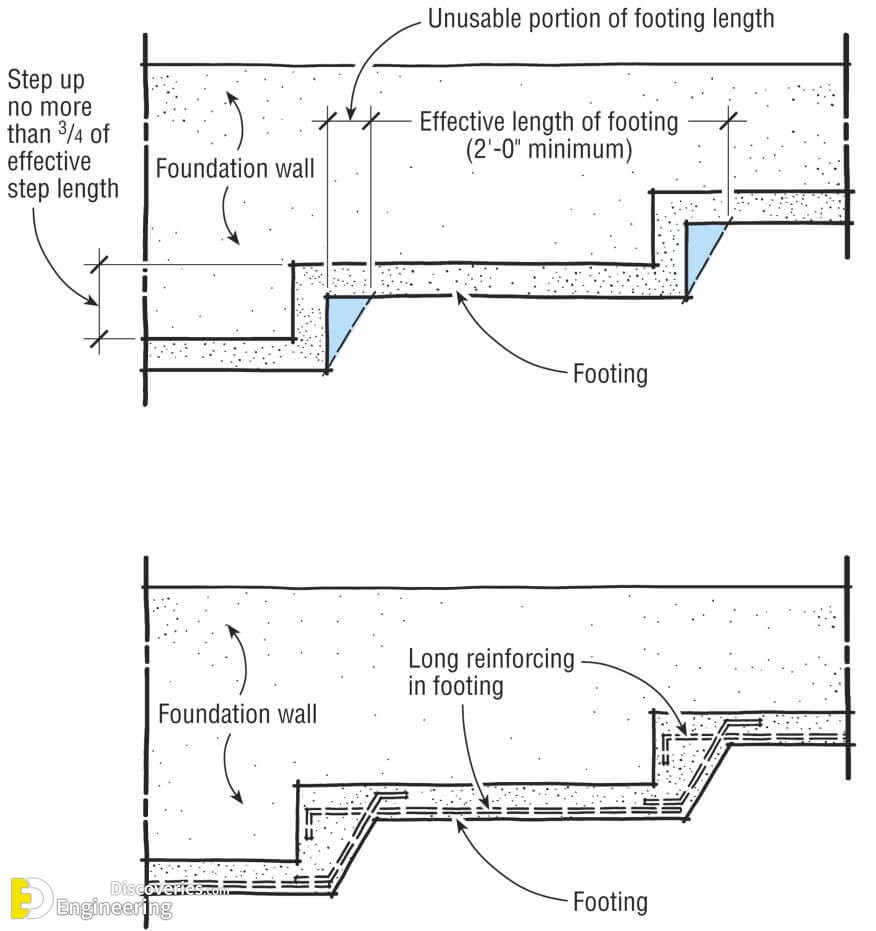
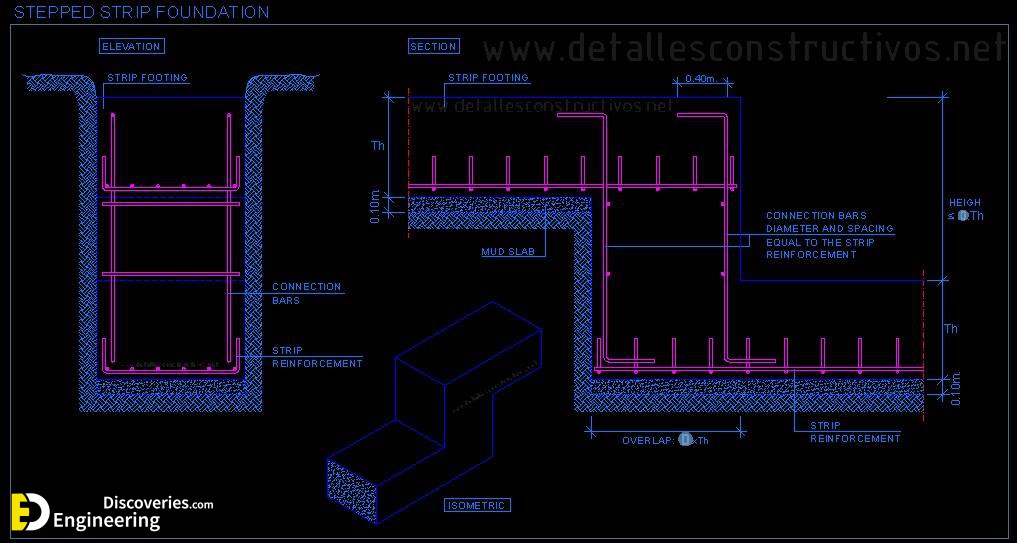
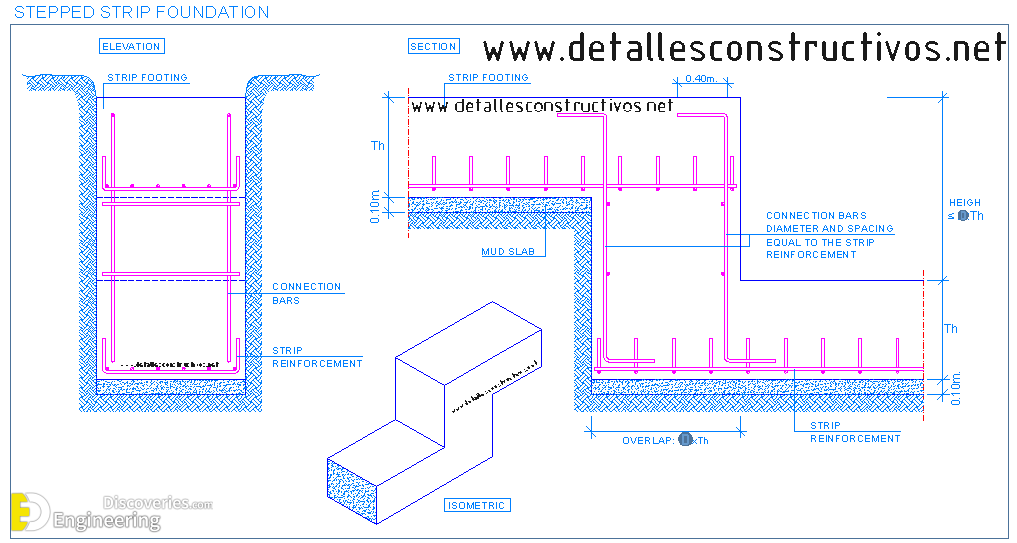
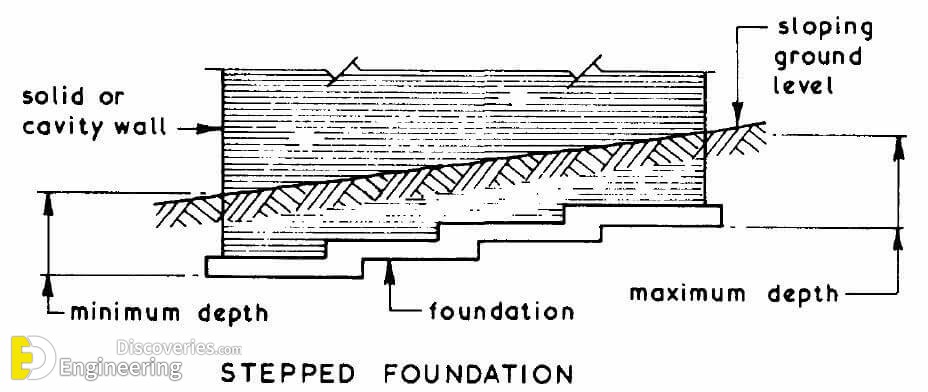
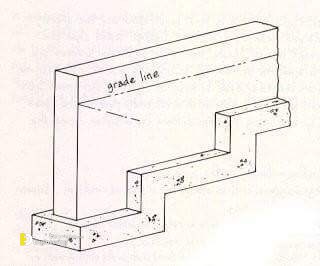
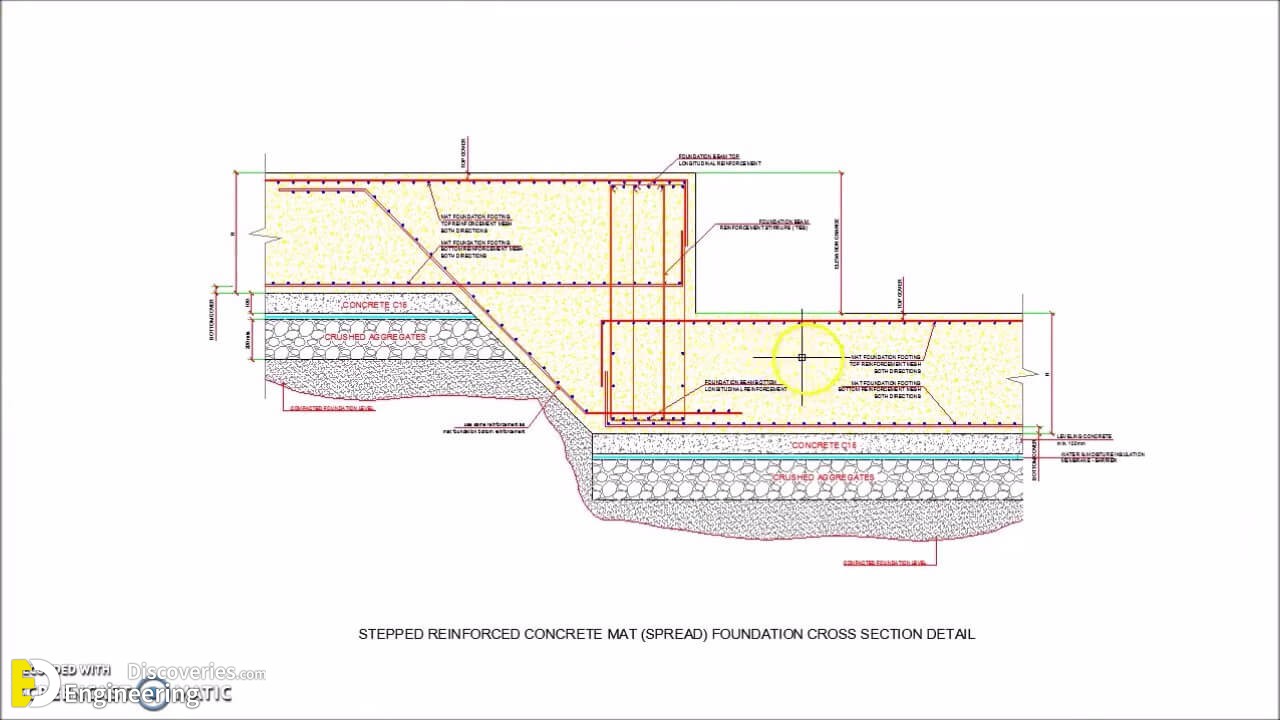
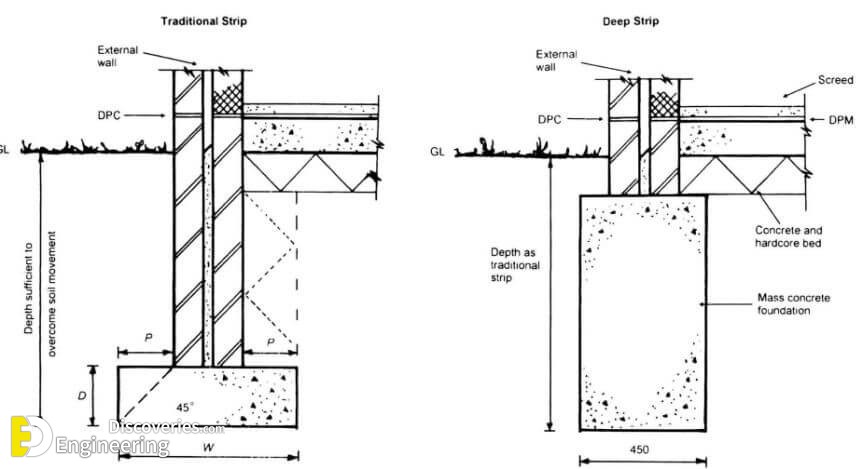
Strip foundations (or strip footings) are a type of shallow foundation used to provide a continuous, level (or sometimes stepped) strip of support to a linear structure such as a wall or closely-spaced rows of columns built centrally above them. Where the natural surface of the ground is sloped, the most economical solution may be a stepped foundation. In this case, the foundation takes the form of a series of concrete horizontal steps following the slope of the ground.
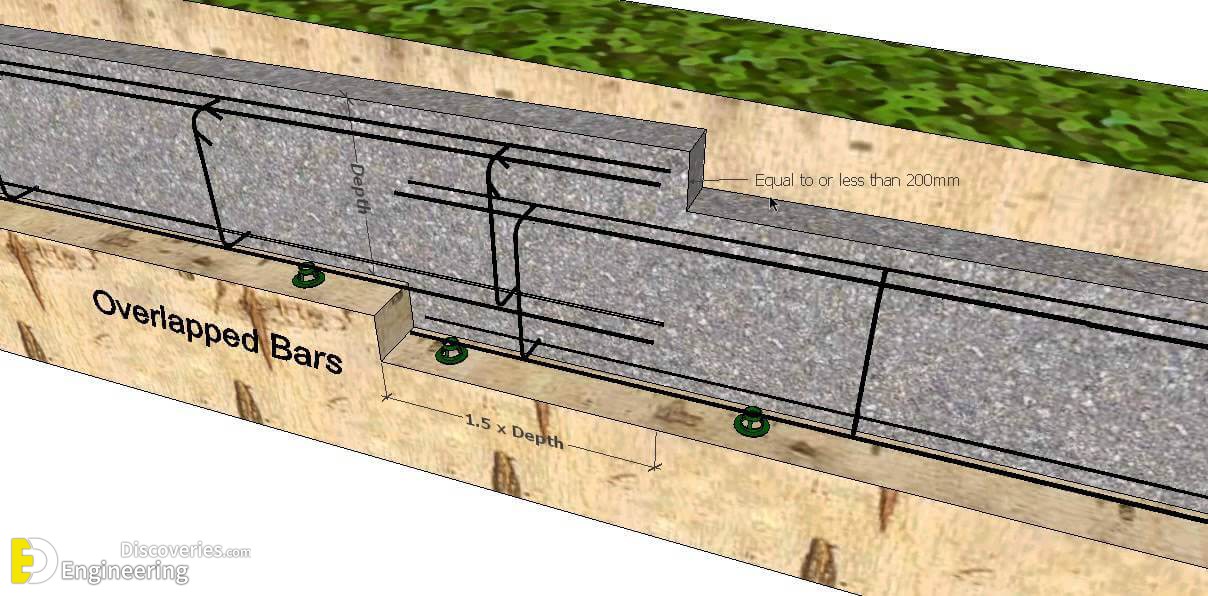
Each step in the foundation should be no higher than the thickness of the foundation. The foundation at the higher level should also overlap the lower foundation, typically by at least twice the height of the step, by the thickness of the foundation, or by at least 300 mm (whichever is greatest). Drainage must be carefully designed to eliminate the danger of instability due to accumulating water pressure.