Road construction relies heavily on bitumen, a key material that ensures durability, stability, and long-lasting performance. Understanding the different types of bitumen used in road construction can help engineers, contractors, and decision-makers select the right materials for their projects. This article explores the various bitumen types used in road construction and their specific applications.
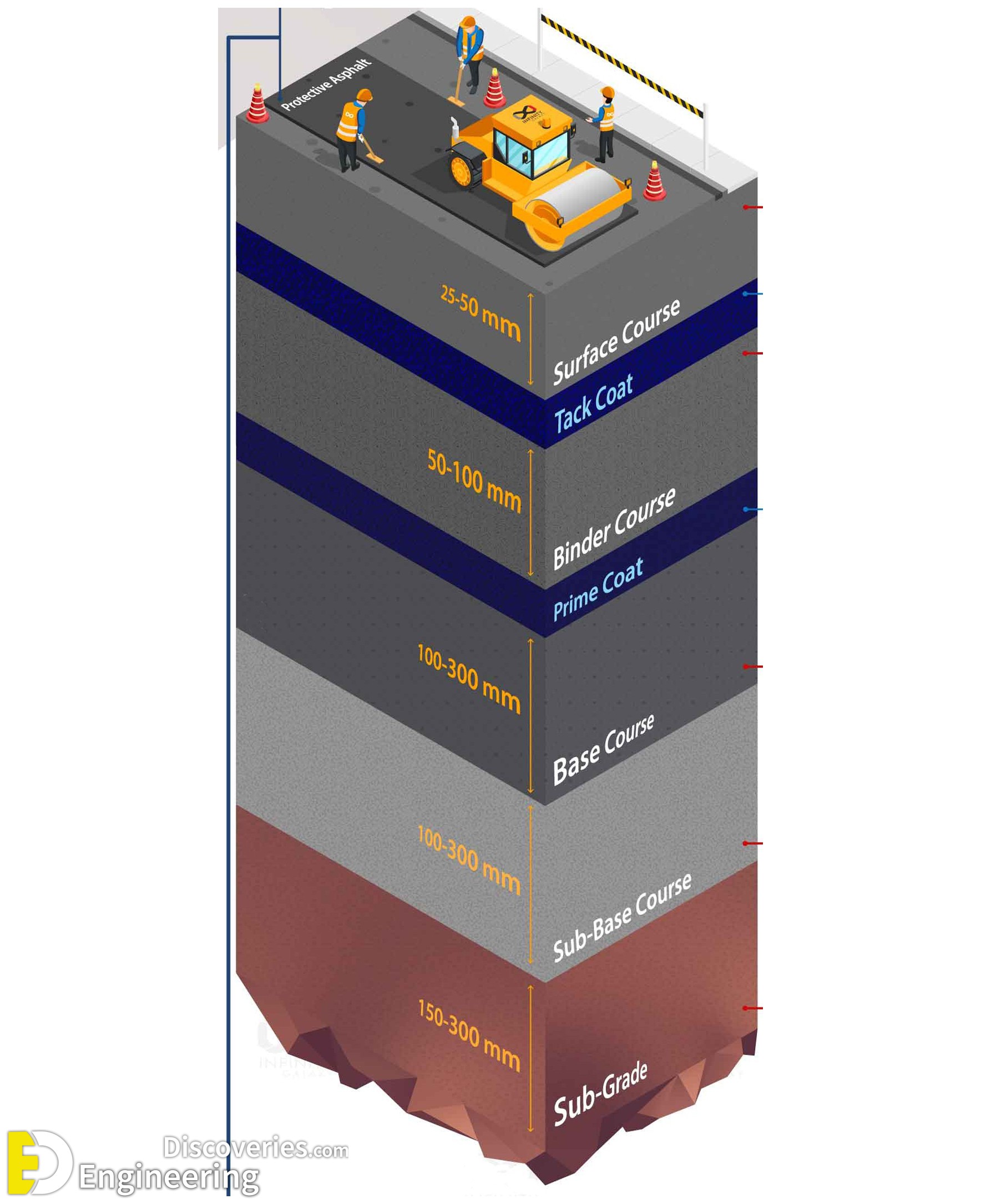
1. Surface Course
The surface course is the topmost layer of the pavement, exposed to traffic and environmental conditions. It is designed to withstand wear and tear while providing a smooth and safe driving surface.
- Hot Asphalt: This type includes penetration grades such as 60/70, 40/50, 80/100, 120/150, and 200/300, offering varying levels of hardness and viscosity.
- Cold asphalt is used for quick repairs and patching, and cutback bitumen types like RC 70, RC 250, and SC 3000 are commonly used.
- Bitumen Emulsion: Bitumen emulsion is available in both anionic and cationic types and is widely used for road construction and maintenance.
2. Tack Coat
A tack coat is a thin layer of liquid bitumen applied between two asphalt layers to enhance bonding.
- Cut Back Bitumen: MC 30 is a widely used grade.
- Bitumen Emulsion: CRS-1 and CRS-2 are common choices for tack coat applications.
3. Binder Course
The binder course is placed between the surface and base course to distribute loads effectively.
- Viscosity Grades: VG 10, VG 20, VG 30, and VG 40 are common grades used for binder layers.
- Penetration Grades: 30/40, 40/50, 60/70, 80/100, 120/150.
4. Prime Coat
A prime coat is applied to prepare the base course for asphalt layers by ensuring proper adhesion.
- Cut Back Bitumen: MC 30, SC 70, MC 70, RC 70, SC 250, MC 250, RC 250.
- Bitumen Emulsion: Various anionic and cationic emulsions.
5. Base Course
The base course distributes loads from the upper layers to the lower layers while maintaining the structural integrity of the road. It is constructed using durable aggregates.
6. Sub-Base Course
The sub-base course lies below the base course and consists of crushed aggregates or gravel. It provides additional support and load distribution.
7. Sub-Grade
The subgrade is the natural ground layer where all other layers are placed. It must be compacted and strong enough to bear traffic loads.
Protective Asphalt for Road Longevity
Protective asphalt treatments enhance road durability by making the surface impermeable, increasing strength, and preventing damage. Several types of protective asphalt treatments include:
- Seal Coat: Improves asphalt appearance and prevents wear. (Emulsion: CSS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1h)
- Slurry Seal: Used for maintenance of airport runways and urban roads. (Emulsion: SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1, CQS-1h)
- Chip Seal: Applied on rural roads with lower traffic volumes. (Emulsion: CRS-2, RS-2, HFRS-2, PMB)
- Micro Surfacing: Fills cracks and restores oxidized surfaces. (PMB: PMQCS-1h, PMQS-1h, CQS-1P)
- Fog Seal: Seals minor cracks and improves aerated surfaces. (Emulsion: SS-1, SS-1h, CSS-1)
Conclusion
Bitumen plays a crucial role in road construction, ensuring strength, durability, and longevity. The different layers and coatings used in pavement construction contribute to overall performance, safety, and maintenance efficiency. Understanding these materials allows engineers to design roads that are sustainable, cost-effective, and suitable for varying traffic conditions.
Click Here To See Construction Of Low-Traffic Roads by Using Old Tires