Passive cooling systems are a great way to cool buildings without using any electricity. They are becoming increasingly popular as people become more aware of the need to reduce their environmental impact. There are many different types of passive cooling systems, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
The best passive cooling system for your building will depend on several factors, including:
- The climate of your location
- The size and shape of your building
- Your budget
- Your personal preferences
Here are some of the most common types of passive cooling systems:
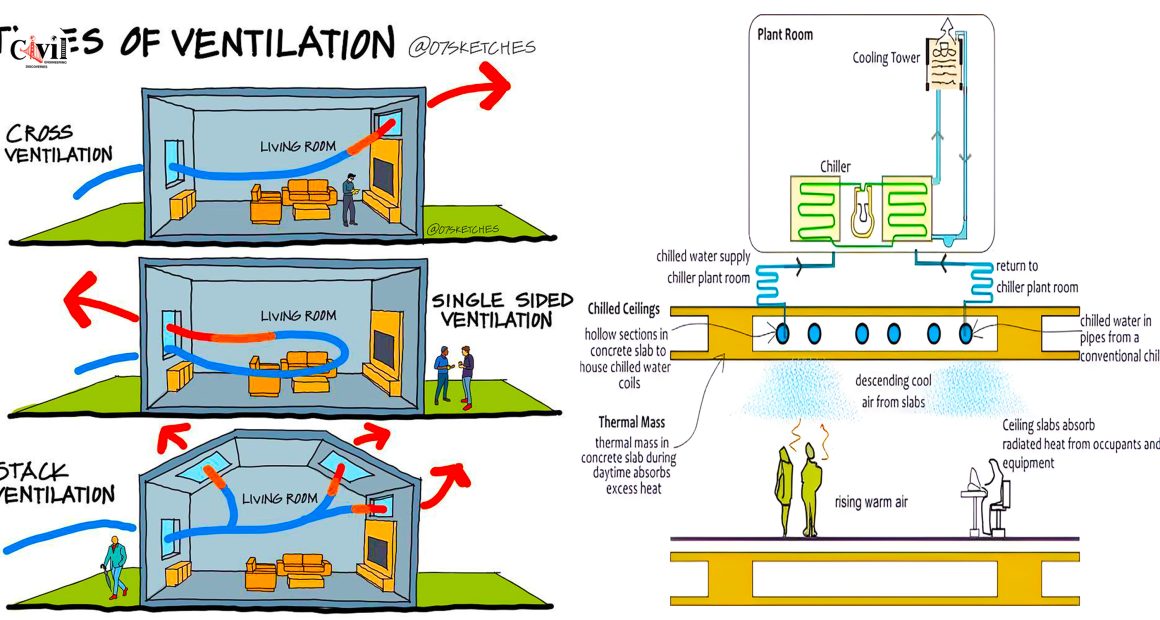
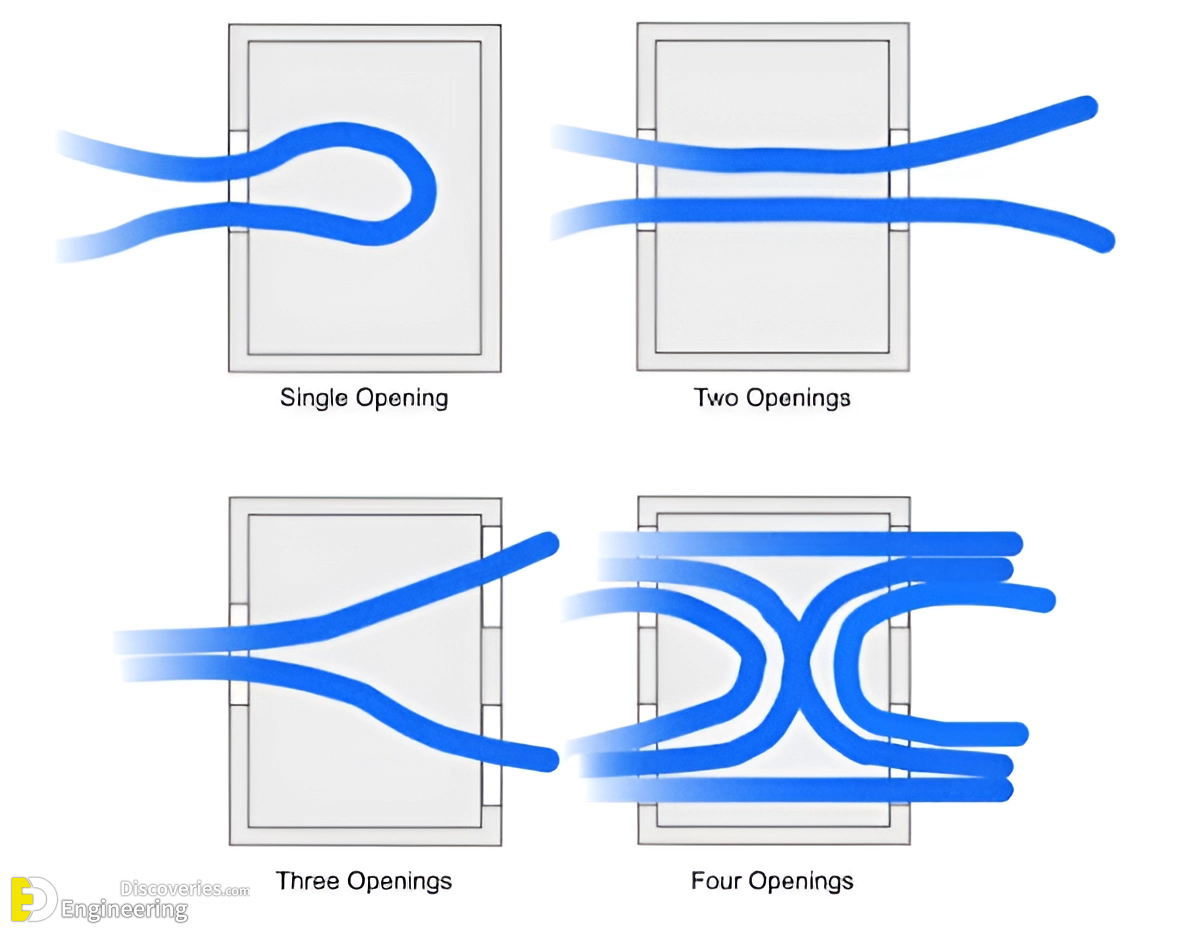
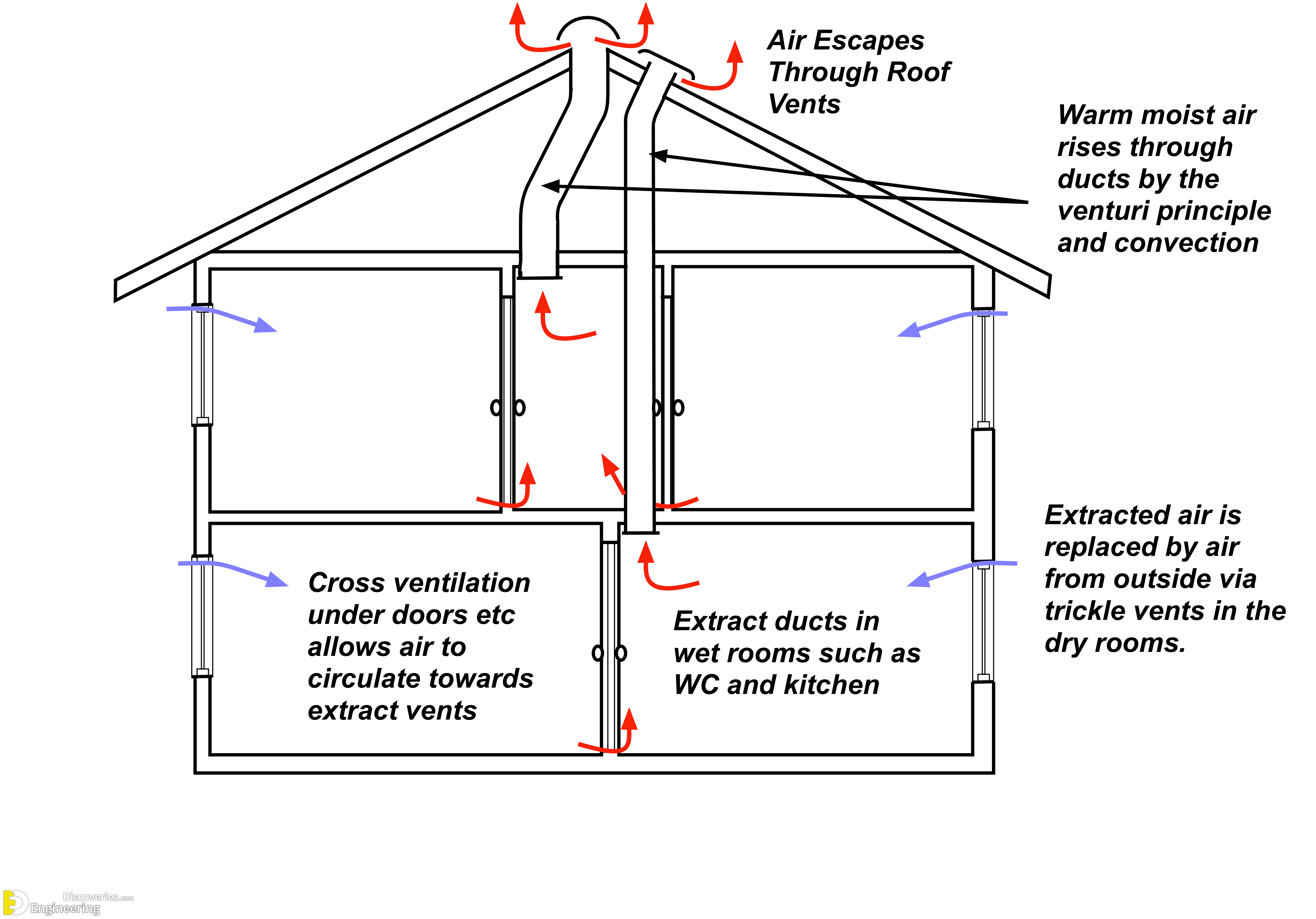
1. Natural ventilation: This is the simplest and most effective type of passive cooling. It involves using windows, doors, and other openings to allow cool air to flow into a building and warm air to escape. Natural ventilation can be very effective in climates with mild temperatures and consistent breezes.
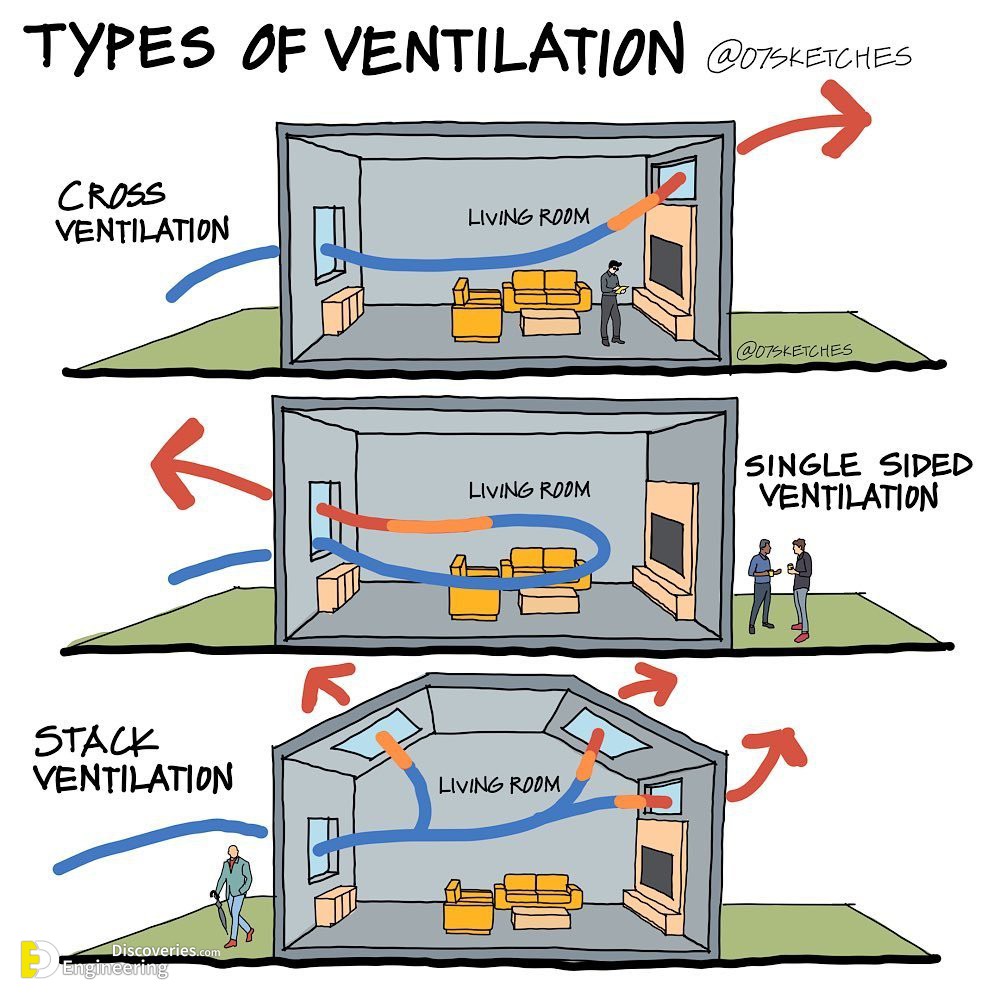
2. Cross ventilation: This is a type of natural ventilation that uses two or more openings on opposite sides of a building to create a flow of air. Cross ventilation can be more effective than natural ventilation alone, especially in hot and humid climates.
3. Stack ventilation: This type of passive cooling uses the natural buoyancy of warm air to draw it up and out of a building. Stack ventilation can be created by using a tall chimney or other vertical opening.
4. Evaporative cooling: This type of passive cooling uses the process of evaporation to cool air. Evaporative coolers work by drawing in warm air and passing it over a wet pad. As the water evaporates, it cools the air. Evaporative coolers can be very effective in hot and dry climates.
5. Radiant cooling: This type of passive cooling uses cool surfaces to radiate heat away from the body. Radiant cooling can be achieved by using materials such as stone, concrete, or metal in the walls, floors, and ceilings of a building.