Crowned roadways play a crucial role in road design, ensuring both safety and functionality. A crowned roadway features a slight slope, highest in the center, which helps in efficient drainage. This design prevents water accumulation, a common issue that can lead to road damage and dangerous driving conditions. But what exactly makes a crowned roadway effective, and why is it necessary for proper drainage? Let’s dive in.
What is a Crowned Roadway?
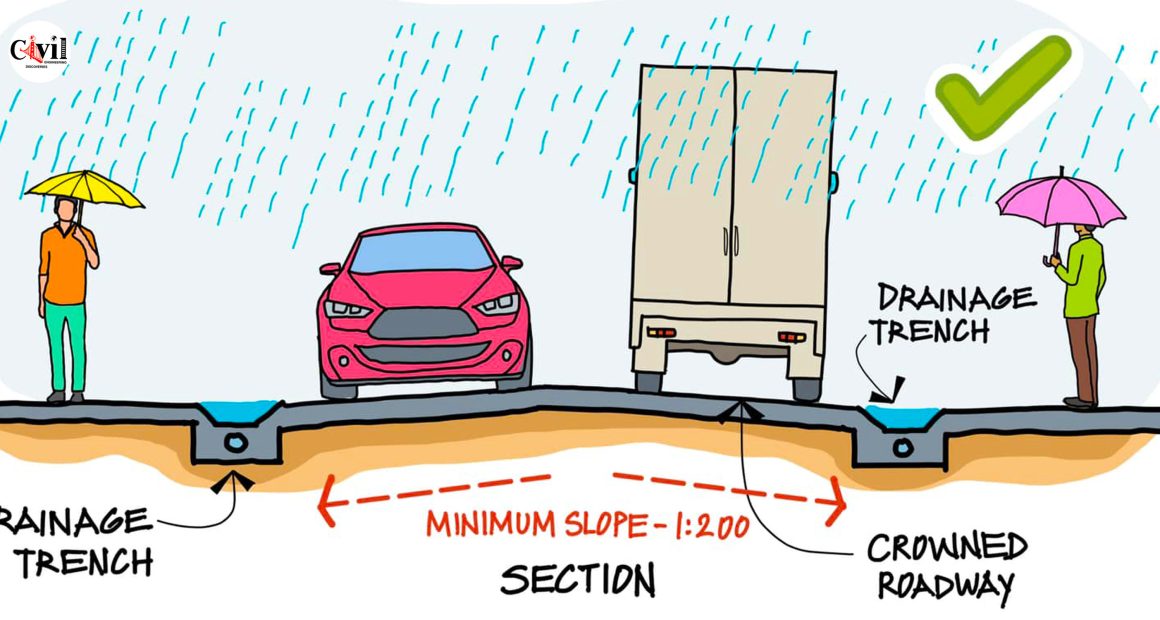
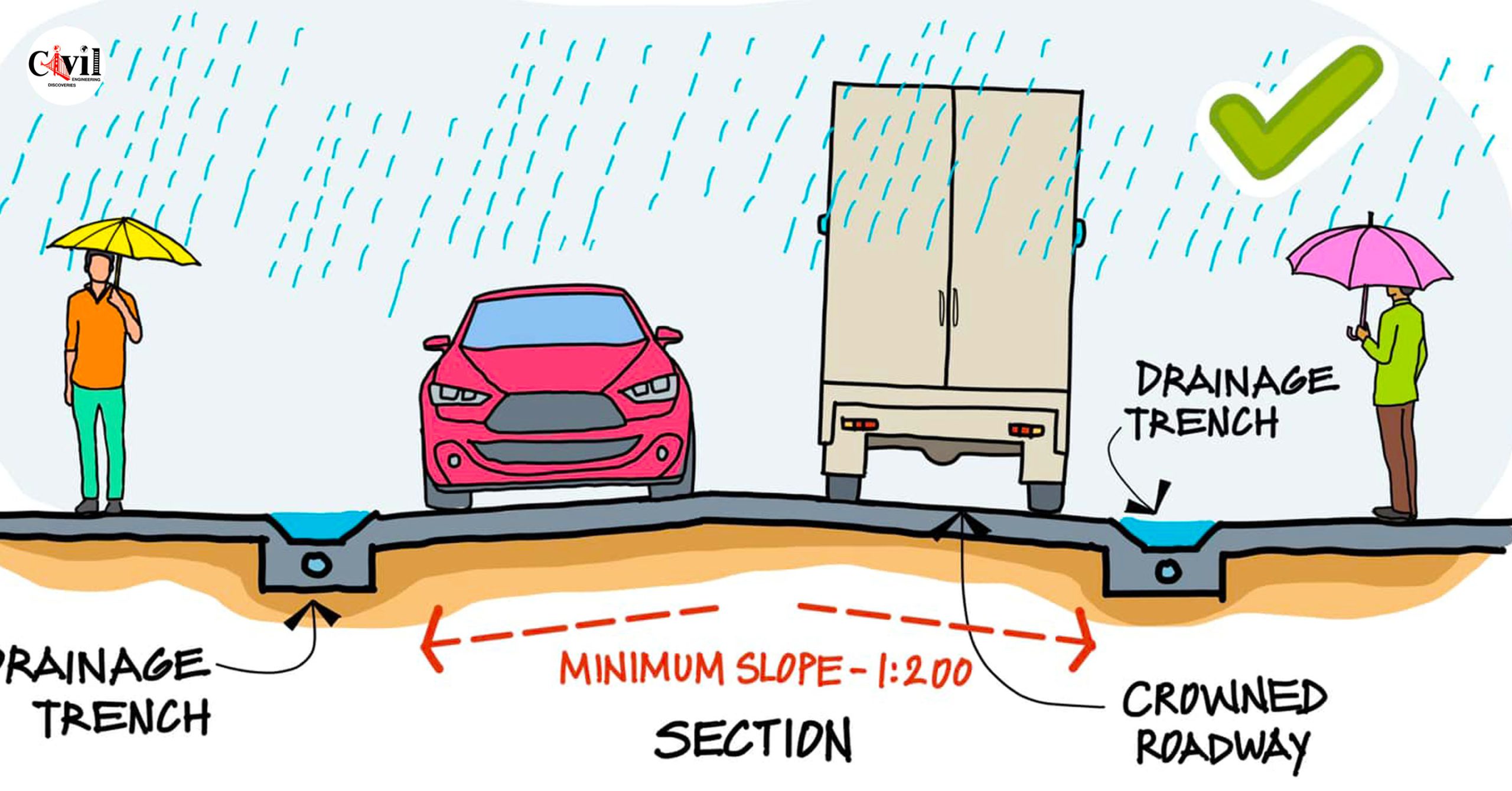
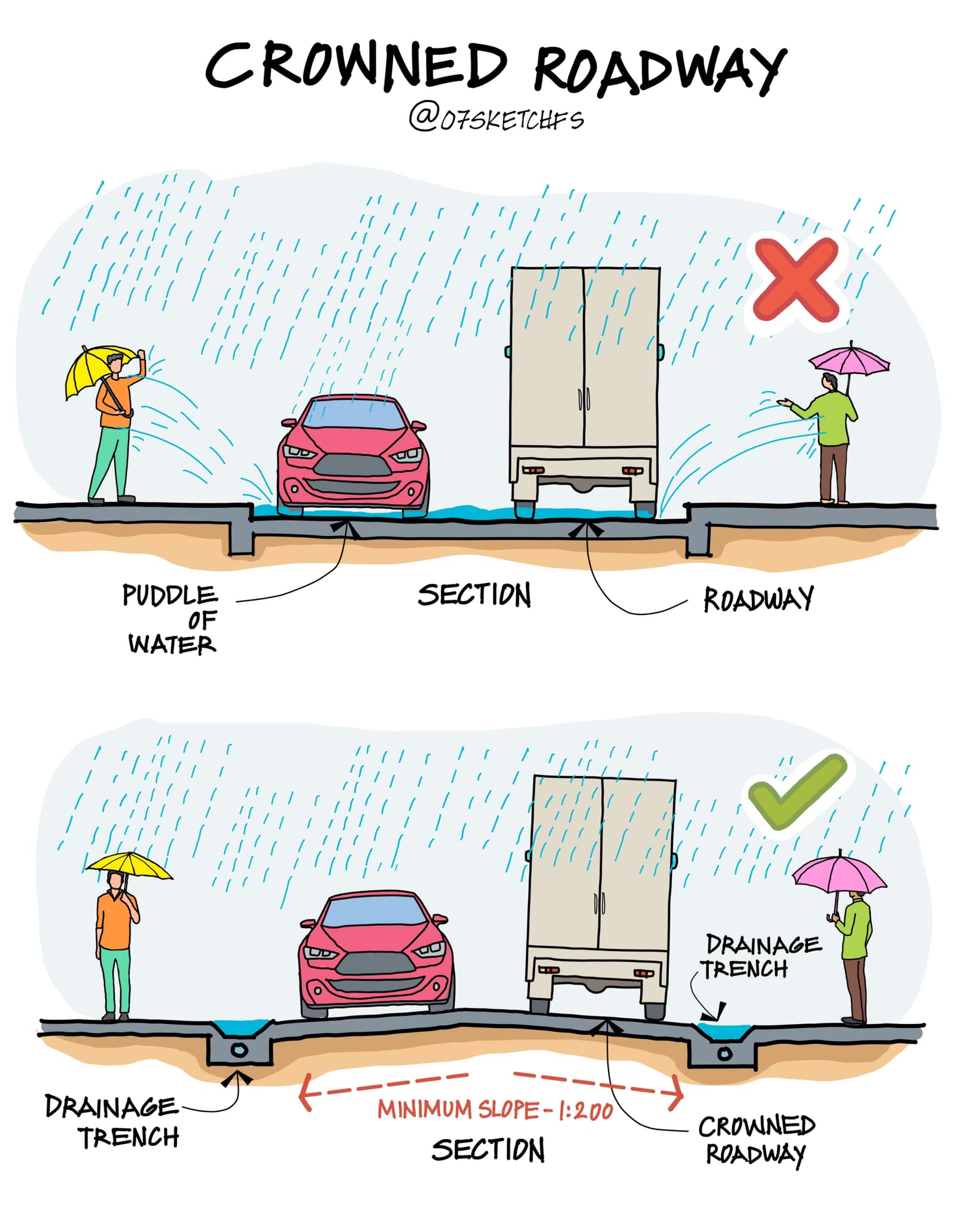
A crowned roadway is a road surface that slopes from the centerline towards both edges. This design allows rainwater to flow off the road instead of collecting in the center or along the sides. The crown is essentially the highest point, and the slope of the roadway helps guide water to drainage channels or ditches.
Why Crowned Roadways Are Important
The primary purpose of a crowned roadway is to manage water runoff. Without a proper slope, water can pool on the road surface, leading to hydroplaning hazards and potential road damage. Over time, standing water can cause potholes, erosion, and cracks, compromising the integrity of the road. A crowned roadway prevents these issues by directing water away from the road surface.
Minimum Slope for Crowned Roadways
For effective drainage, a crowned roadway typically has a minimum slope of 1:200. This means that for every 200 units of horizontal distance, the road surface should drop by one unit. This gentle slope is sufficient to ensure that water flows away from the road, preventing accumulation without causing discomfort for drivers.
The Need for Drainage in Roadway Design
Drainage is a critical aspect of roadway design, especially in areas prone to heavy rainfall. Without proper drainage, roads can become dangerous and require frequent repairs. Crowned roadways provide a natural and cost-effective solution to these problems by encouraging water to flow off the road surface into designated drainage areas.
TechniqueConsiderations for Crowned Roadways
When designing a crowned roadway, several factors need to be considered to ensure that the road meets safety and durability standards. These factors include:
- Road Type and Location: The type of road (e.g., highway, rural road, urban street) and its location (e.g., flat terrain, hilly area, coastal region) will influence the design of the crown and the slope required for proper drainage.
- Climate: Areas with high levels of precipitation or frequent snowmelt will require more attention to drainage. The slope may need to be adjusted to handle larger volumes of water.
- Pavement Material: The type of material used for the pavement can also impact drainage. Permeable materials, such as certain types of asphalt, allow water to seep through, while non-permeable surfaces require a more efficient drainage design.
- Maintenance: A well-maintained crowned roadway will continue to provide effective drainage over time. Regular inspection and repair of the pavement, as well as cleaning of drainage systems, are necessary to prevent water accumulation and roadway damage.
Photo Credit: 07sketches