Introduction to Punching in Spread Footing
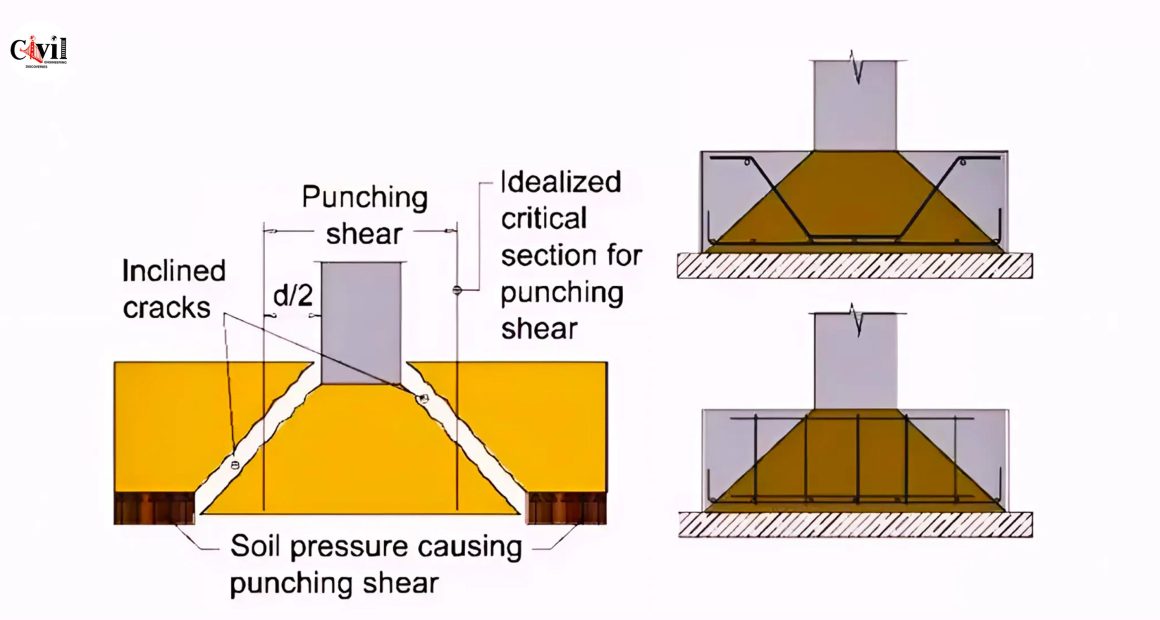
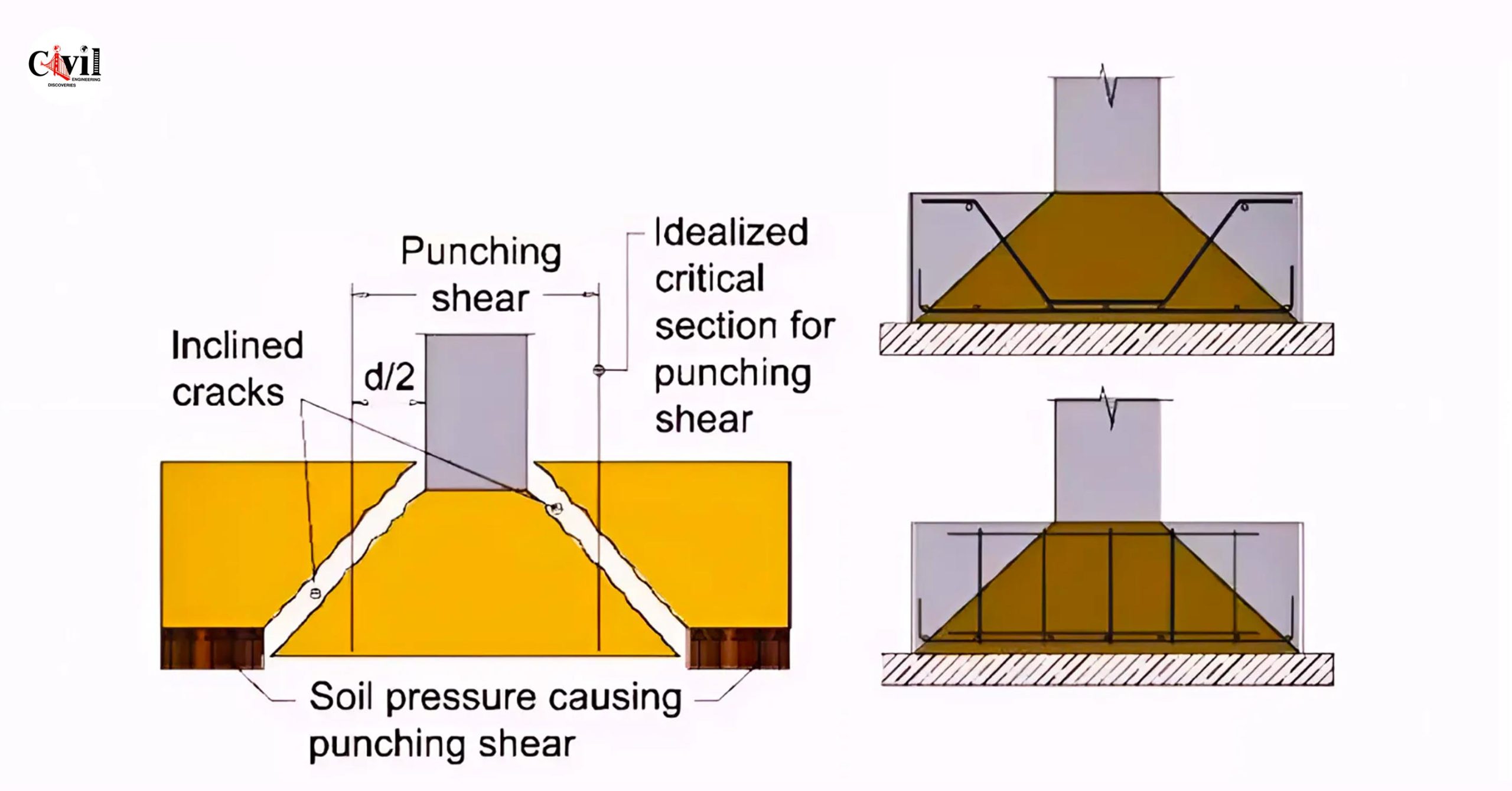
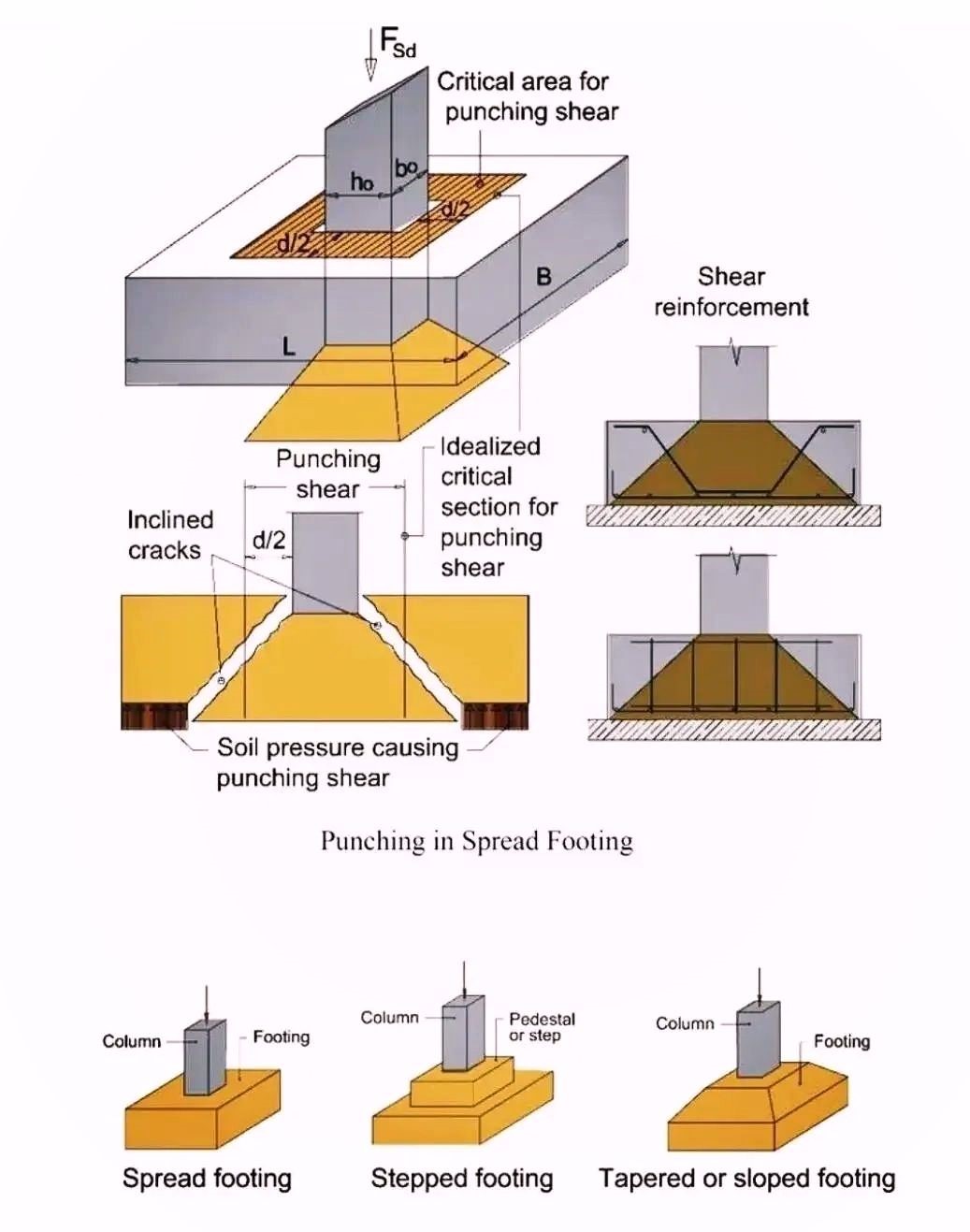
Punching in spread footing is a critical issue in structural engineering. It occurs when concentrated loads cause failure in the footing, leading to significant structural problems. This phenomenon often results from improper design or inadequate load distribution. Understanding the causes of punching in spread footing is essential to ensure structural stability.
What Causes Punching in Spread Footing?
Several factors contribute to punching in spread footing. One of the most common causes is overloading a small footing area. When excessive force is applied to a localized point, the footing cannot distribute the load evenly, leading to a punching shear failure.
Inadequate reinforcement is another reason behind punching. If the reinforcement is not properly designed or installed, the footing may lack the strength to resist punching. Poor soil conditions also play a major role. Weak or loose soil underneath the footing can compromise its ability to bear heavy loads, leading to failure.
How to Prevent Punching in Spread Footing
To prevent punching in spread footing, it is crucial to ensure proper load distribution. This can be achieved by designing the footing with adequate size and thickness to handle the expected load. The use of reinforcement is essential as well. Properly designed and placed reinforcement helps distribute the load evenly, preventing localized stress that can cause punching.
Soil testing is equally important. Before construction, it’s vital to assess the soil conditions at the site. Weak soils should be improved, or alternative foundation solutions should be considered to avoid punching.
Conclusion: Ensuring Structural Integrity
Punching in spread footing is a serious structural concern that can be avoided with proper planning and design. By considering factors such as load distribution, reinforcement, and soil conditions, engineers can ensure the stability and longevity of a building’s foundation.