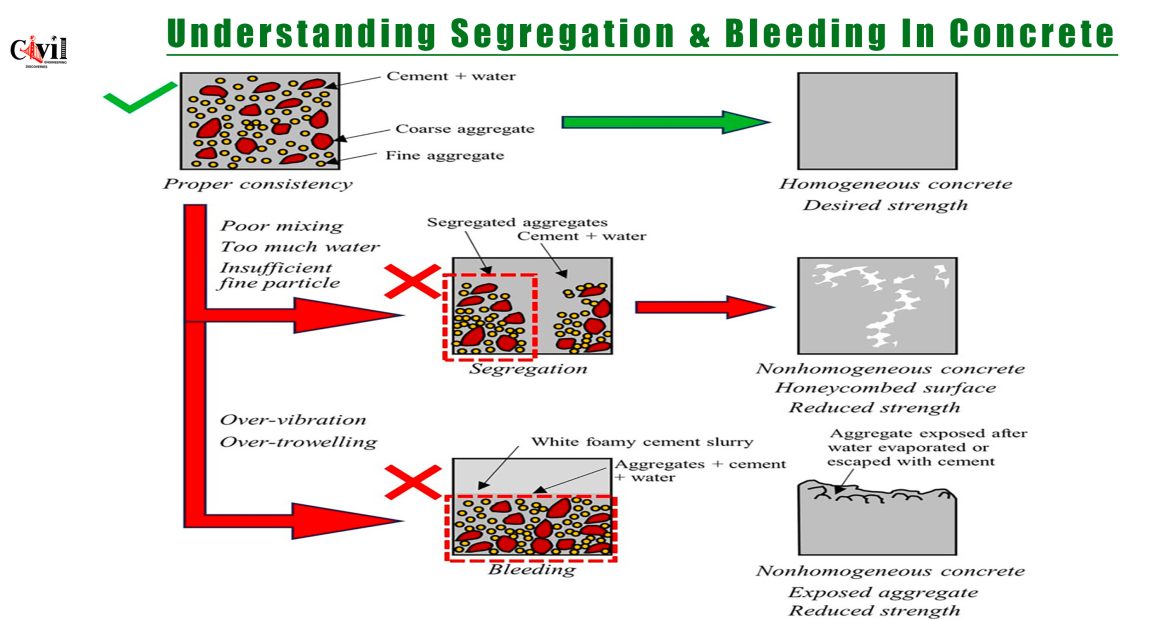
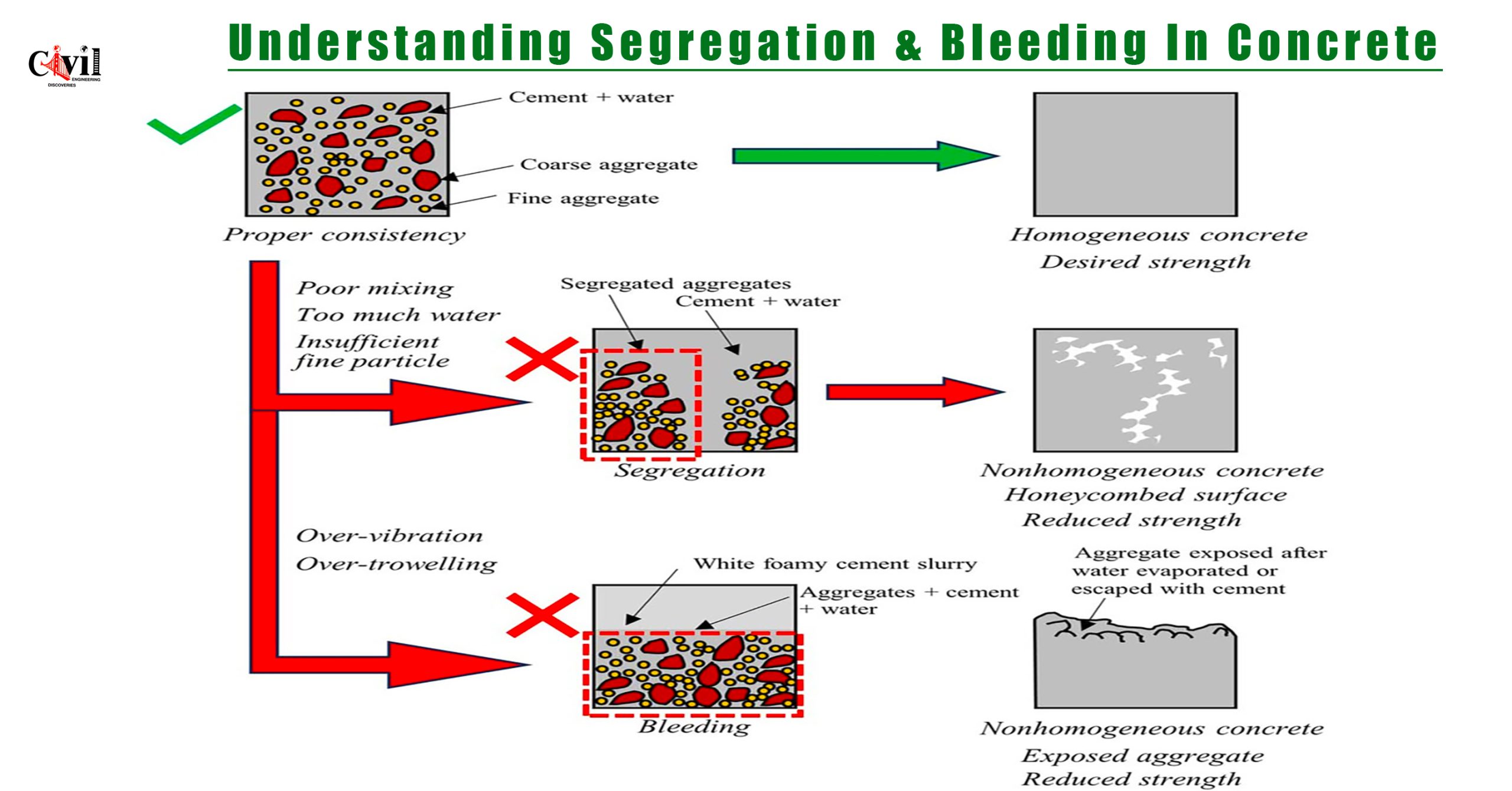
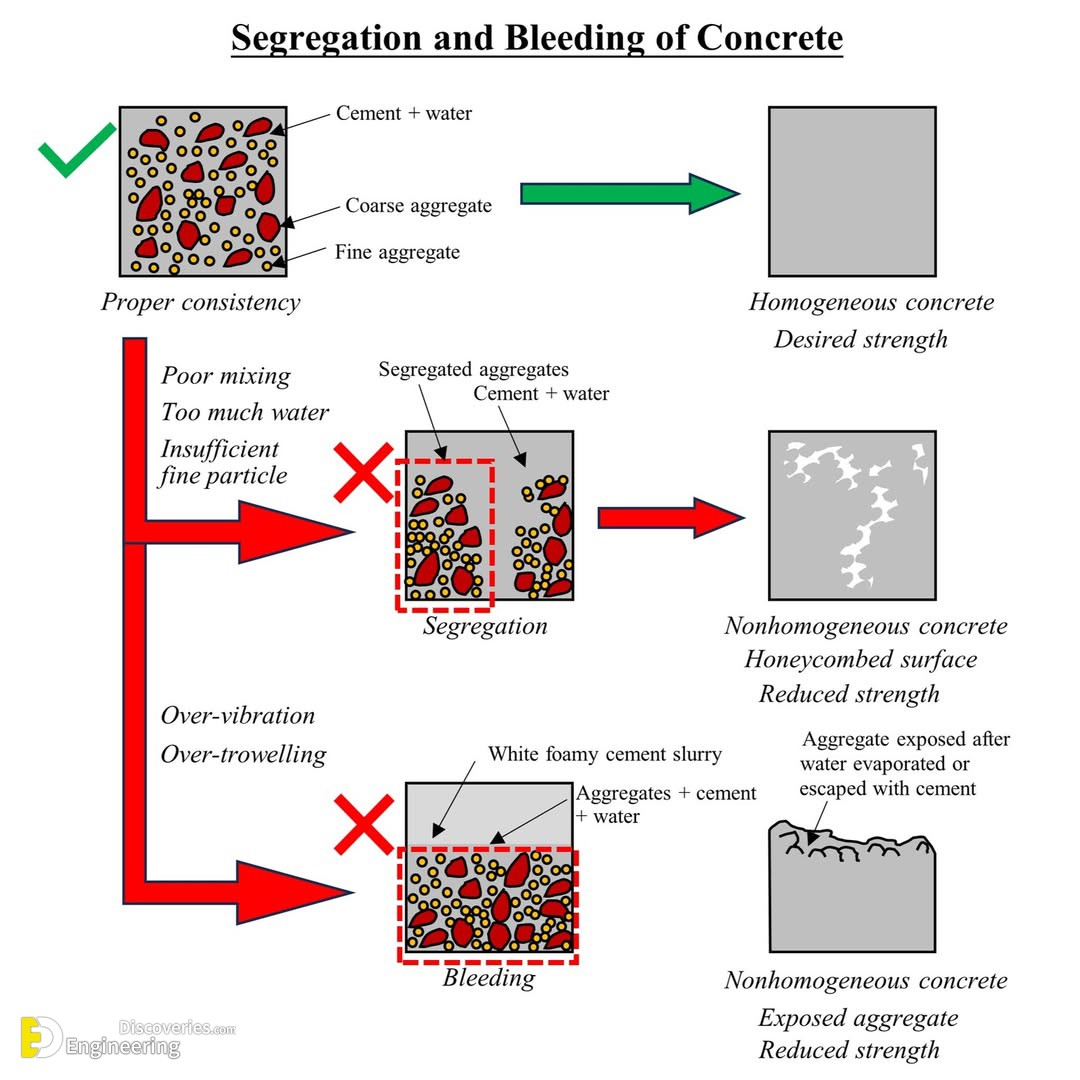
Concrete is one of the most widely used construction materials, valued for its strength and versatility. However, achieving optimal strength and durability requires precise mixing and consistency. Improper handling can lead to segregation and bleeding, two common issues that compromise the quality of concrete. Let’s explore these issues in detail.
What Is Segregation in Concrete?
Segregation occurs when the components of concrete—such as coarse aggregates, fine aggregates, cement, and water—separate during mixing, transportation, or placement. This separation disrupts the homogeneity of the mix and results in weaker structures.
Causes of Segregation
- Excess Water: Adding too much water to the mix reduces cohesion between particles.
- Poor Mixing: Inadequate mixing leads to uneven distribution of materials.
- Inappropriate Aggregates: Using aggregates of varying sizes can result in uneven settling.
Effects of Segregation
- Creates a honeycombed texture in the hardened concrete.
- Reduces compressive strength and durability.
- Leads to uneven load distribution and surface defects.
What Is Bleeding in Concrete?
Bleeding is the upward movement of water in freshly mixed concrete. This results in the formation of a water layer or cement slurry on the surface. While some bleeding is normal, excessive bleeding can weaken the concrete’s properties.
Causes of Bleeding
- High Water-to-Cement Ratio: Excessive water in the mix promotes bleeding.
- Over-Vibration: Over-compacting the mix encourages water to rise.
- Improper Proportioning: Incorrect ratios of fine and coarse aggregates can contribute to bleeding.
Effects of Bleeding
- Formation of weak cement layers on the surface.
- Increased porosity and reduced bonding strength.
- Exposed aggregates that lead to surface defects.
Preventing Segregation and Bleeding
Achieving Proper Consistency
- Maintain an optimal water-to-cement ratio to ensure a cohesive mix.
- Use high-quality aggregates with consistent gradation.
Effective Mixing Practices
- Mix thoroughly to ensure uniformity.
- Avoid over-vibration and over-trowelling to prevent material displacement.
Use Admixtures
- Incorporate water-reducing or air-entraining admixtures to minimize bleeding.
- Use bonding agents to improve cohesion between particles.
Monitor Placement and Finishing
- Place concrete carefully to avoid dislodging aggregates.
- Ensure proper curing to maintain strength and durability.
Conclusion
Segregation and bleeding are critical issues that can significantly reduce the quality and strength of concrete. By understanding their causes and effects, construction professionals can take preventive measures to produce durable and homogenous concrete structures. Proper mixing, proportioning, and curing practices are essential for avoiding these problems and ensuring the long-term performance of concrete.
Click Here To See Types Of Concrete Cracks And How To Prevent Them