The water-cement ratio is a critical factor in determining the strength and durability of concrete. Understanding the right balance of water and cement can significantly affect the performance of your construction project. In this article, we will dive deep into the importance of the water-cement ratio, how it impacts the quality of concrete, and best practices to achieve optimal results.
What Is the Water-Cement Ratio?
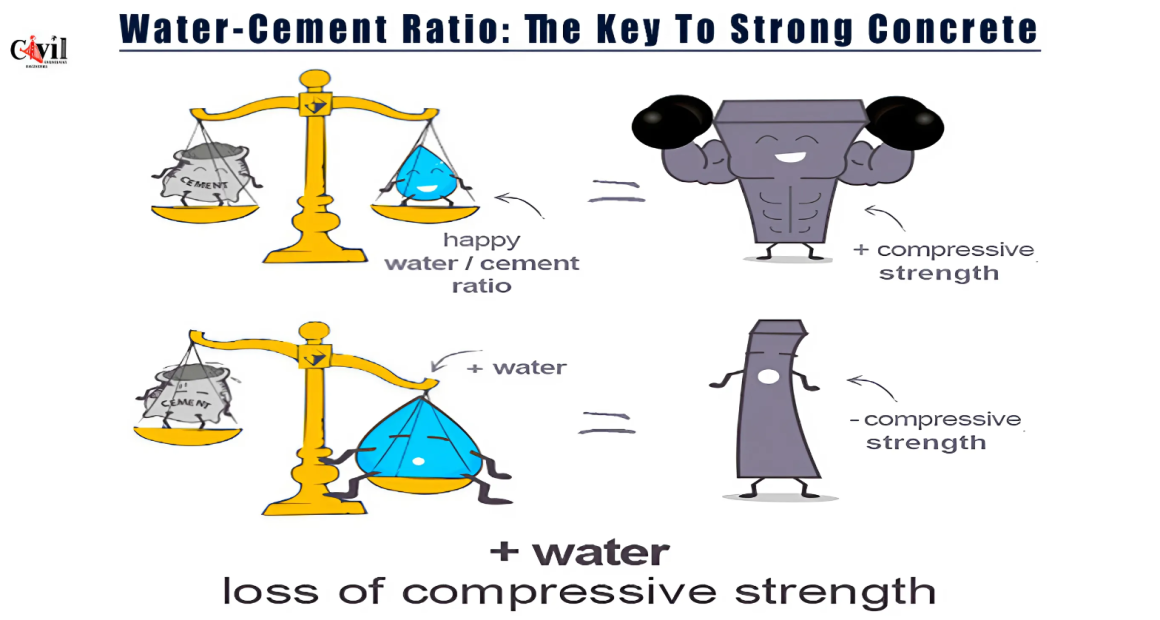
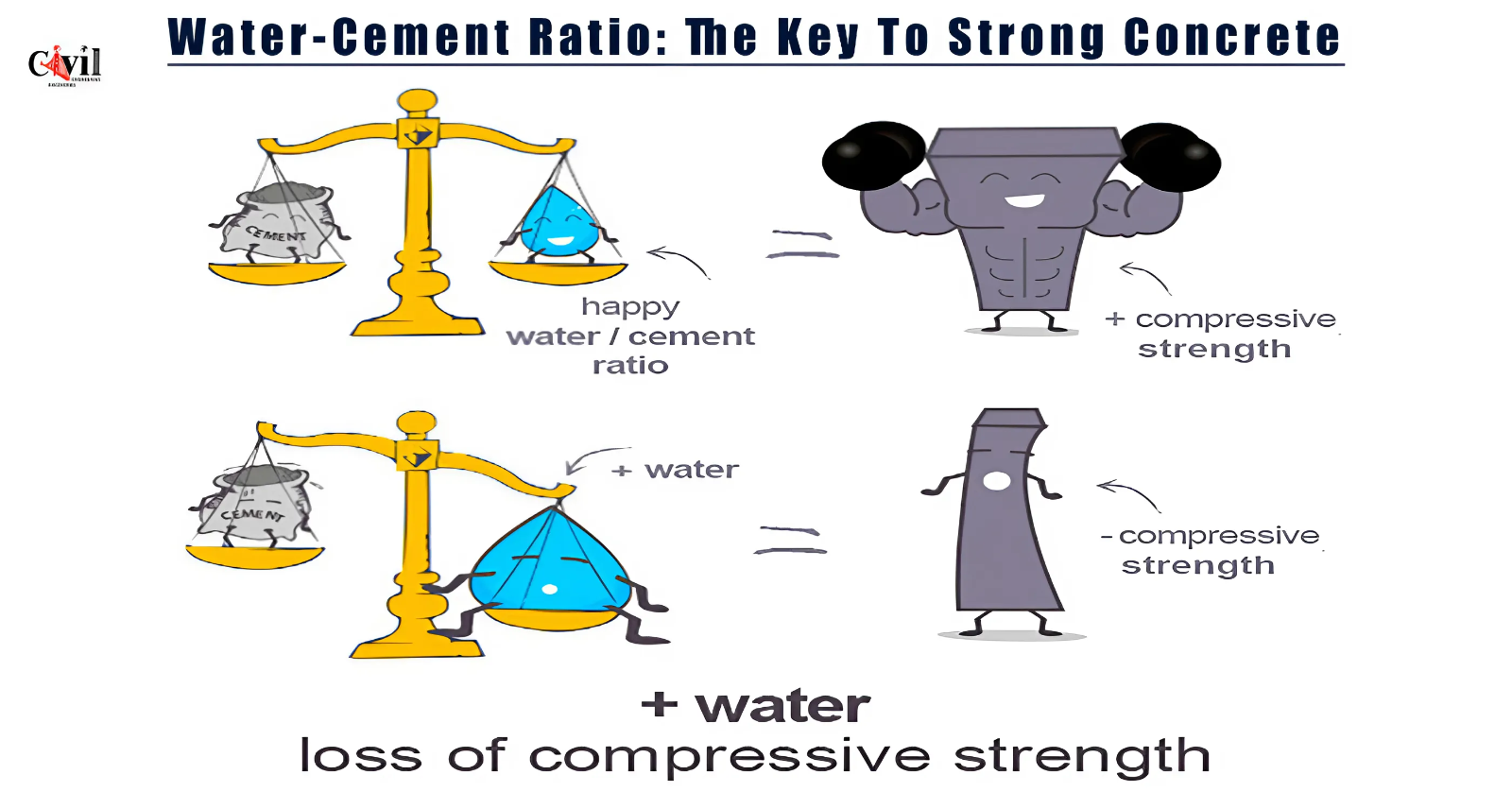
The water-cement ratio refers to the proportion of water to cement in a concrete mix. This ratio is crucial because it determines the consistency, workability, and strength of the concrete. A lower water-cement ratio increases strength and durability, while a higher ratio can cause weaker concrete.
The ratio is calculated by dividing the water weight by the cement weight in the mix. For example, a water-cement ratio of 0.5 means that for every pound of cement, half a pound of water is added. Finding the right balance is essential for ensuring that the concrete is strong enough for its intended use.
W = C x 0.5
Importance of Water-Cement Ratio in Concrete
The water-cement ratio is a critical determinant of the properties of concrete. Here’s why it matters:
- Strength: Concrete with a lower water-cement ratio tends to be stronger. This is because there is less water to evaporate, which means the cement particles can bond more closely together, resulting in a denser and stronger structure.
- Durability: A lower water-cement ratio also improves the durability of concrete. Less water means fewer voids and air pockets, which can weaken the concrete over time. Durable concrete is less susceptible to cracking and weathering.
- Workability: The water-cement ratio also affects the workability of concrete. A higher ratio makes the mix more fluid and easier to work with, but it compromises strength. Conversely, a lower ratio results in a stiffer mix that may be more challenging to handle, but it produces stronger concrete.
How to Achieve the Ideal Water-Cement Ratio
Finding the right water-cement ratio is essential for producing high-quality concrete. Here are some best practices to achieve the ideal ratio:
- Accurate Measurements: Always measure the water and cement accurately. Too much water can reduce the strength of the concrete, while too little can make it difficult to work with.
- Use Admixtures: Admixtures can help improve the workability of concrete without increasing the water content. These chemicals allow for better handling of the mix while maintaining a lower water-cement ratio.
- Mix Consistency: Ensure that the concrete mix is consistent throughout the batch. Uneven mixing can result in parts of the concrete having a different water-cement ratio, leading to weak spots in the finished structure.
Common Mistakes in Water-Cement Ratio
Even small mistakes in the water-cement ratio can lead to significant problems in concrete construction. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Adding Extra Water: Adding water to the mix to improve workability is a common mistake. While it may make the concrete easier to handle, it can significantly reduce its strength.
- Inaccurate Mixing: Failing to mix the concrete properly can result in an uneven distribution of water and cement, leading to weak spots and a lack of uniformity.
- Ignoring Environmental Conditions: Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can affect the water-cement ratio. In hot or dry conditions, more water may evaporate from the mix, altering the ratio. Adjust the water content accordingly to compensate for these conditions.





The ratio of C-40 concrete with box size
Perfect information