In the ever-evolving world of construction and civil engineering, selecting the right type of cement is crucial for ensuring structural integrity, durability, and efficiency. Civil engineers must be well-versed in the various types of cement available in the market to make informed choices depending on the project requirements, environmental exposure, and desired performance characteristics. Here, we explore in detail the 10 most essential types of cement that every civil engineer should master for successful project execution.
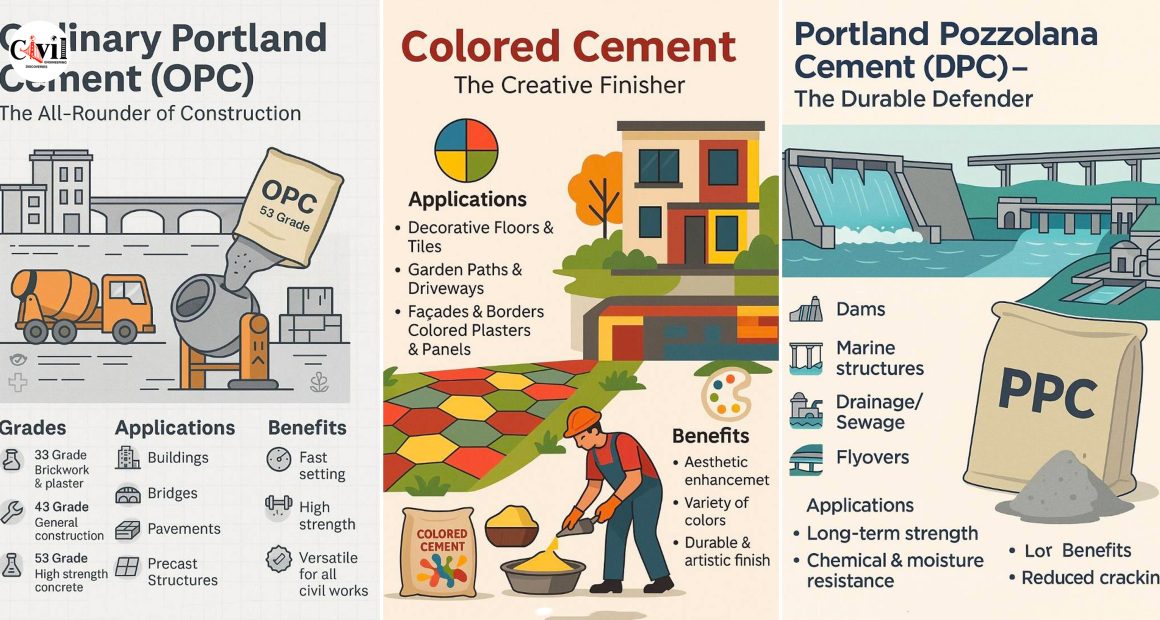
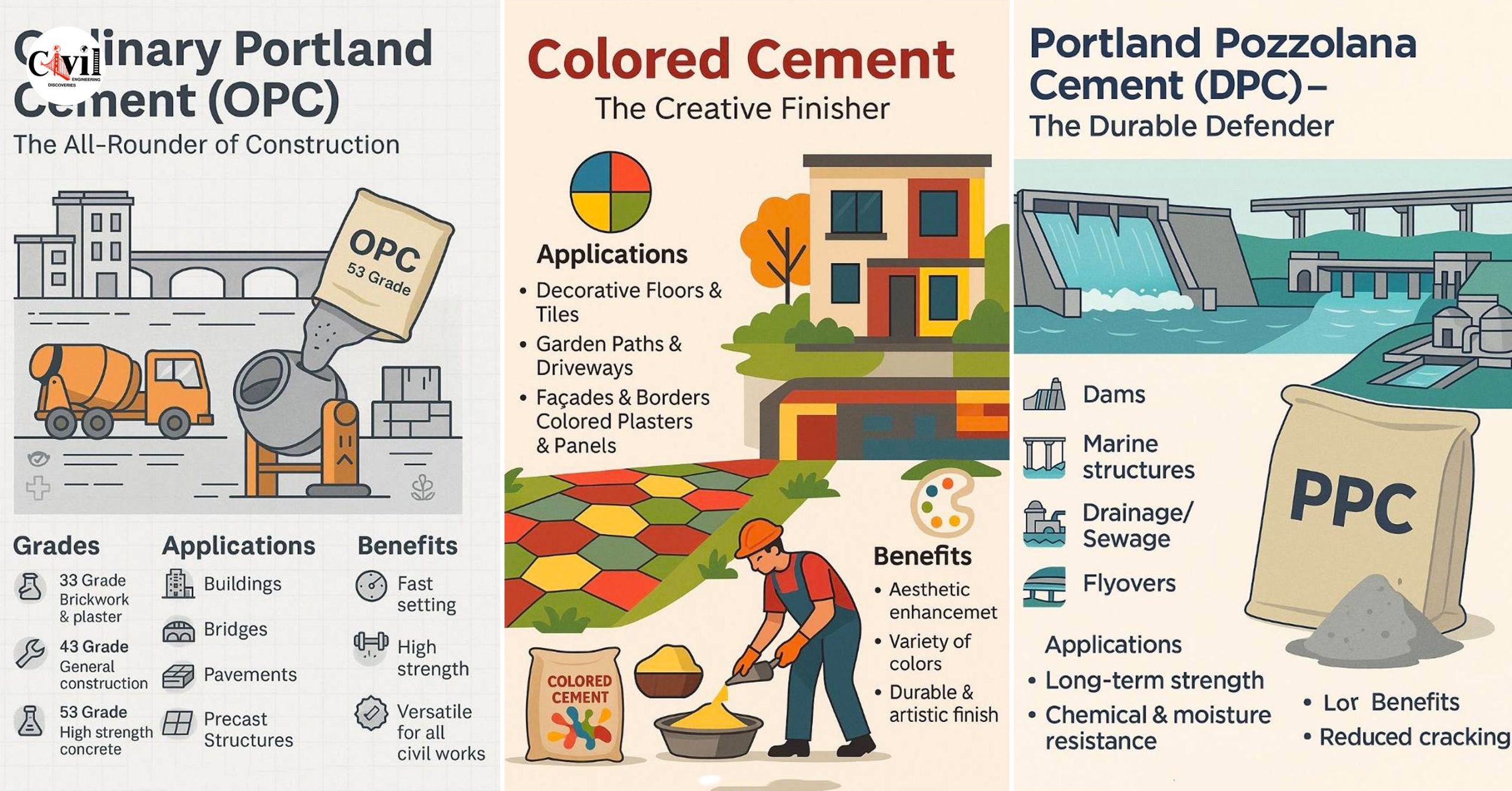
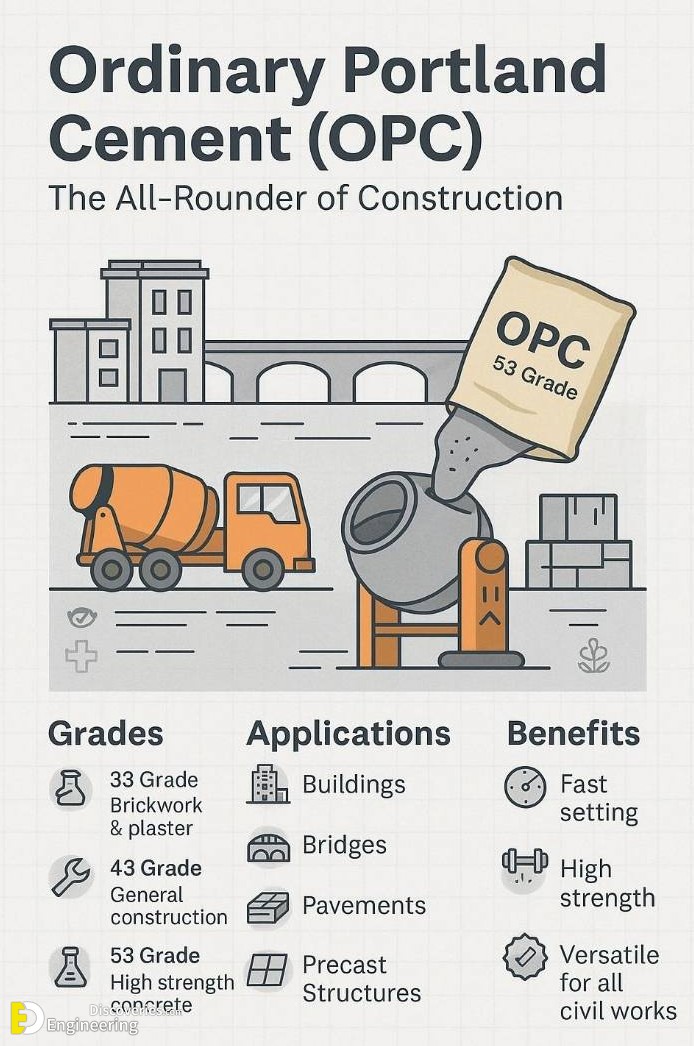
1. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC): The All-Rounder of Construction
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is the most widely used type of cement and serves as the foundation for countless civil structures. Available in 33, 43, and 53 grades, OPC is ideal for a range of applications:
Applications:
Residential and commercial buildings
Bridges and flyovers
Road pavements
Precast concrete products
Benefits:
Fast setting time
High strength gain
Versatile for all types of civil works
Whether you’re constructing high-rise buildings or rural homes, OPC remains the go-to cement for its balanced performance and availability.
2. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC): The Durable Defender
Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) is made by blending pozzolanic materials such as fly ash with OPC. It is highly favored for its resistance to chemical attacks and long-term strength development.
Applications:
Dams and marine structures
Drainage and sewage systems
Bridges and flyovers
Benefits:
Reduced thermal cracking
Increased durability
Cost-effective for large projects
Civil engineers prefer PPC in environments where moisture and chemicals can degrade ordinary concrete over time.
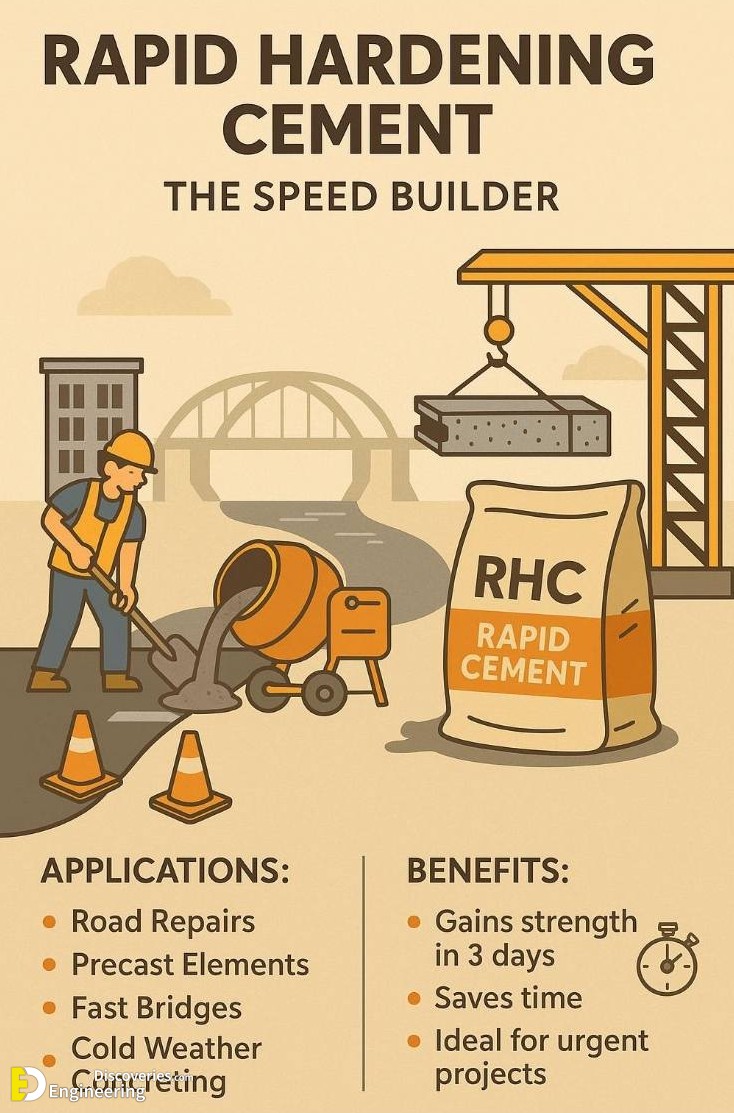
3. Rapid Hardening Cement (RHC): The Speed Builder
When time is of the essence, Rapid Hardening Cement (RHC) offers the solution. This type of cement develops strength quickly, often within 3 days, making it perfect for fast-track projects.
Applications:
Road repairs
Precast concrete elements
Cold weather concreting
Benefits:
Accelerated construction timeline
Saves time and labor costs
Useful in critical infrastructure repair
Its fast strength development is especially useful in urban environments where downtime must be minimized.
4. Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC): The Corrosion Fighter
Sulphate Resisting Cement (SRC) is specially formulated to resist sulphate attacks in aggressive environments.
Applications:
Coastal and marine construction
Sewage treatment and drainage systems
Chemical and fertilizer plants
Benefits:
Improved durability in hostile environments
Prevents sulphate-induced cracks
Extends structure lifespan
SRC is essential for use in sub-grade structures that come into contact with sulphate-rich soils and water.
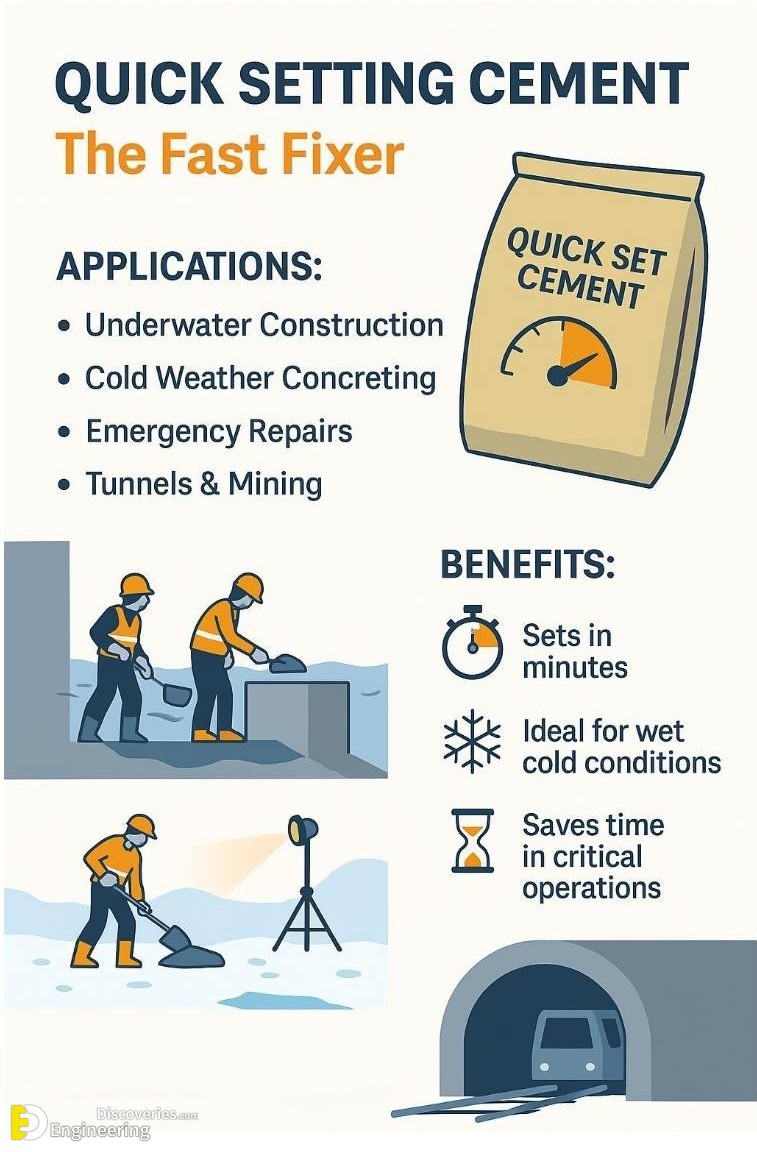
5. Quick Setting Cement: The Fast Fixer
Quick-setting cement is known for its exceptionally short setting time, making it indispensable in emergencies.
Applications:
Underwater construction
Tunnels and mines
Cold weather concreting
Emergency repairs
Benefits:
Sets in minutes
Ideal for wet and cold conditions
Time-saving in critical operations
Quick-setting cement is a must-have in a civil engineer’s arsenal for urgent construction scenarios.
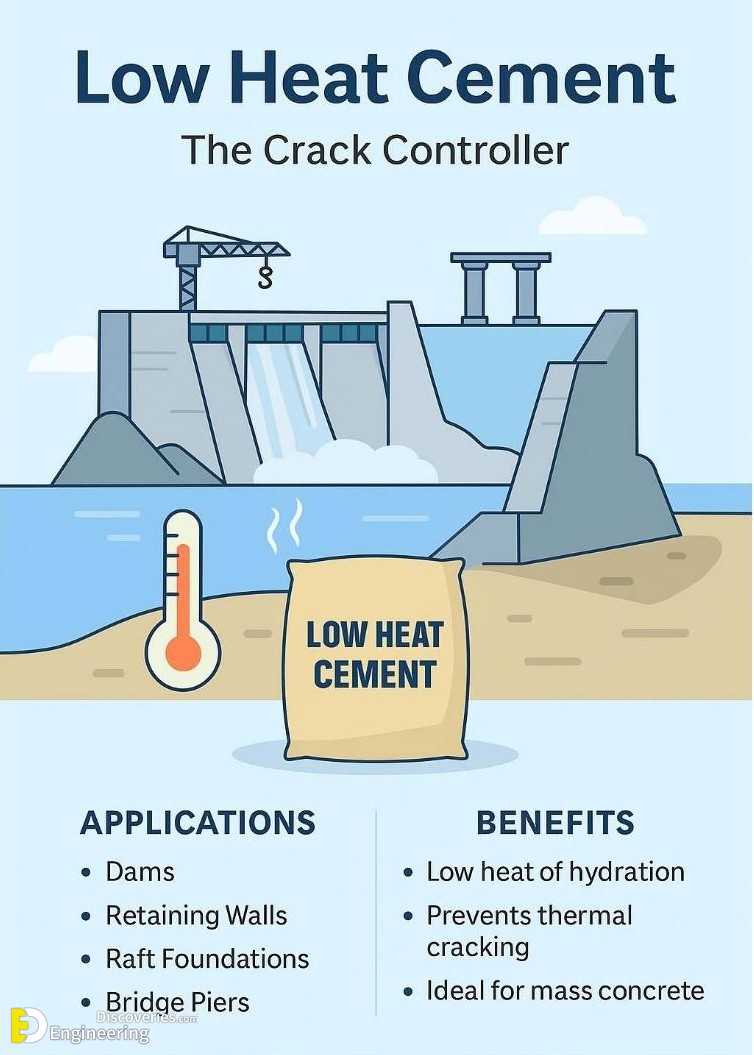
6. Low Heat Cement: The Crack Controller
Designed to reduce the heat of hydration, Low Heat Cement is ideal for mass concrete works where controlling internal temperature is vital.
Applications:
Dams
Bridge piers
Retaining walls
Raft foundations
Benefits:
Minimizes thermal cracks
Sustains structural integrity
Best suited for large volume pours
This cement is essential for preventing structural cracking in large infrastructure projects.
7. White Cement: The Aesthetic Artist
White Cement is prized for its aesthetic appeal and is used where visual appearance is as important as structural performance.
Applications:
Architectural designs
Decorative floors and tiles
Sculptures and artistic works
Benefits:
Bright, smooth finish
Superior blending with pigments
Ideal for luxury interiors and exteriors
White Cement elevates the visual quality of structures while maintaining durability.
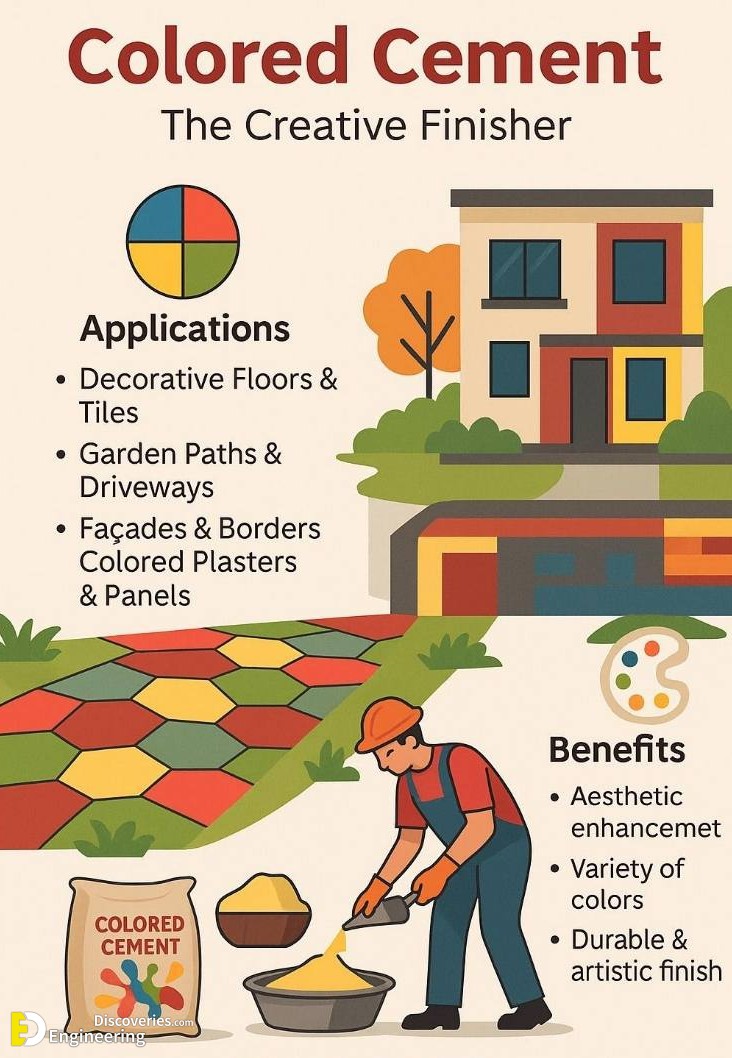
8. Colored Cement: The Creative Finisher
Colored Cement is ordinary cement blended with mineral pigments to achieve a variety of hues.
Applications:
Pavements and walkways
Garden paths
Façades and walls
Tiles and panels
Benefits:
Aesthetic enhancement
Available in diverse colors
Maintains durability and finish
This type of cement is popular in landscaping and urban beautification projects.
9. High Alumina Cement: The Heat Warrior
High Alumina Cement contains a high percentage of aluminum oxide, giving it remarkable resistance to high temperatures and chemical attacks.
Applications:
Kilns and furnaces
Marine and sewage works
Chemical processing plants
Benefits:
Rapid strength development
Withstands extreme temperatures
Corrosion-resistant
It is the preferred choice for industrial construction in extreme environments.
10. Expansive Cement: The Gap Filler
Expansive Cement is specially formulated to compensate for shrinkage and prevent cracking during hardening.
Applications:
Grouting and anchoring
Bridge joint repairs
Pre-stressed concrete
Benefits:
Fills gaps effectively
Prevents shrinkage cracks
Maintains dimensional stability
It is beneficial in precision structural repairs and retrofits.
Conclusion
Every civil engineer must understand various cement types’ unique properties and applications to ensure project success. Whether the goal is aesthetic appeal, rapid construction, or long-term durability, a cement is tailored for every need. The ability to choose the right cement is not just technical — it’s strategic, influencing both project efficiency and structural resilience.
Click Here To See How To Calculate The Quantity Of Cement, Sand, And Bricks For 1 Cubic Meter









Very easy to understand. Thanks very much