Walls are essential components in building structures, each serving unique purposes and offering various benefits depending on the type of construction. In this article, we will delve into the four major wall types in construction: Load-Bearing Walls, Curtain Walls, Shear Walls, and Retaining Walls. Each of these plays a critical role in the design and structural integrity of buildings.
1. Load-Bearing Wall
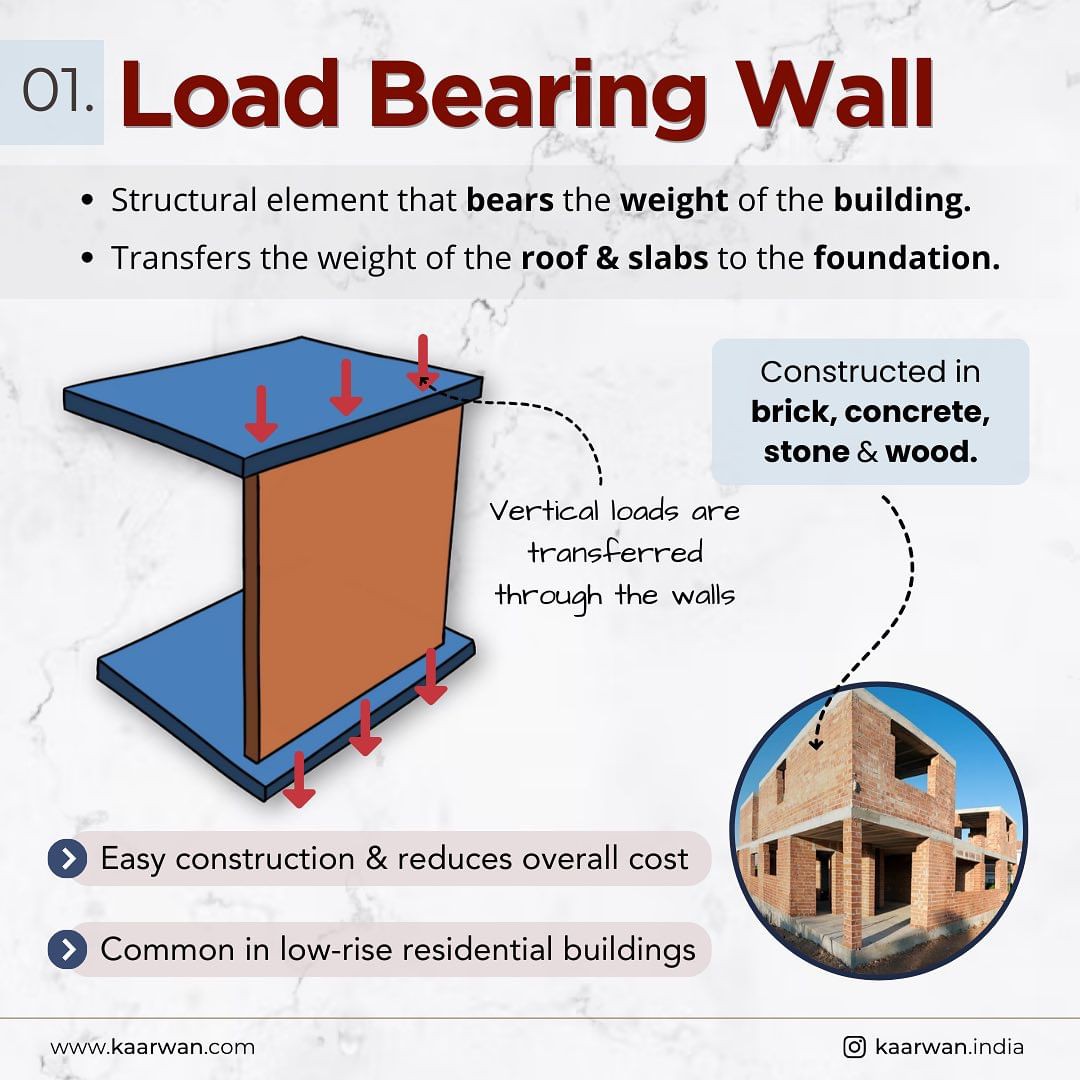
A load-bearing wall is a structural element responsible for bearing the weight of the building. It transfers the loads from the roof and slabs directly to the foundation, ensuring stability and support.
- Key Benefits:
- Easy to construct, making it a popular choice for low-rise residential buildings.
- Cost-effective since it minimizes the need for additional structural elements.
Application: Commonly found in low-rise residential buildings, load-bearing walls are integral to the stability and strength of the structure, reducing overall construction costs.
2. Curtain Wall
Unlike load-bearing walls, a curtain wall is a lightweight wall that does not support the building’s weight. Instead, it acts as a weather barrier and allows natural light to penetrate the building, enhancing energy efficiency.
- Key Benefits:
- Improves indoor lighting and reduces energy consumption.
- Adds aesthetic appeal to modern commercial and office buildings.
Application: Typically used in high-rise office and commercial buildings, curtain walls are designed to protect the interior from external elements while maintaining a sleek appearance.
3. Shear Wall
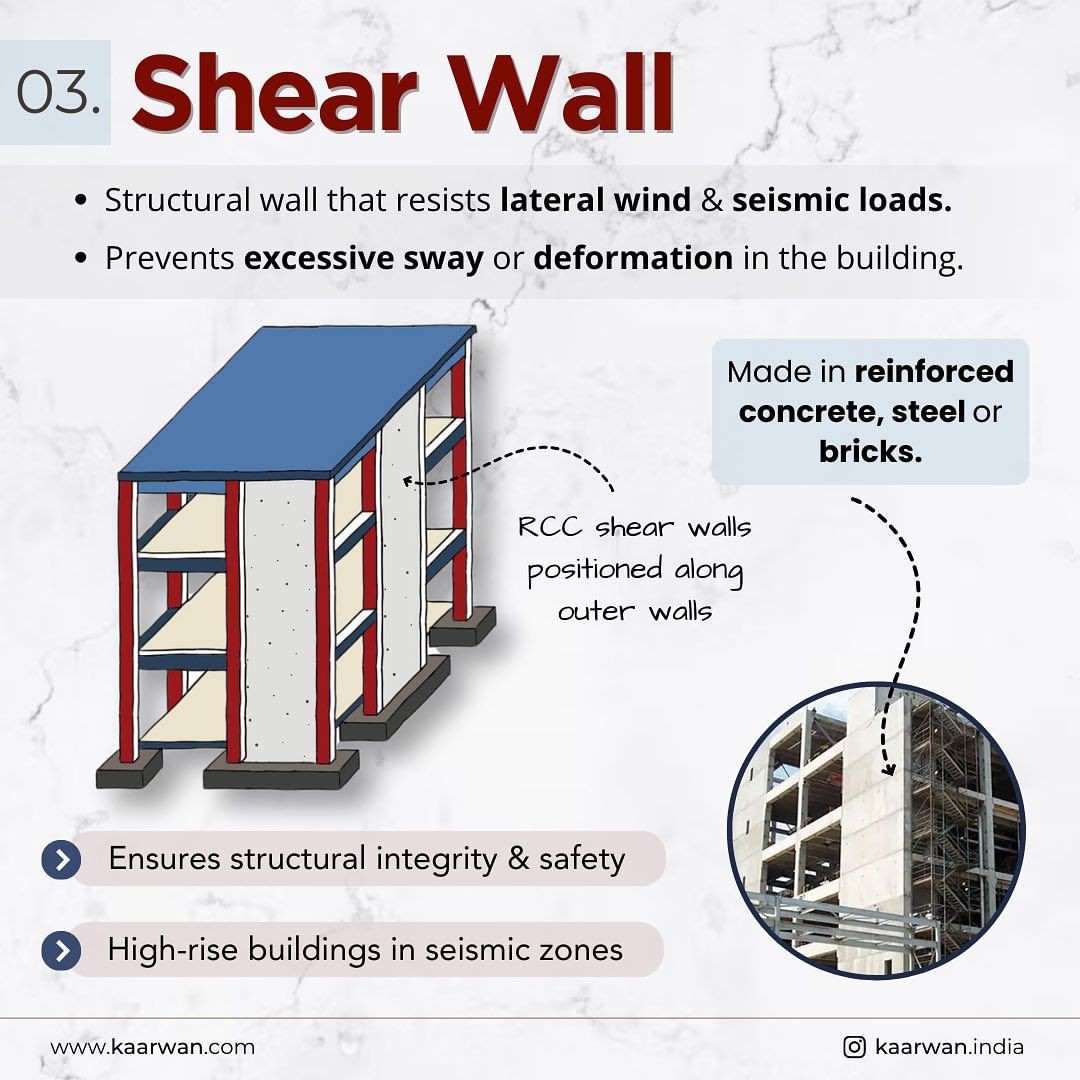
A shear wall is a structural element designed to resist lateral forces such as wind and seismic loads. This wall type prevents excessive sway and deformation, ensuring the building’s safety and structural integrity.
- Key Benefits:
- Essential in providing lateral stability.
- Ensures the safety of high-rise buildings in seismic zones.
Application: Shear walls are crucial in high-rise buildings, particularly in areas prone to earthquakes or strong winds. They help maintain the structural integrity of the building by absorbing and distributing lateral forces.
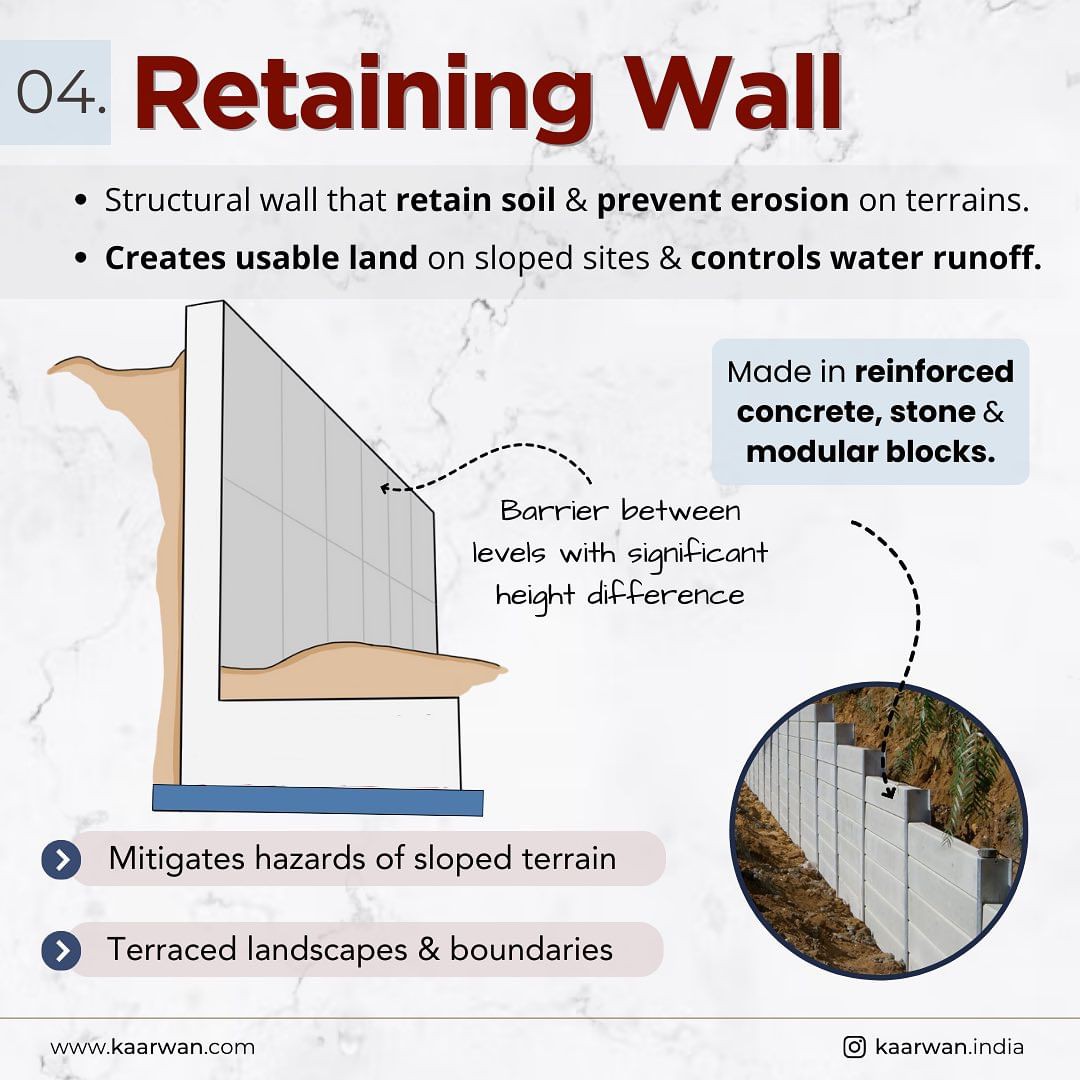
4. Retaining Wall
A retaining wall serves as a barrier that retains soil on sloped terrains. It helps prevent erosion and creates usable land on uneven sites. Retaining walls also control water runoff and help manage drainage.
- Key Benefits:
- Essential in terracing landscapes and controlling slope hazards.
- Helps in creating level surfaces on sloped land.
Application: Retaining walls are commonly used in landscaping projects, creating terraced gardens, and defining property boundaries on sloped terrain.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of walls in construction is crucial for selecting the right one for your project. Load-bearing walls provide essential support for low-rise buildings, while curtain walls enhance the aesthetic and energy efficiency of high-rise commercial structures. Shear walls offer necessary protection in seismic zones, and retaining walls are vital in managing landscapes on sloped terrain. Each wall type plays a distinct role, in ensuring the overall stability, safety, and functionality of buildings.
Click Here To See Water-Cement Ratio: The Key To Strong Concrete
Photo Credit: kaarwan