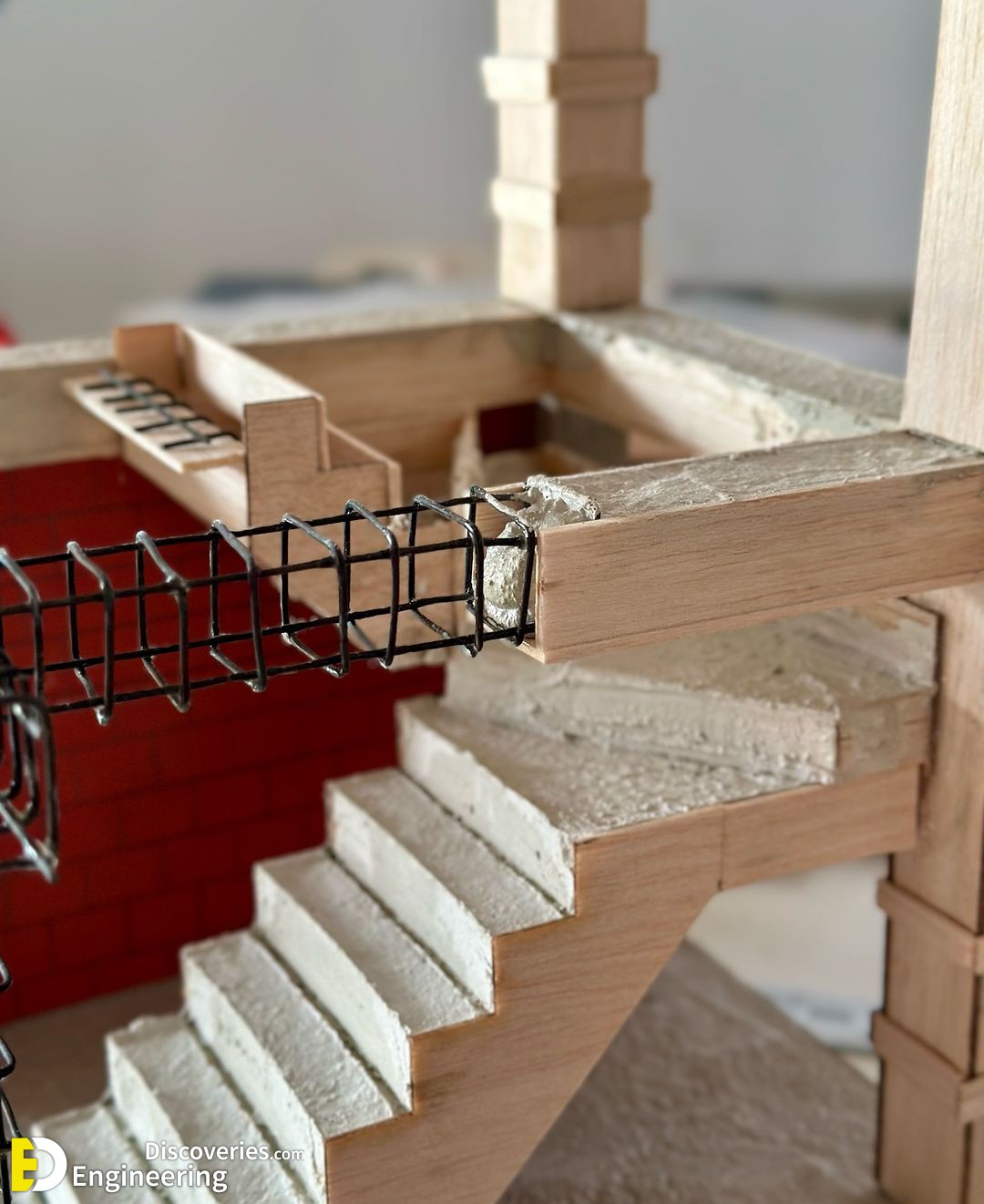
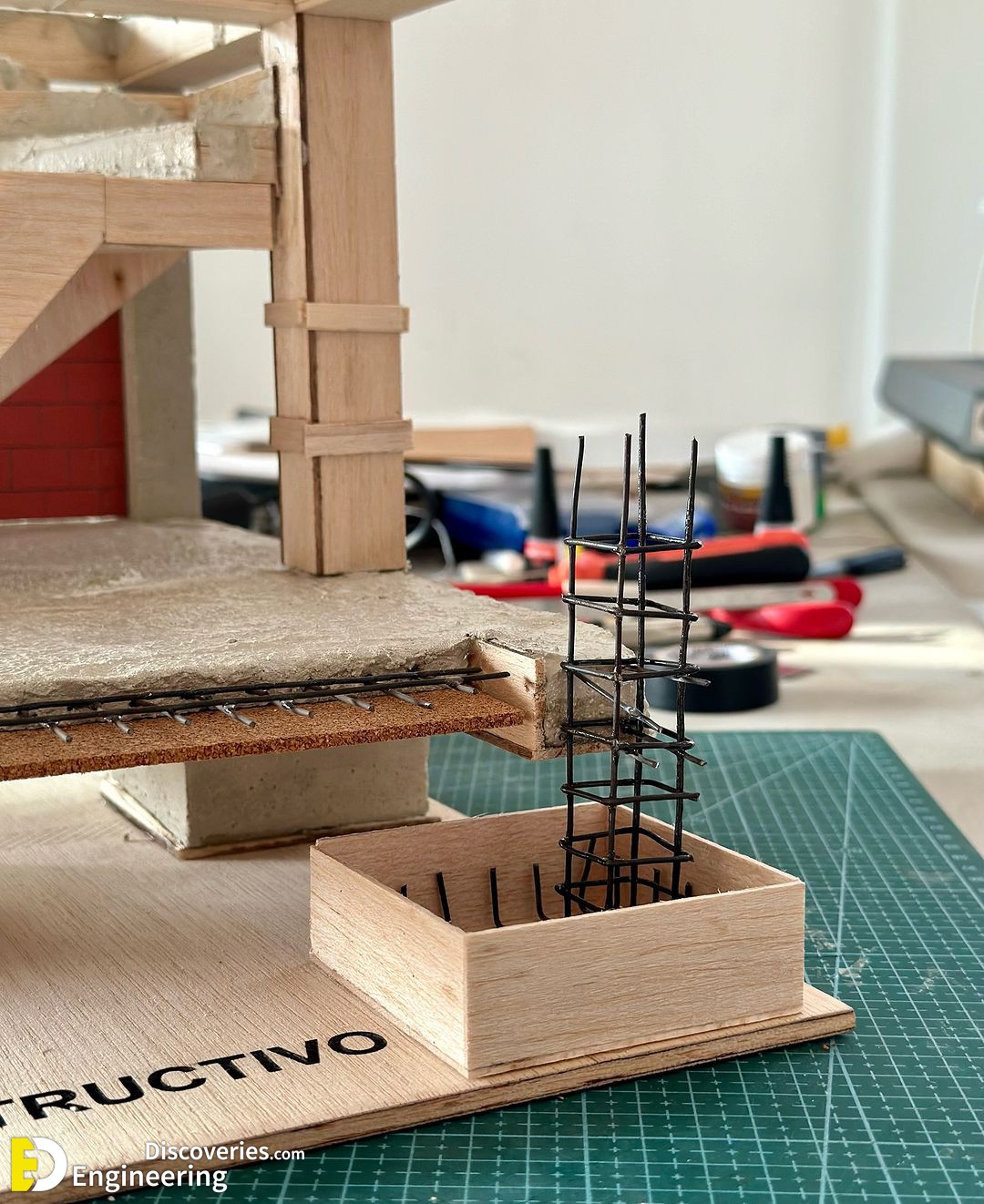
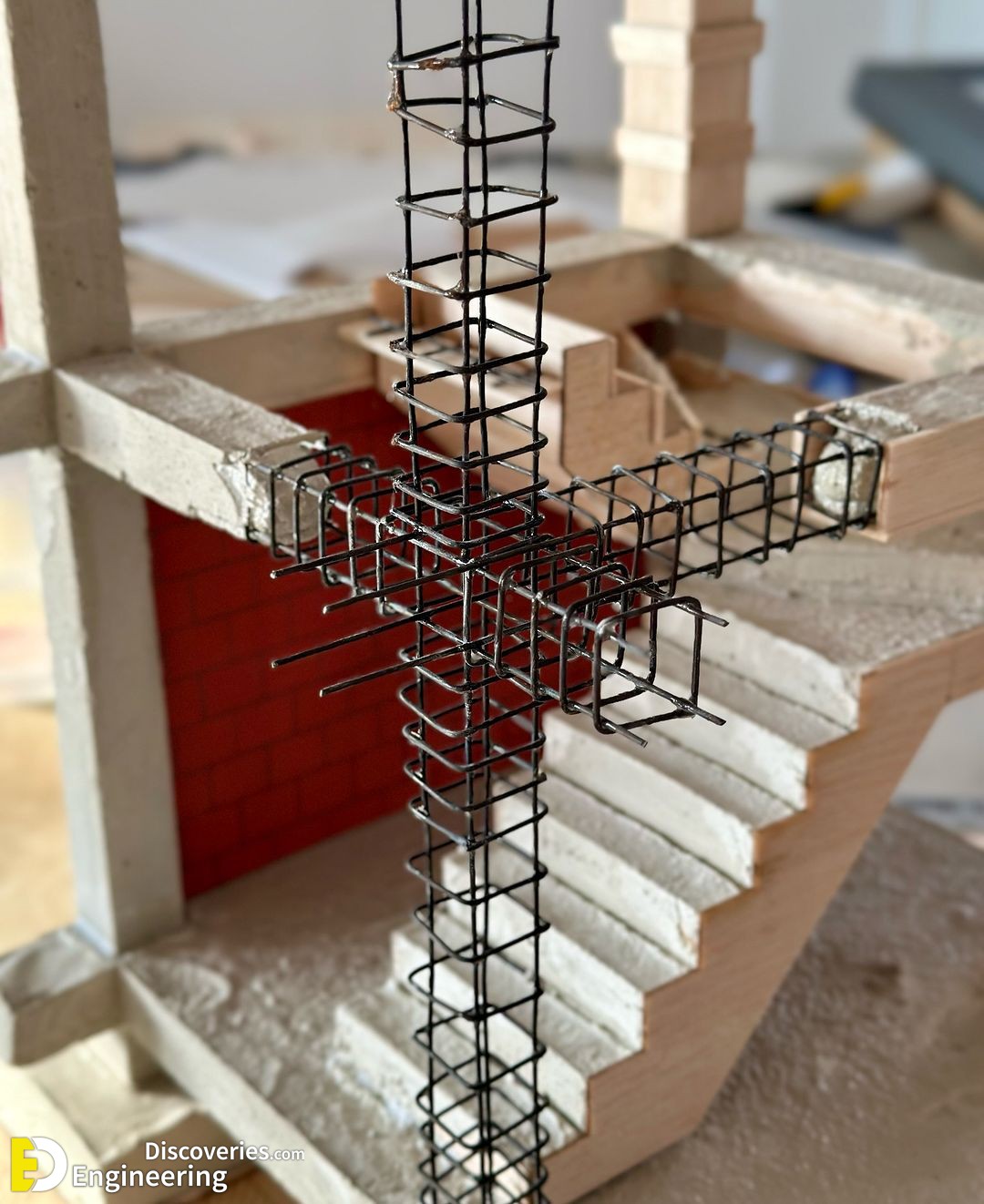
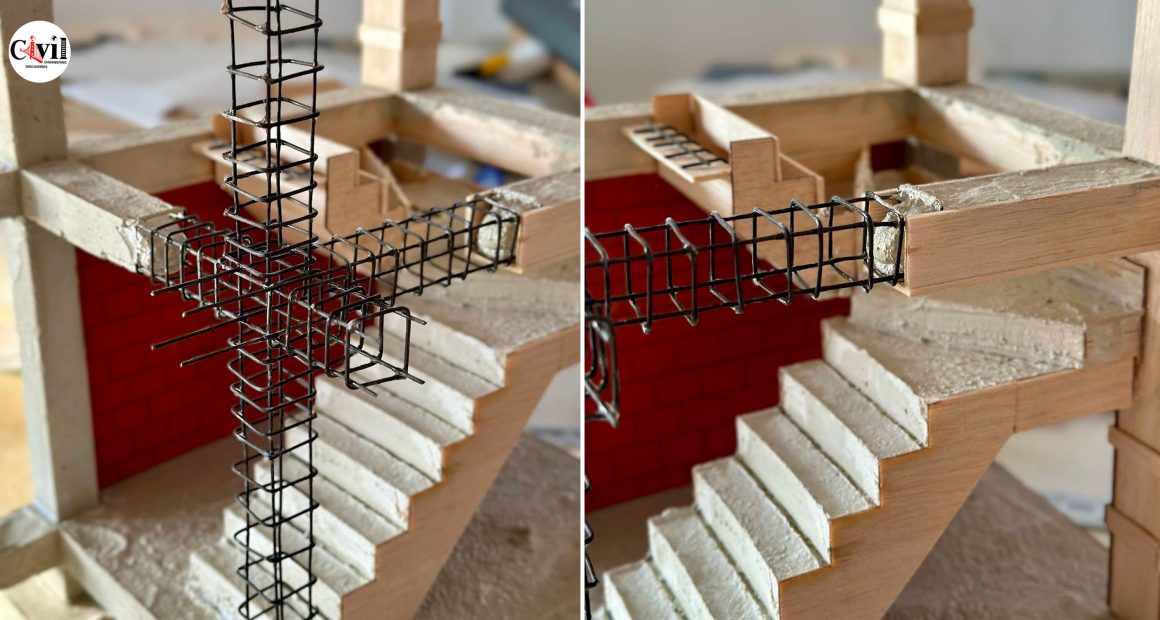
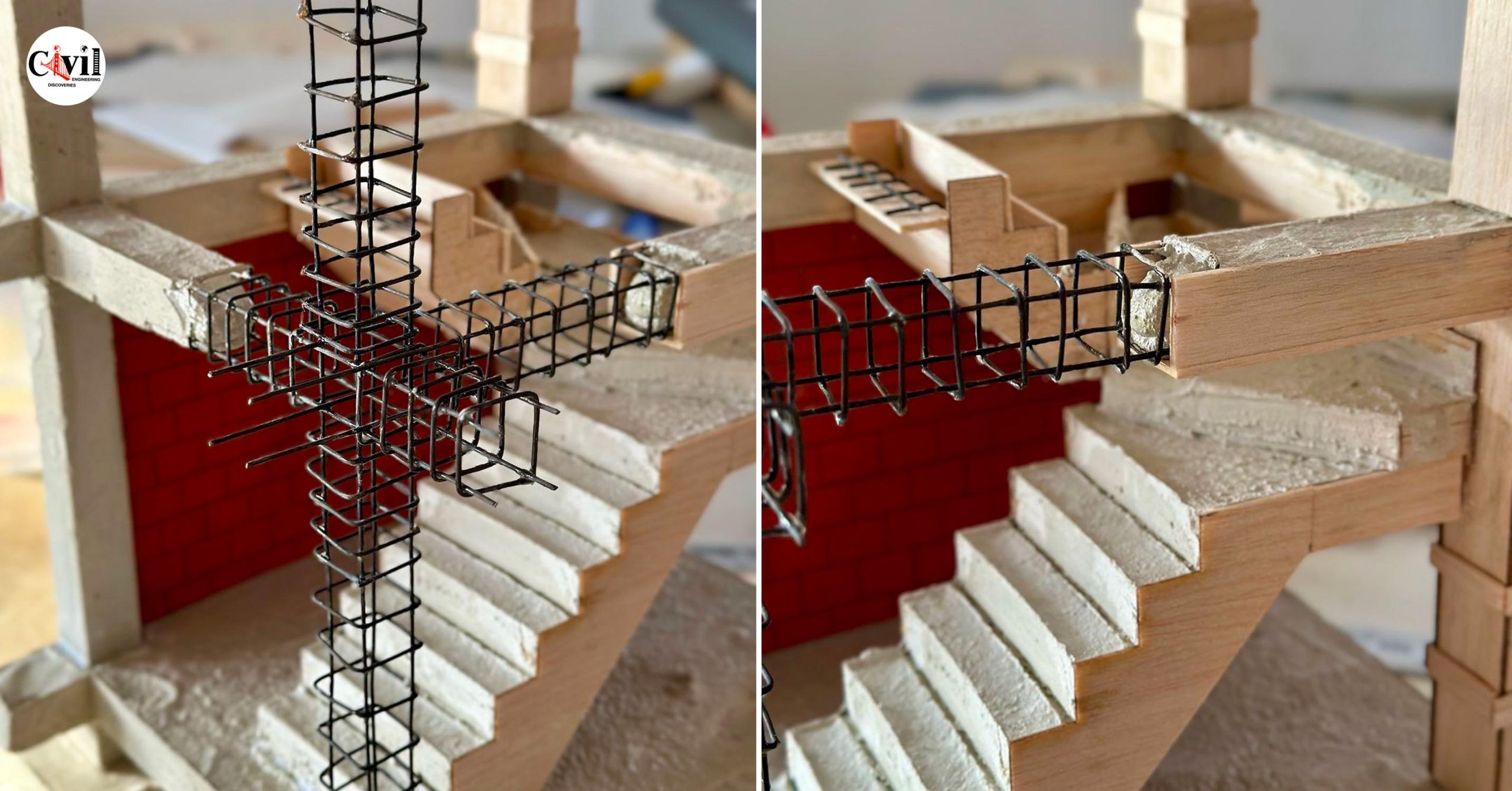
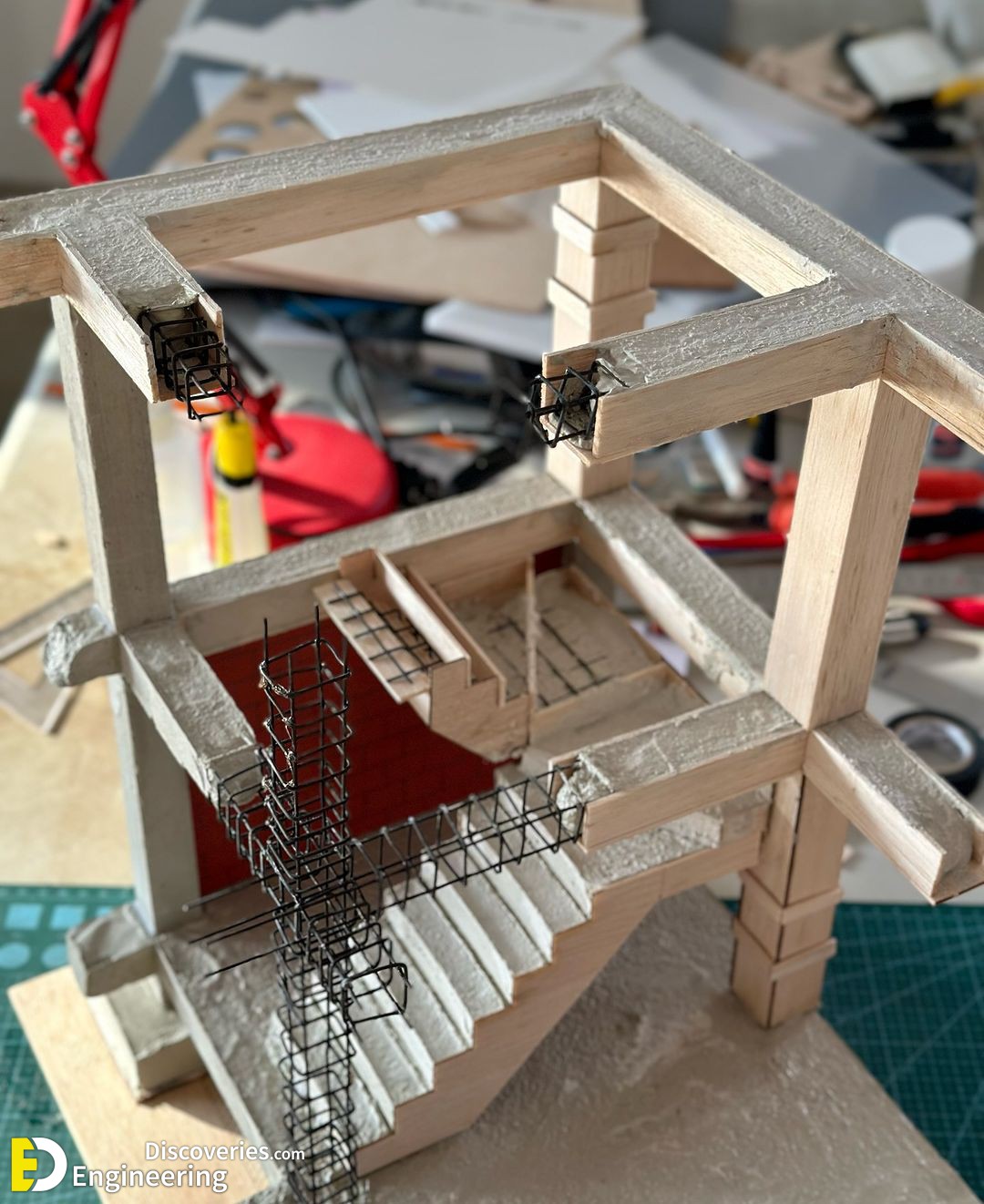
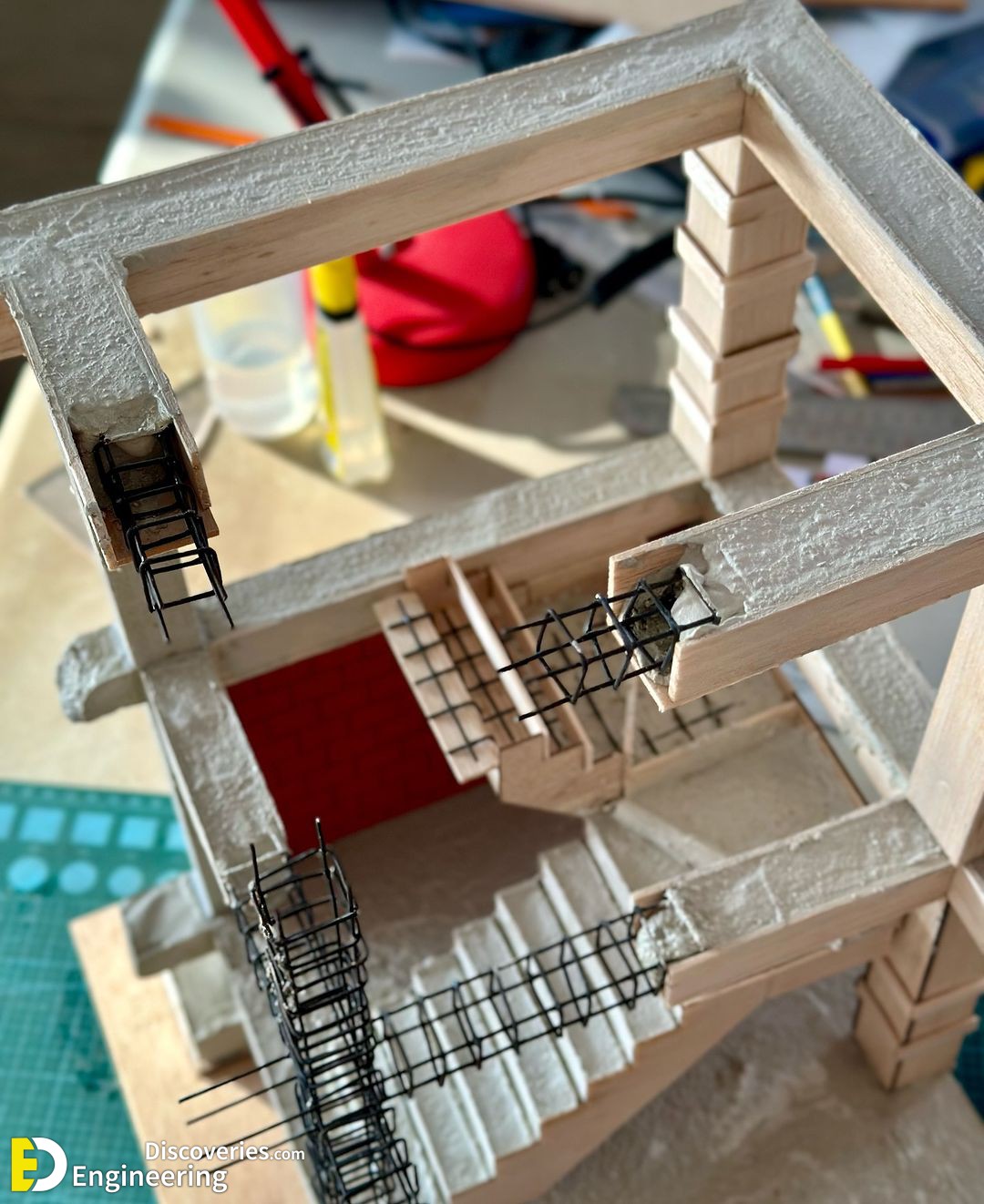
The design of stirrups in columns is crucial to ensure the resistance of the structure to internal forces, especially shear and those caused by earthquakes. The fundamental aspects of the design:
1. Structural function: The stirrups act as transverse reinforcement, confining the concrete and preventing the buckling of the longitudinal bars under compressive loads. This improves both the shear resistance and the ductility of the column, being essential in seismic zones.
2. Stirrup spacing: It should be reduced in the most critical areas of the column, such as the ends, where the forces are most intense. Generally, the recommendation is to keep the space no greater than 150 mm (15 cm) in these areas.
3. Diameter and number of stirrups: The diameter of the stirrup bars and their number depend on the strength required. It is common to use diameters from 6 mm (6 cm) to 12 mm (12 cm), depending on the load to be supported and the dimensions of the column.
4. Distribution and configuration: Stirrups can be closed, rectangular, square, or circular, depending on the geometry of the column. They must be distributed so that they efficiently encompass and confine the longitudinal bars.
5. Regulations: The design of stirrups must comply with current building codes and regulations, which establish minimum requirements for spacing, diameter, and strength of stirrups in columns.
Credit: Maqueto
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Newest