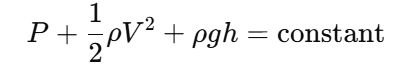Introduction to Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics
Fluid mechanics and hydraulics play a crucial role in engineering and industrial applications. These fields focus on the behavior of fluids and their interaction with surfaces and other systems. Understanding fluid flow and pressure principles is essential for designing efficient and functional systems.
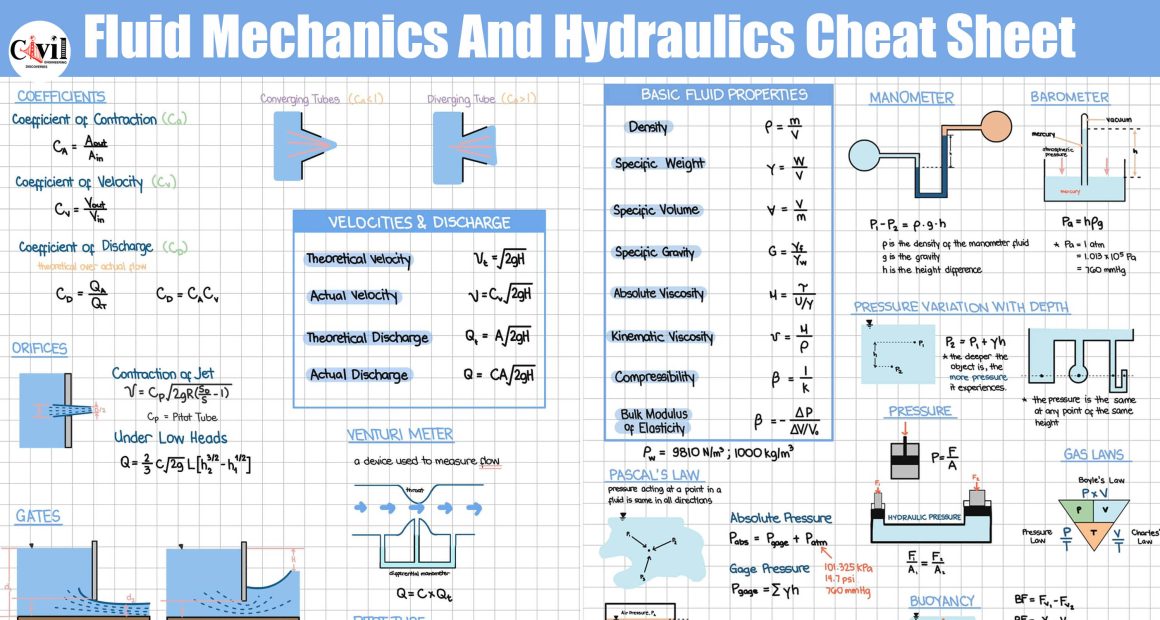
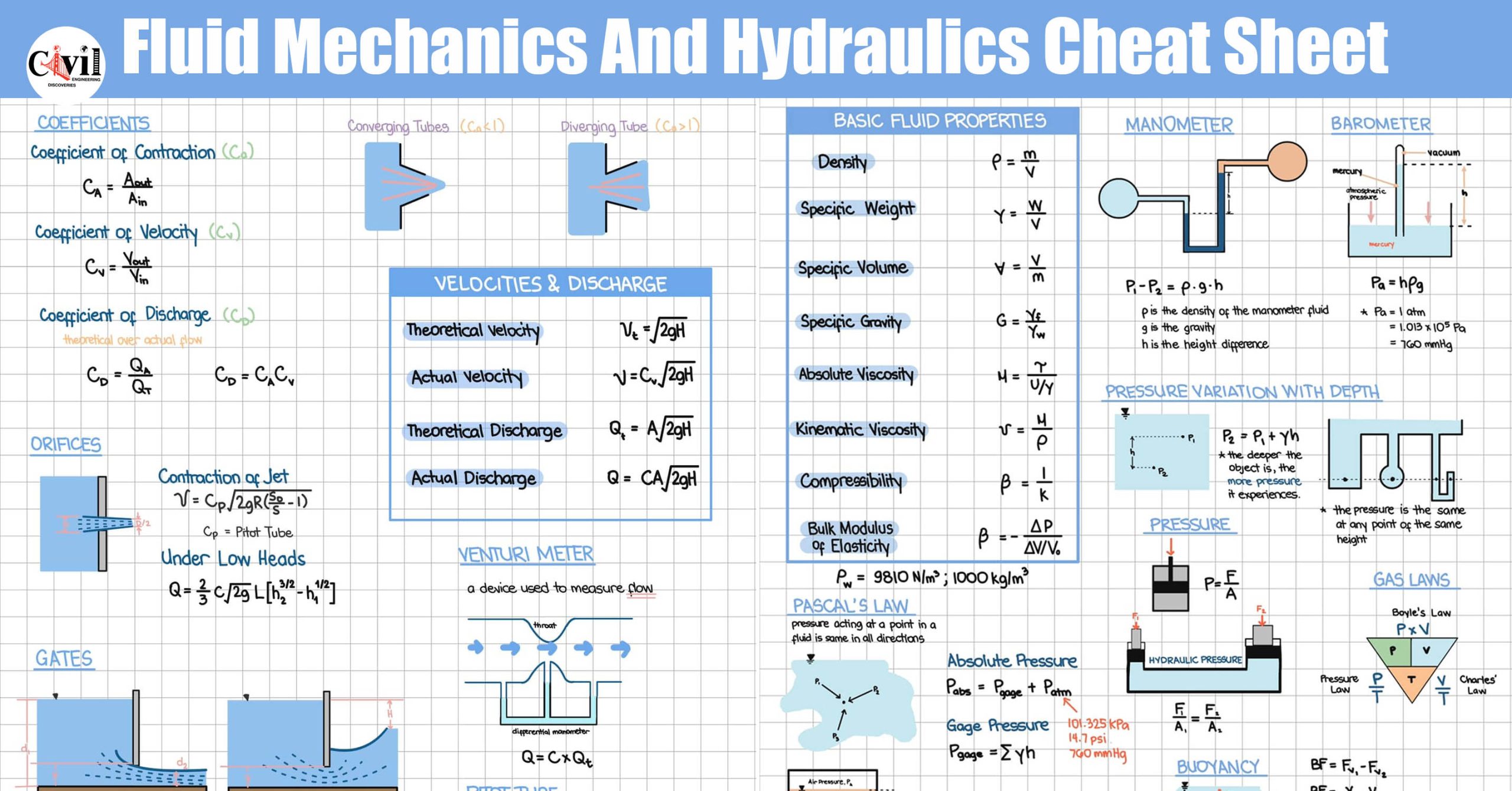
Key Principles of Fluid Mechanics
Types of Fluids
- Ideal Fluids: Hypothetical fluids with no viscosity.
- Real Fluids: Actual fluids with viscosity and resistance to flow.
- Compressible and Incompressible Fluids: Depending on their density variation during flow.
Fluid Properties
- Density: Mass per unit volume of a fluid.
- Viscosity: A measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow.
- Surface Tension: The cohesive force at a fluid’s surface.
Fundamental Equations in Fluid Mechanics
Continuity Equation
This equation ensures mass conservation in fluid flow:
A1V1 = A2V2
Where A is the cross-sectional area and V is the velocity.
Bernoulli’s Equation
This principle states that the sum of pressure, kinetic energy, and potential energy remains constant along a streamline:
Applications of Hydraulics
Water Supply Systems
Hydraulic principles are used to design pipelines and distribution networks for efficient water flow.
Hydraulic Machines
- Hydraulic Pumps: Essential for fluid transfer in industrial processes.
- Hydraulic Presses: Used in manufacturing for high-force applications.
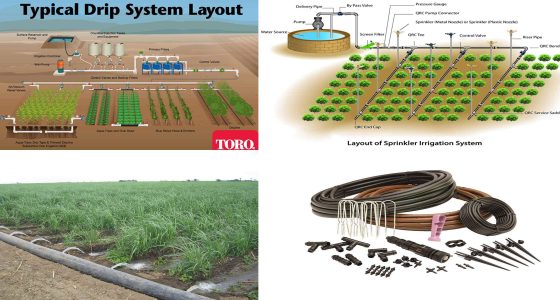
Irrigation Systems
Hydraulic concepts are used in designing efficient irrigation channels and systems for agricultural use.
Importance of Fluid Mechanics in Engineering
Fluid mechanics supports various fields, including:
- Mechanical Engineering: In HVAC and combustion engine designs.
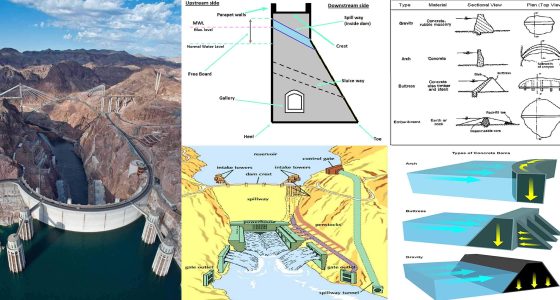
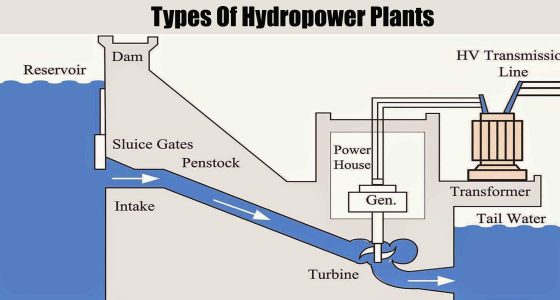
- Civil Engineering: For dam construction and flood management systems.
- Aerospace Engineering: To design aerodynamically efficient structures.
Challenges in Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics
Understanding fluid dynamics requires handling complex variables and turbulent flow patterns. Engineers often use simulation software to model and optimize systems.
Click Here To See Comprehensive Guide To Weirs: Types, Equations, And Applications