Understanding Key Surveying Terms
Before starting, familiarize yourself with these essential terms:
BS (Backsight) – A staff reading taken at a known elevation point.
FS (Foresight) – A staff reading taken at a new point to determine its elevation.
RL (Reduced Level) – The elevation of a point relative to a known benchmark.
TBM (Temporary Benchmark) – A reference point with a known RL used for leveling.
HI (Height of Instrument) – The height of the instrument line of sight above a known point.
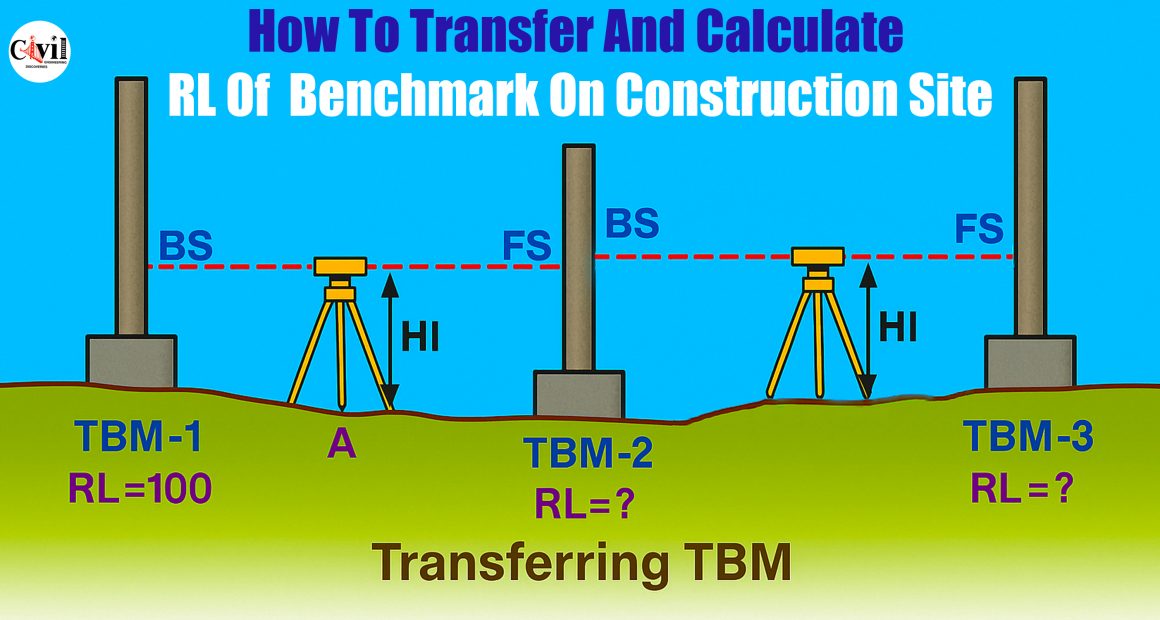
Procedure to Transfer RL from One TBM to Another
1. Setting Up the Instrument
Set your leveling instrument at Station A. Ensure the staff held vertically over TBM-1 and TBM-2 is visible from this position.
2. Taking Initial Readings
Record a Backsight (BS) reading over TBM-1. Then, take a Foresight (FS) reading over TBM-2.
3. Shifting the Instrument
Move the instrument to Station B. After proper leveling, take a BS reading on TBM-2 and an FS reading on TBM-3. Never move the staff on TBM-2 before both readings are taken.
4. Using an Assumed RL for TBM-1
If the RL of TBM-1 isn’t known, assume it as 100.000. This assumption allows accurate calculations for subsequent TBMs.
RL Calculation Formula
HI = RL of TBM + BS
RL of new point = HI – FS
Apply these formulas at each station to find RL values of new TBMs.
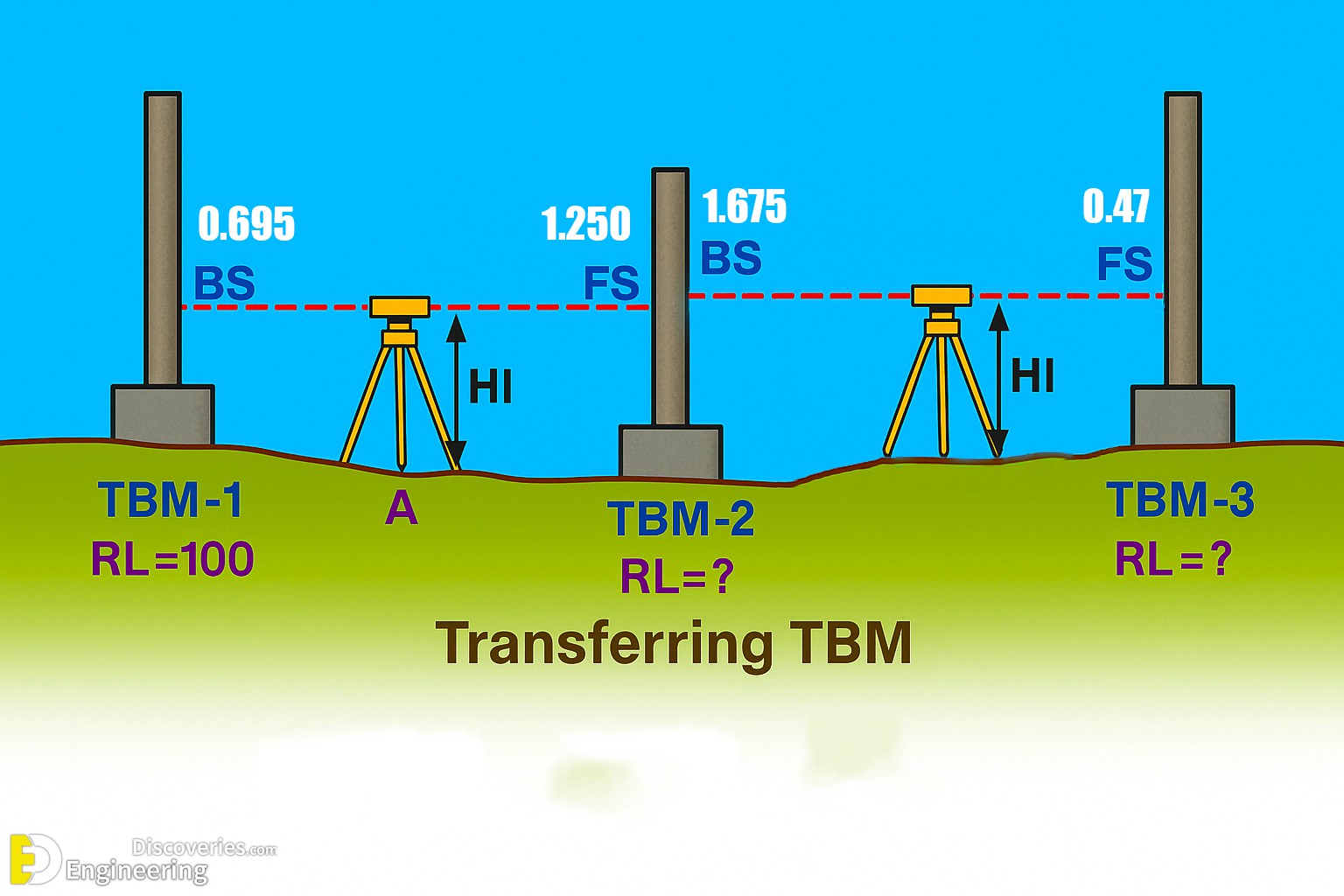
Step-by-Step Example with Real Data
Let’s work with this set of leveling readings:
0.695, 1.250, 1.675, 0.470
The instrument is shifted after the 2nd reading.
Assigning Readings
1st and 3rd readings = BS = 0.695 and 1.675
2nd and 4th readings = FS = 1.250 and 0.470
Assumed RL of TBM-1
We begin with:
RL of TBM-1 = 100.000
Now calculate:
HI at Station A
HI = RL + BS
HI = 100.000 + 0.695 = 100.695
RL of TBM-2
RL = HI – FS
RL = 100.695 – 1.250 = 99.445
HI at Station B
HI = RL of TBM-2 + BS
HI = 99.445 + 1.675 = 101.120
RL of TBM-3
RL = HI – FS
RL = 101.120 – 0.470 = 100.650
Final RL Results
TBM-1 RL = 100.000 (assumed)
TBM-2 RL = 99.445
TBM-3 RL = 100.650
Important Tips for Accuracy
Always take BS and FS without moving the staff.
Ensure the instrument is correctly leveled at each station.
Use consistent and clear note-keeping for all readings.
Never skip readings between shifts of the instrument.