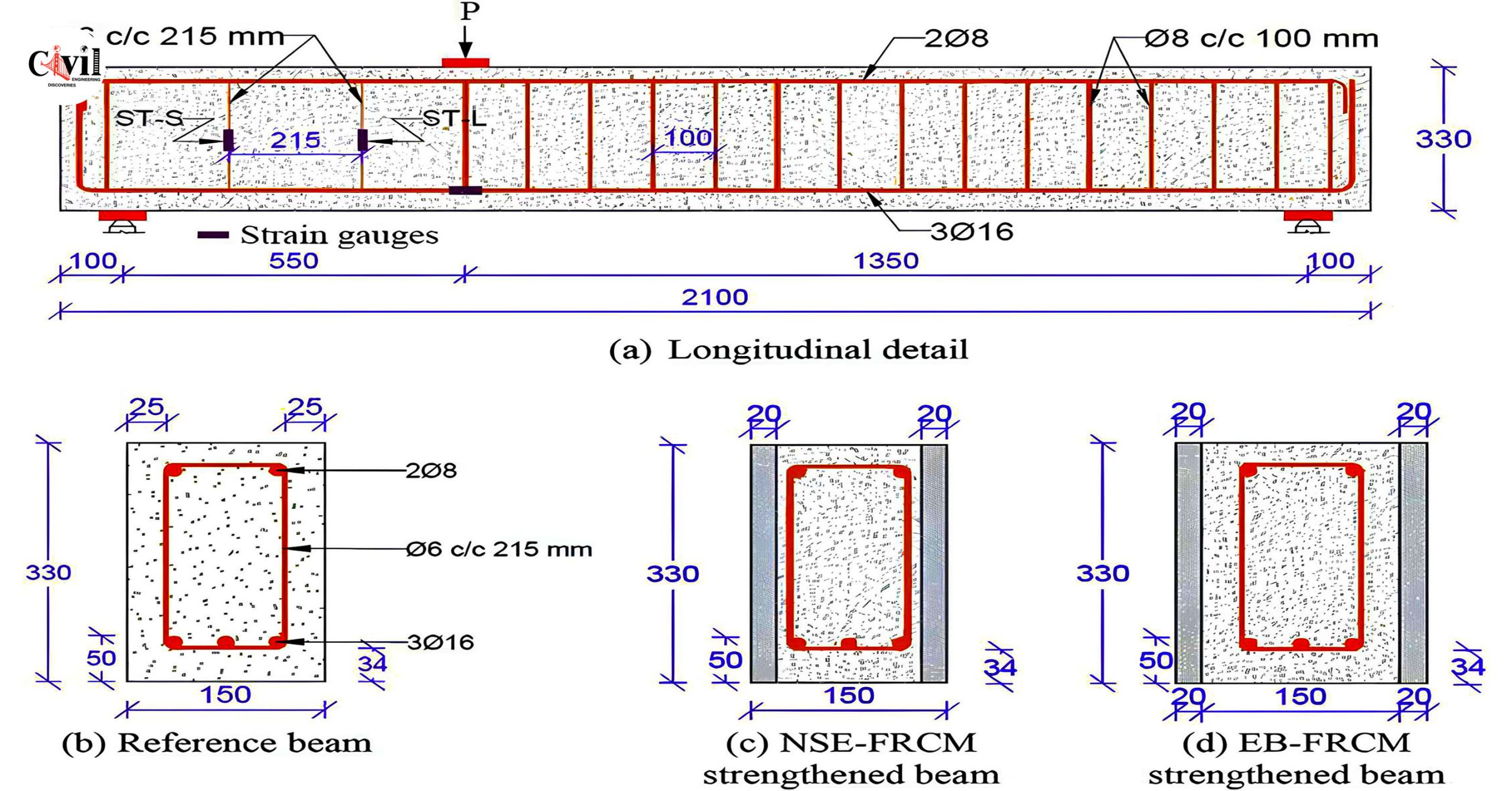
Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) is an essential material in modern construction, and every engineer needs to understand its design details and structural components. RCC structures include several key elements: footings, columns, beams, slabs, and stairs, each of which plays a critical role in ensuring the overall strength and stability of the building.
RCC footings are designed to distribute loads to the ground and can take forms such as isolated, combined, or raft foundations. Columns provide vertical support and must be properly reinforced to resist axial and lateral forces. Beams transfer loads between columns and support the slabs; thus, they require careful reinforcement detailing to prevent failures due to shear and bending.
Slabs, which can be one-way or two-way, form the floors and roofs of a structure. They need to have adequate thickness and reinforcement to handle both live and dead loads effectively. Staircases, which are crucial for multi-story buildings, are designed with rise, tread, and reinforcement considerations to ensure safe accessibility.
Engineers must adhere to standard design codes and reinforcement guidelines, including aspects such as cover, spacing, and bar lapping, to maintain the project’s structural integrity. Additionally, well-detailed diagrams and specifications are essential for executing RCC designs effectively on-site.
Click Here To See 4 Important Rules When Designing A Concrete Torsion-Exposed Beam