Septic System Design or Septic Tanks Design can be done in various process, but most of them are critical and time taking laborious process. Here in this article, I have given a tutorial on how to design Septic Tank Easily within 5 minutes and Determine Septic Tank Size.
Design of Septic Tank
In any septic system design, this is a very very important step as it will determine the total capacity of the septic tank required
The capacity of the septic tank depends on a number of users and the interval of sludge removal. Normally sludge should be removed every 2 years. The liquid capacity of the tank is taken as 130 litres to 70 litres per head. For a small number of users 130ltr per head is taken.
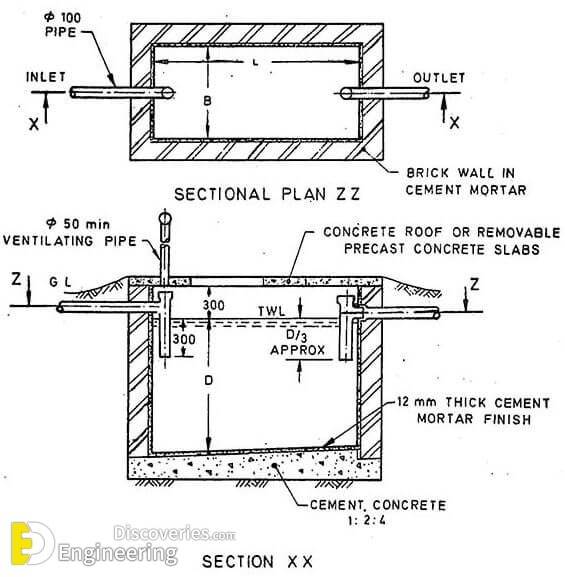
A septic tank is usually provided with a brick wall in which cement mortar [not less than 20cm (9 inches)] thick and the foundation floor is of cement concrete 1:2:4. Both inside and outside faces of the wall and top of the floor are plastered with a minimum thickness of 12mm (one-half inch) thick cement mortar 1:3 mix.
All inside corners of the septic tank are rounded. Waterproofing agent such as Impermo, Cem-seal or Accoproof etc. is added to the mortar at the rate of 2% of the cement weight. Waterproofing agent is to be added in similar proportion into the concrete also for making the floor of the tank.
For proper convenience in collection and removal of the sludge, the floor of septic tank is given a slope of 1:10 to 1:20 towards the inlet side. Which means that the floor of the outlet side will be on the higher elevation than the floor at the inlet side.
Dimensions of Septic Tank Components
1- Length, Width and Depth of Septic Tank
Width = 750mm(min)
Length = 2 to 4 times width
Depth = 1000 to 1300mm. (min below water level) + 300 to 450mm freeboard
Maximum depth = 1800mm + 450 mm freeboard
Capacity = 1 cubic meter (10 cubic feet) minimum
2- Detention period
Detention period of 24hrs (mostly) considered in septic tank design. The rate of flow of effluent must be equal to the rate of flow of influent.
3- Inlet and outlet pipes
An elbow or T pipe of 100mm diameter is submerged to a depth of 250-600mm below the liquid level. For outlet pipe, an elbow or T type of 100mm diameter pipe is submerged to a depth of 200-500mm below the liquid level. Pipes may be of stoneware or asbestos.
4- Baffle Walls of Septic Tank
For small tanks, RCC hanging type scum baffle walls are provided in septic tanks. Baffle walls are provided near the inlet. It is optional near the outlet.
The inlet baffle wall is placed at a distance of L/5 from the wall, where L is the length of the wall. The baffle wall is generally extended 150mm above to scum level and 400-700mm below it.
Scum being light generally floats at the water level in the tank. The thickness of the wall varies from 50mm to 100mm. for large tanks lower portion are having holes for the flow of sludge.
5- Roofing Slab of Septic Tank
The top of the septic tank is covered with an RCC slab of the thickness of 75-100mm depending upon the size of the tank. Circular manholes of 500mm clear diameter are provided for inspection and desludging. In case of rectangular opening clear size is kept as 600X450mm.
6- Ventilation Pipe
For outlet of foul gases and ventilation purpose cast iron or asbestos pipe of 50-100mm diameter is provided which should extend 2m (min) above ground level. Top of the ventilation pipe is provided with a mosquito-proof wire mess or cowl.
Fig: Sectional plan ZZ shoes the typical layout of the septic tank. Section XX shows the Cross-Sectional detail of septic tank.