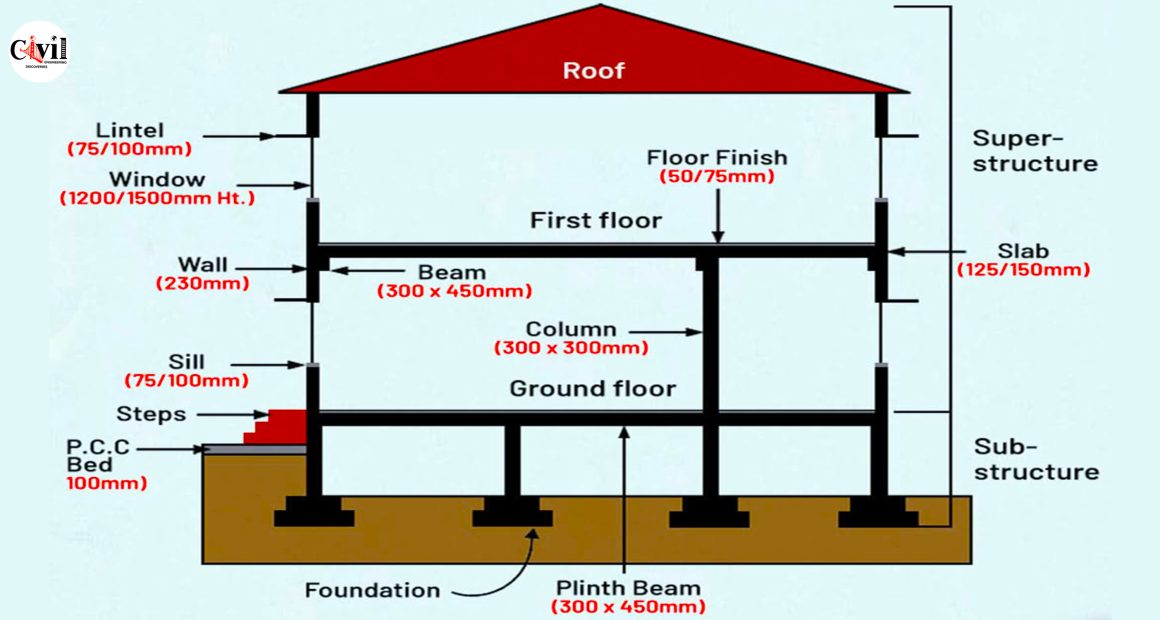
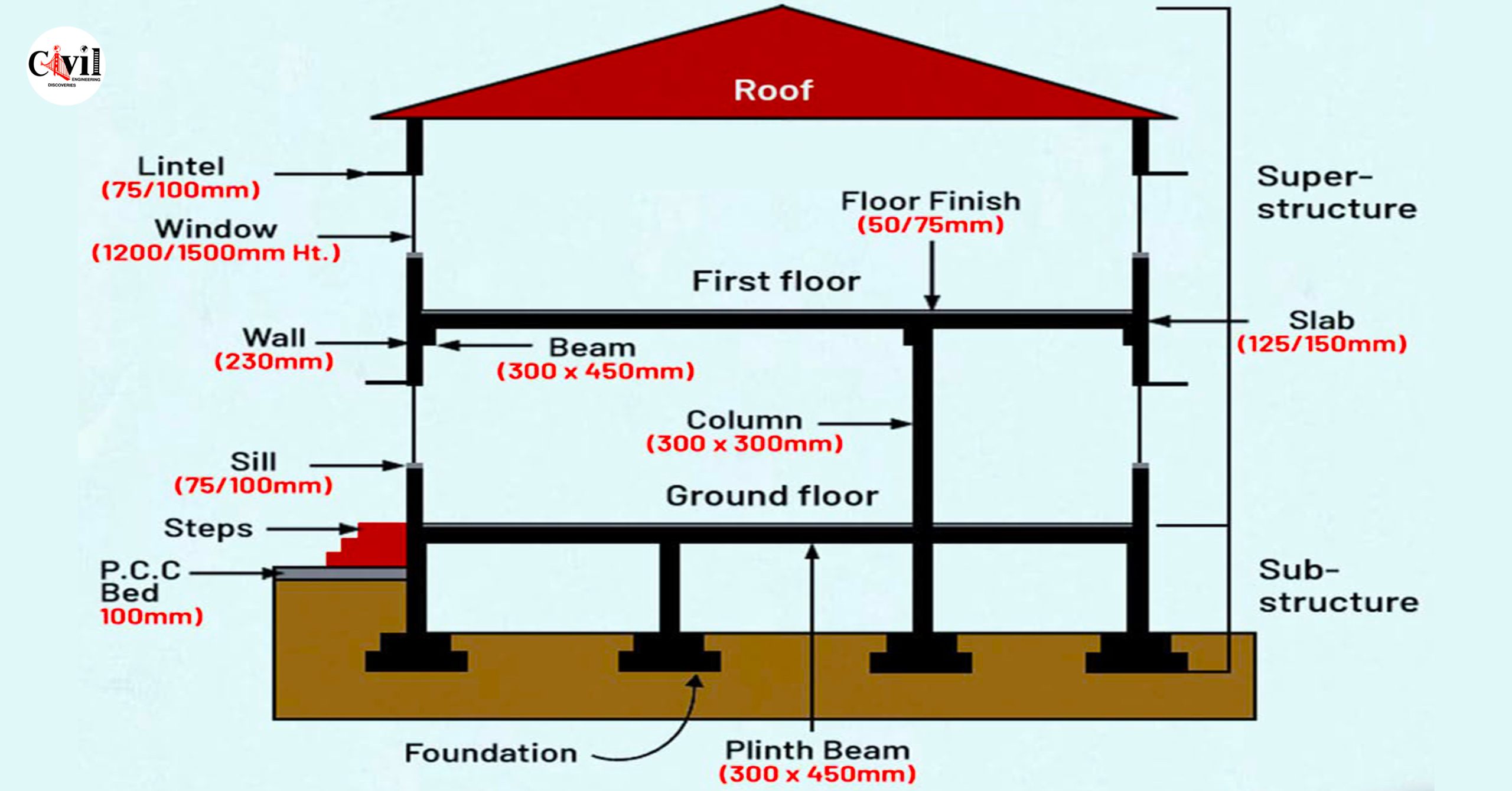
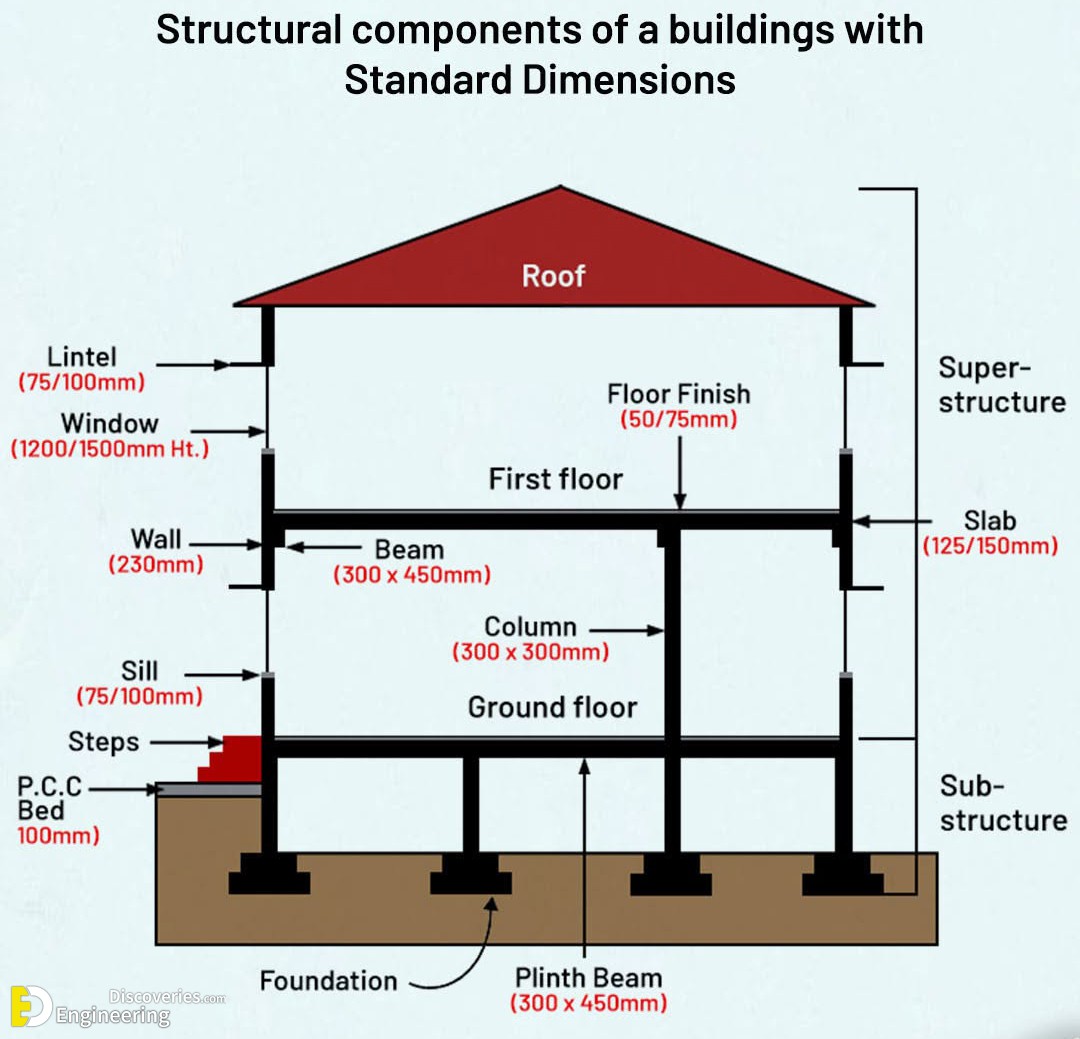
When designing a building, understanding its structural components and standard dimensions is crucial. This guide explores the key elements of a building’s structure, offering insights into both the superstructure and substructure.
Key Structural Components of a Building
Buildings are constructed in two major segments: the substructure, which lies below ground, and the superstructure, which stands above it. Each segment comprises essential elements that ensure stability and functionality.
1. Substructure Components
Foundation
The foundation is the base of a building, designed to distribute its load evenly to the ground. The standard dimensions depend on soil type and load-bearing requirements. Generally, reinforced concrete is used for durability.
Plinth Beam
The plinth beam is a horizontal structural element (300 mm x 450 mm) that connects columns at the ground level. It prevents cracks and uneven settlement in the walls due to foundation shifts.
PCC Bed
A Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) bed of 100 mm thickness is placed below the foundation to provide a level base. It also acts as a barrier against moisture.
Steps
Steps are provided at the entrance for accessibility. They are designed ergonomically to ensure safety and ease of use.
2. Superstructure Components
Columns
Columns are vertical structural members (300 mm x 300 mm) that transfer the load from beams and slabs to the foundation. Their dimensions are designed to withstand axial and lateral forces.
Beams
Beams (300 mm x 450 mm) are horizontal members that support loads from walls and slabs. They provide stability and prevent the structure from bending under pressure.
Walls
Walls, with a thickness of 230 mm, enclose the building and provide support. They also act as barriers against environmental elements.
Lintels and Sills
- Lintels (75 mm to 100 mm) are horizontal elements placed above windows and doors to bear the load of the wall above.
- Sills (75 mm to 100 mm) are horizontal structures at the base of windows for stability and aesthetics.
Windows
Windows are typically 1200 mm to 1500 mm in height, allowing for ventilation and light penetration into the interior spaces.
Slab
The slab is a horizontal plate (125 mm to 150 mm thick) forming floors or roofs. It provides a surface for occupancy and is often made of reinforced concrete.
Floor Finish
The floor finish (50 mm to 75 mm thick) is the top layer of the slab, designed for aesthetics and functionality. Materials like tiles, marble, or wood are commonly used.
Roof
The roof protects the structure from environmental elements like rain, sun, and wind. Its design varies based on climatic conditions and architectural preferences.
Importance of Standard Dimensions in Construction
Adhering to standard dimensions ensures structural integrity, safety, and compliance with building codes. Each component is designed to withstand specific loads and environmental stresses.
Click Here To See Understanding Bridge Components: A Comprehensive Guide